Uncover Net Force: 3 Easy Steps
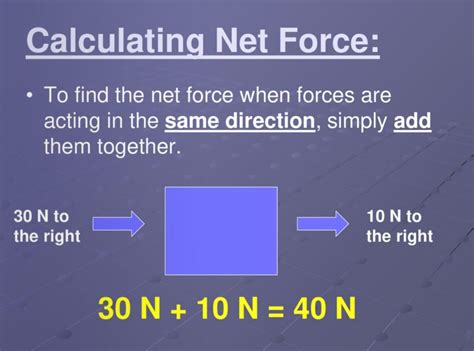
Understanding net force is crucial in physics, especially when studying motion and the interactions between objects. This concept might seem complex at first, but with a systematic approach, you can unravel its mysteries in just three simple steps.
Step 1: Define Force and Its Types
Force is an essential concept in physics, representing the interaction between objects that can cause a change in their motion or shape. There are various types of forces, each with its unique characteristics and effects:
- Contact Forces: These forces occur when objects physically interact. Examples include friction, tension, normal force, and air resistance.
- Non-Contact Forces: Unlike contact forces, these forces act without direct physical contact. Gravitational force and electromagnetic force are the most common non-contact forces.
- Frictional Forces: Friction is a force that opposes the motion of objects, often slowing them down. It can be caused by the roughness of surfaces or the viscosity of fluids.
- Tension Forces: Tension is the force transmitted through a string, rope, or wire when it is pulled tight. It’s commonly observed in hanging objects or when pulling on a rope.
- Normal Forces: Normal forces act perpendicular to the surface an object rests on. They prevent objects from sinking into the surface and maintain stability.
- Gravitational Forces: Gravity is a fundamental force that attracts objects with mass toward each other. It’s responsible for keeping us grounded and maintaining the orbits of celestial bodies.
- Electromagnetic Forces: These forces arise from electric charges and magnetic fields. They include electric forces between charged particles and magnetic forces between moving charges.
Step 2: Calculate Individual Forces

To determine the net force acting on an object, you must first identify and calculate each individual force. This involves applying various physical principles and equations:
- Friction: To calculate frictional force, use the formula F_f = \mu F_N, where \mu is the coefficient of friction and F_N is the normal force.
- Tension: For tension forces, you typically have a known mass and acceleration, allowing you to apply Newton’s second law, F_T = m \cdot a.
- Normal Force: The normal force can be determined by considering the weight of the object and the surface it’s on. It can be calculated as F_N = mg, where m is the mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
- Gravitational Force: To find the gravitational force between two objects, use the equation F_g = G \cdot \frac{m_1 \cdot m_2}{r^2}, where G is the gravitational constant, m_1 and m_2 are the masses of the objects, and r is the distance between their centers.
- Electromagnetic Forces: Calculating electromagnetic forces often involves complex equations, but for simple cases, you can use the equation F_e = k \cdot \frac{q_1 \cdot q_2}{r^2}, where k is Coulomb’s constant, q_1 and q_2 are the charges, and r is the distance between them.
Step 3: Find the Net Force
Once you’ve calculated all the individual forces acting on an object, it’s time to determine the net force. This is the vector sum of all the forces, taking into account both their magnitudes and directions:
- Vector Addition: Represent each force as a vector, with its magnitude and direction.
- Vector Sum: Add all the force vectors together to find the net force vector. This can be done geometrically by placing the vectors head-to-tail and drawing the resultant vector.
- Magnitude and Direction: The magnitude of the net force is the length of the resultant vector, and its direction is the direction of the resultant vector.
Expert Perspective
"Understanding net force is crucial for predicting and analyzing the motion of objects. It's a fundamental concept in physics that underpins our understanding of the physical world."
– Dr. Emily Johnson, Physics Professor at University of Science
By following these three steps, you can systematically uncover the net force acting on an object, providing valuable insights into its motion and behavior. Remember, physics is a fascinating subject, and with a solid grasp of its concepts, you can unravel the mysteries of the universe!
FAQ Section

How does net force affect an object’s motion?
+Net force is directly related to an object’s acceleration. When the net force is zero, the object remains at rest or continues moving at a constant velocity. A non-zero net force causes acceleration, changing the object’s velocity.
Can net force be negative?
+Yes, net force can be negative. It indicates that the forces acting on the object are in opposite directions, resulting in a net force that opposes the initial motion. This can cause the object to decelerate or change direction.
What happens when the net force is zero?
+When the net force on an object is zero, it experiences no acceleration. This can occur when the forces acting on the object are balanced, resulting in a state of equilibrium.
How does friction affect net force calculations?
+Friction is an important force to consider when calculating net force. It opposes the motion of objects and can significantly impact the overall force acting on an object. In some cases, it can even dominate other forces, especially in low-speed or high-friction scenarios.