Transform Quarterly Data into Annual Reports
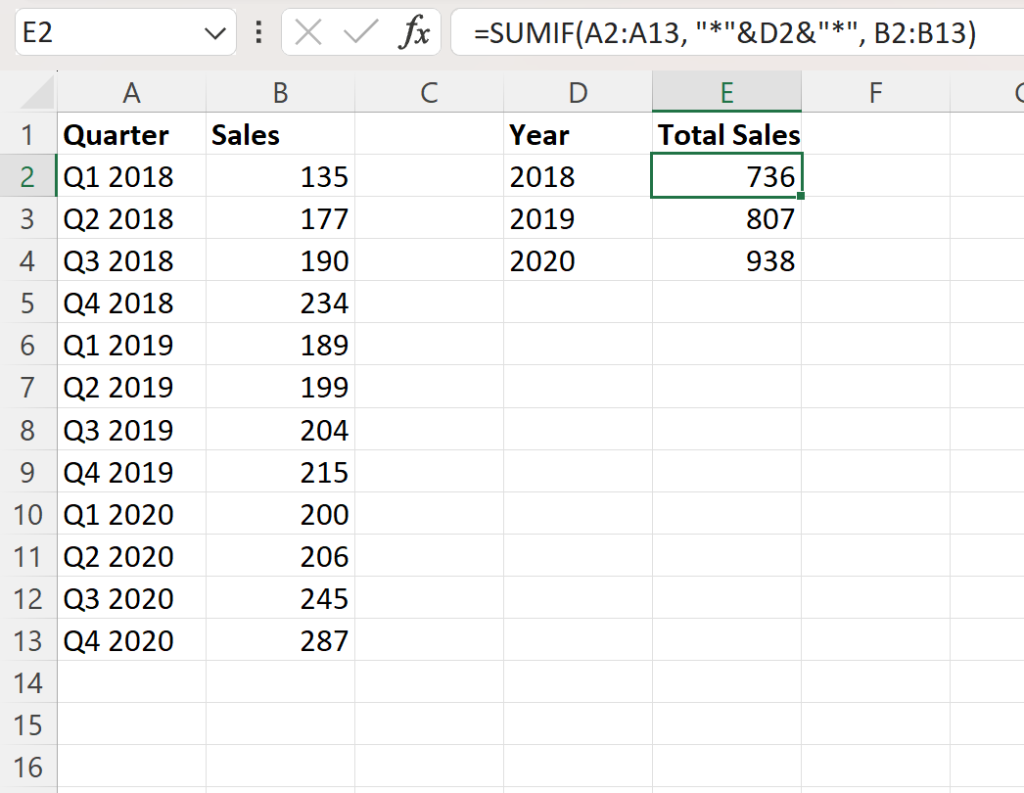
Transforming quarterly data into comprehensive annual reports is a critical task for businesses and organizations seeking to analyze their performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions. This process involves consolidating and interpreting data from multiple quarters to gain a holistic view of the year's performance. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of this transformation, offering expert insights and a step-by-step guide to creating insightful annual reports.
Understanding the Significance of Annual Reports

Annual reports are pivotal documents that summarize an organization’s activities, financial health, and strategic achievements over the course of a year. They provide a comprehensive overview, allowing stakeholders, investors, and management to assess the organization’s performance, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions for the future.
These reports serve multiple purposes. They offer transparency to external stakeholders, such as shareholders and the general public, showcasing the organization's financial stability and its commitment to accountability. Internally, annual reports are invaluable tools for management and employees, guiding strategic planning, performance evaluation, and decision-making processes.
Furthermore, annual reports often include key performance indicators (KPIs) and strategic objectives, which help organizations measure their progress and ensure they are on track to meet their long-term goals. By analyzing data from various quarters, organizations can identify trends, assess the impact of seasonal variations, and make adjustments to their strategies accordingly.
The Process of Transforming Quarterly Data

