Mastering I-Chart Forecasts: 5 Easy Steps
Welcome to the world of accurate and efficient forecasting using I-Charts, a powerful tool that has revolutionized the way businesses and professionals make informed decisions. In today's fast-paced business environment, precise forecasting is not just a luxury but a necessity for staying ahead of the competition. This article will guide you through the step-by-step process of mastering I-Chart forecasts, unveiling the secrets behind their simplicity and effectiveness.
Understanding the Power of I-Charts

I-Charts, or Innovation Charts, are a versatile and intuitive tool designed to assist in forecasting a wide range of business metrics, from sales and production to market trends and consumer behavior. Their unique structure and methodology offer a clear and concise approach to data analysis, making them an indispensable asset for any organization aiming to optimize its decision-making processes.
What sets I-Charts apart is their ability to simplify complex data, providing a comprehensive overview of key performance indicators. By employing a systematic and visual approach, these charts allow users to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies with ease, enabling them to make data-driven decisions with confidence.
Moreover, I-Charts facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing within teams. Their straightforward design ensures that insights derived from the data are easily communicated and understood by all stakeholders, fostering a culture of informed decision-making throughout the organization.
Step 1: Gather Relevant Data

The foundation of an effective I-Chart forecast lies in the quality and relevance of the data collected. Begin by identifying the specific metrics that are critical to your business objectives. These could include sales figures, production outputs, customer feedback, or any other key performance indicators unique to your industry.
Utilize a variety of data sources to ensure a comprehensive understanding of your market and operations. This may involve analyzing historical data, monitoring real-time metrics, and collecting feedback from customers and stakeholders. By combining these diverse data points, you create a robust dataset that forms the basis of your I-Chart forecast.
| Data Source | Relevance |
|---|---|
| Historical Records | Provides a baseline for comparison and identifies long-term trends. |
| Real-Time Metrics | Offers up-to-date insights into current performance and market dynamics. |
| Customer Feedback | Captures valuable insights into consumer preferences and market gaps. |

Remember, the accuracy of your I-Chart forecast is directly proportional to the quality and relevance of the data you gather. Take the time to meticulously collect and analyze your data, ensuring that it represents a true reflection of your business environment.
Step 2: Define Clear Objectives
Before diving into the creation of your I-Chart, it's crucial to establish clear objectives. Define the specific business questions you aim to answer with your forecast. Are you seeking to predict sales trends for the upcoming quarter? Or perhaps you want to optimize production schedules based on projected demand? Clearly defined objectives will guide the entire forecasting process and ensure that your I-Chart remains focused and relevant.
Additionally, consider the timeframe for your forecast. I-Charts can be utilized for both short-term and long-term predictions, so tailor your objectives accordingly. Short-term forecasts might focus on optimizing daily or weekly operations, while long-term forecasts could involve strategic planning for the next fiscal year or beyond.
By clearly defining your objectives and timeframes, you establish a roadmap for your I-Chart forecast, ensuring that it aligns with your business goals and provides actionable insights.
Step 3: Construct Your I-Chart
With your data gathered and objectives defined, it's time to construct your I-Chart. This step involves organizing your data in a structured manner that facilitates analysis and interpretation.
Start by creating a table or spreadsheet that aligns with the metrics you've identified. Each metric should have its own column, with rows representing different time periods or categories. For instance, if you're forecasting sales, you might have columns for different product categories and rows for each month of the year.
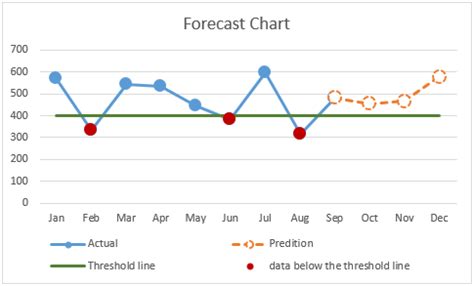
As you populate your I-Chart with data, consider the visual representation. I-Charts often utilize color-coding or shading to highlight trends and anomalies. For example, you might shade cells based on whether the data point is above or below a certain threshold, making it easier to identify areas of concern or opportunity.
Remember, the goal is to create a clear and concise visual representation of your data. By organizing your I-Chart effectively, you'll be able to quickly identify patterns and make informed decisions based on your analysis.
Step 4: Analyze and Interpret the Data

Once your I-Chart is constructed, the real work begins. This step involves a deep dive into the data, where you'll uncover valuable insights and make informed predictions.
Begin by reviewing the overall trends and patterns that emerge from your I-Chart. Are there any consistent increases or decreases over time? Are there specific time periods or categories that stand out as high-performing or underperforming? Identifying these trends is crucial for understanding the broader context of your data.
Next, delve into the specifics. Examine individual data points and their relationships to one another. Look for correlations or anomalies that might provide insights into underlying causes or future outcomes. For example, if you notice a significant drop in sales during a particular month, investigate potential reasons such as seasonal trends, economic factors, or marketing campaigns.
Utilize additional analytical tools or techniques as needed. This could involve regression analysis to identify relationships between variables, or time series analysis to forecast future trends. By employing these methods, you enhance the accuracy and reliability of your I-Chart forecast.
Step 5: Make Informed Decisions and Act
The final step in the I-Chart forecasting process is where the real value is realized. Based on the insights derived from your analysis, it's time to make informed decisions and take action.
Start by prioritizing the actions that align with your business objectives. If your forecast indicates a potential dip in sales, consider strategies to mitigate this risk, such as adjusting marketing campaigns or exploring new product offerings. On the other hand, if your forecast predicts a surge in demand, ensure you have the necessary resources and capacity to meet this demand effectively.
Remember, the I-Chart is a dynamic tool. As you implement your decisions and observe the outcomes, continuously update your I-Chart with new data. This iterative process ensures that your forecasts remain accurate and relevant, allowing you to adapt and optimize your strategies as your business evolves.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I ensure the accuracy of my I-Chart forecast?
+
The accuracy of your I-Chart forecast relies on the quality of your data and the effectiveness of your analysis. Ensure you collect relevant and reliable data from diverse sources, and thoroughly analyze your I-Chart to identify trends and patterns. Regularly updating your I-Chart with new data and refining your forecasting models can further enhance accuracy.
Can I-Charts be used for long-term forecasting?
+
Absolutely! I-Charts are versatile and can be adapted for both short-term and long-term forecasting. When forecasting over an extended period, ensure you have a robust dataset that captures historical trends and consider using advanced analytical techniques to account for potential changes in market dynamics.
What if my data shows inconsistent patterns or anomalies?
+
Inconsistent patterns or anomalies in your data can provide valuable insights. These deviations could indicate underlying issues or opportunities that require further investigation. Analyze these anomalies to understand their causes and implications, and use this information to refine your forecasting models and decision-making processes.
How often should I update my I-Chart forecast?
+
The frequency of updating your I-Chart forecast depends on the nature of your business and the dynamics of your industry. In rapidly changing environments, more frequent updates may be necessary to adapt to market fluctuations. As a general guideline, consider updating your I-Chart at least quarterly to ensure your forecasts remain accurate and relevant.
Are there any limitations to using I-Charts for forecasting?
+
While I-Charts are a powerful tool for forecasting, they are most effective when used in conjunction with other analytical techniques and domain expertise. I-Charts provide a high-level overview of data, but more nuanced insights may require additional analysis. It’s important to consider the limitations of your data and the complexity of your business when interpreting I-Chart forecasts.