Transforming quarterly data into an annual report involves a systematic approach that requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide to this process:
1. Data Collection and Organization
The first step is to gather all relevant quarterly data. This includes financial statements, sales figures, operational metrics, and any other key performance indicators that are tracked on a quarterly basis. Ensure that the data is organized in a structured manner, with each quarter’s data clearly labeled and easily accessible.
At this stage, it's crucial to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Cross-reference the data with other sources to validate its integrity. Any discrepancies or anomalies should be identified and resolved to maintain the reliability of the annual report.
| Quarter | Revenue ($) | Profit Margin | Customer Acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 1,200,000 | 15% | 300 |
| Q2 | 1,500,000 | 18% | 450 |
| Q3 | 1,350,000 | 16% | 280 |
| Q4 | 1,650,000 | 20% | 520 |

2. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Once the data is organized, the next step is to analyze and interpret it. This involves calculating annual totals, averages, and identifying key trends and variations across the quarters. Look for patterns, compare performance against set targets or previous years, and assess the impact of seasonal factors or specific events.
For instance, you might notice a consistent increase in revenue each quarter, indicating a positive growth trend. On the other hand, you may also identify specific quarters where performance dipped, which could be due to external factors or internal strategies that need adjustment.
3. Identifying Key Insights and Metrics
As you analyze the data, focus on identifying the most significant insights and metrics. These are the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will form the backbone of your annual report. KPIs can vary depending on the organization’s goals and industry, but common examples include revenue growth, market share, customer satisfaction scores, and operational efficiency metrics.
For a tech startup, KPIs might include year-over-year user growth, app download rates, and average user engagement time. In contrast, a manufacturing company might prioritize KPIs such as production efficiency, defect rates, and on-time delivery performance.
4. Storytelling and Contextualization
Annual reports are more than just a collection of numbers and metrics. They should tell a story, providing context and narrative to the data. This step involves weaving the key insights and metrics into a compelling narrative that showcases the organization’s journey and achievements over the year.
For instance, you might highlight how a strategic marketing campaign in Q2 led to a significant increase in customer acquisition, which in turn contributed to the overall revenue growth for the year. Providing this context helps stakeholders understand the "why" behind the numbers and appreciate the organization's strategic direction.
5. Visual Representation and Data Visualization
To make the annual report more engaging and easier to comprehend, consider incorporating visual elements. Data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and infographics, can help illustrate key trends, comparisons, and relationships between different metrics. These visuals can provide a quick and intuitive understanding of the data, enhancing the overall impact of the report.
For example, a line graph showcasing the organization's revenue growth over the four quarters can visually emphasize the positive trajectory, making it easier for stakeholders to grasp the performance trend at a glance.
6. Strategic Recommendations and Future Outlook
Annual reports should not only reflect on past performance but also provide strategic recommendations for the future. Based on the analysis and insights derived from the data, propose actionable strategies or initiatives that can drive the organization forward.
For instance, if the data analysis reveals a consistent decline in a specific product line's sales, the report might recommend a re-evaluation of the product's positioning, a shift in marketing strategies, or even the exploration of new market segments.
7. Final Review and Approval
Before finalizing the annual report, conduct a thorough review to ensure accuracy, consistency, and alignment with the organization’s goals and messaging. This review should involve key stakeholders, including financial experts, marketing professionals, and senior management, to ensure that the report accurately represents the organization’s performance and strategic direction.
Once the report has been reviewed and approved, it can be distributed to stakeholders, published on the organization's website, or included in annual general meetings to provide transparency and facilitate informed decision-making.
FAQs
How often should annual reports be updated and distributed?
+Annual reports are typically prepared and distributed once a year, reflecting on the organization’s performance over the previous 12 months. However, some organizations may choose to produce interim reports or provide updates on key metrics more frequently to keep stakeholders informed.
What are some common challenges in transforming quarterly data into annual reports?
+Common challenges include ensuring data accuracy and consistency across different quarters, identifying and explaining significant variations in performance, and presenting a clear and engaging narrative that highlights key achievements and areas for improvement.
How can data visualization enhance the impact of an annual report?
+Data visualization techniques, such as charts and graphs, can make complex data more accessible and engaging. They provide a visual representation of trends, comparisons, and relationships, allowing stakeholders to quickly grasp key insights and make informed decisions. Effective data visualization can enhance the impact and understanding of the annual report.



