Motherboard Battery Lifespan: An Ultimate Guide
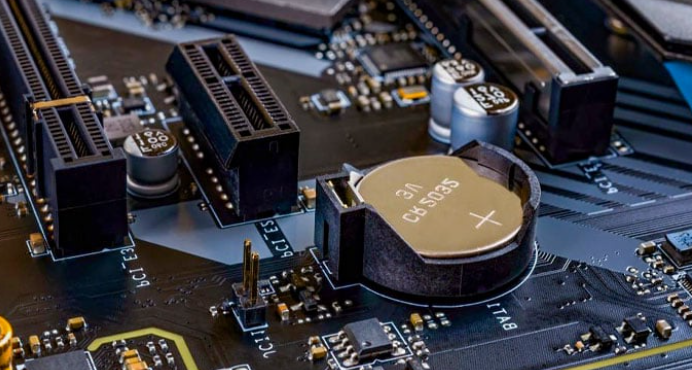
The motherboard battery, often overlooked, is a critical component that plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality and longevity of your computer system. This small yet essential power source, typically a lithium-ion or lithium-polymer battery, ensures that your computer's real-time clock (RTC) continues to operate, even when the main power is off. It also maintains the CMOS settings, ensuring your system boots up correctly each time. Despite its importance, many users are unaware of the motherboard battery's role and its potential impact on their computing experience.
In this ultimate guide, we will delve deep into the world of motherboard batteries, exploring their types, functions, lifespan, and the factors that influence their performance. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of these miniature powerhouses and the steps you can take to ensure their optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding Motherboard Batteries

Motherboard batteries, often referred to as CMOS batteries, are designed to provide a continuous power source for the Real-Time Clock (RTC) and the Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) memory on your motherboard. This ensures that crucial information, such as the system time, date, and BIOS settings, is retained even when the main power is switched off.
Types of Motherboard Batteries
Over the years, motherboard manufacturers have utilized various types of batteries to power the RTC and CMOS. The most common types include:
- Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: These are the most widely used batteries in modern motherboards. They offer a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness, providing a stable power source for an extended period.
- Lithium-Polymer (Li-Po) Batteries: These batteries are gaining popularity due to their flexibility and slim profile. They offer a high energy density, making them ideal for compact motherboard designs.
- Coin-Cell Batteries: Older motherboards often used coin-cell batteries, which are small, round, and resemble a coin. These batteries, while reliable, have a shorter lifespan compared to their modern counterparts.
The choice of battery type depends on the motherboard's design, intended use, and the manufacturer's preferences. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, which we will explore further in this guide.
Functionality and Impact
The primary function of the motherboard battery is to maintain the RTC's operation, ensuring accurate timekeeping even during power outages. This is particularly crucial for systems that rely on time-sensitive operations, such as servers or systems with scheduled tasks.
Additionally, the battery powers the CMOS memory, which stores the BIOS settings. This includes critical information like the system boot order, hardware configurations, and power management settings. If the battery fails, the system may encounter boot issues, incorrect date and time settings, or even lose its custom BIOS configurations.
Motherboard Battery Lifespan: What You Need to Know

Understanding the lifespan of a motherboard battery is crucial for effective system management and planning. While the actual lifespan can vary depending on several factors, we'll provide an in-depth analysis to give you a clearer picture.
Expected Lifespan
The expected lifespan of a motherboard battery depends largely on its type and the environmental conditions in which it operates. On average, modern lithium-ion batteries can last between 3 to 5 years, while lithium-polymer batteries can extend up to 7 years or more. Coin-cell batteries, on the other hand, have a shorter lifespan, typically lasting around 2 to 3 years.
However, it's important to note that these are average lifespans, and actual performance can vary. Several factors can influence the battery's longevity, including temperature, usage patterns, and the overall health of the motherboard.
Factors Influencing Lifespan
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can significantly impact the battery's lifespan. High temperatures can accelerate the chemical reactions within the battery, leading to a faster discharge rate and reduced capacity. On the other hand, extremely low temperatures can hinder the battery's performance, causing it to discharge more rapidly or even become non-functional.
- Usage Patterns: The frequency and nature of the motherboard's use can also affect the battery's lifespan. Systems that are frequently powered on and off, or those that experience frequent power outages, may put more strain on the battery, leading to a shorter lifespan. Conversely, systems that remain powered on for extended periods may see a longer battery lifespan.
- Motherboard Health: The overall health and condition of the motherboard can also impact the battery's performance. A faulty or failing motherboard can draw excessive power from the battery, causing it to deplete faster. Additionally, a damaged or corroded battery connector on the motherboard can hinder the battery's ability to provide a stable power source.
Signs of a Failing Motherboard Battery
Identifying a failing motherboard battery is crucial for timely replacement and to prevent potential system issues. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Incorrect Date and Time: One of the earliest signs of a failing battery is an incorrect system date and time. If you notice that your computer's clock is consistently fast or slow, or if it resets to a default date and time after a power outage, it could indicate a battery issue.
- System Boot Problems: A failing battery can also lead to boot-related issues. Your system may take longer to boot up, or it may fail to boot entirely. In some cases, you might encounter error messages related to the BIOS or the CMOS configuration.
- Loss of Custom BIOS Settings: If you've made custom BIOS configurations, such as overclocking settings or power management profiles, and these settings are lost after a power outage or system restart, it could be a sign of a failing battery.
- Visual Indicators: In some cases, you might notice physical signs of a failing battery. This could include corrosion or swelling of the battery, which can indicate a chemical reaction within the battery or a leak. These visual cues are clear indicators that the battery needs immediate replacement.
Maintaining and Replacing Motherboard Batteries
Proper maintenance and timely replacement of motherboard batteries are essential to ensure optimal system performance and prevent unexpected issues.
Maintenance Tips
- Temperature Control: Maintain optimal operating temperatures for your system. Avoid exposing your computer to extreme heat or cold, as this can impact the battery's performance and lifespan.
- Power Management: Implement effective power management strategies. If your system is frequently powered on and off, consider using sleep or hibernate modes instead. This can reduce the strain on the battery and extend its lifespan.
- Regular Updates: Keep your BIOS and firmware up to date. Updates often include optimizations and bug fixes that can improve the overall stability and performance of your system, including the battery's efficiency.
Replacement Process
Replacing a motherboard battery is a relatively straightforward process, but it requires careful handling and attention to detail. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Battery: Locate the battery on your motherboard. It's typically a small, round component, often labeled as "CMOS Battery" or "RTC Battery."
- Disconnect Power: Ensure that your system is powered off and unplugged from the mains. This is crucial for your safety and to prevent any accidental electrical discharge.
- Open the Case: Remove the side panel of your computer case to access the motherboard. Take note of any cables or connectors that may need to be removed or rerouted to access the battery.
- Remove the Battery: Gently pry the battery out of its connector. Use a plastic tool or a flat-head screwdriver to avoid damaging the motherboard or the battery connector.
- Install the New Battery: Place the new battery into the connector, ensuring it's securely seated. Reconnect any cables or connectors you may have removed earlier.
- Reassemble and Power On: Reinstall the side panel and power on your system. Check the date and time settings to ensure the battery is functioning correctly.
It's recommended to use a battery of the same type and specifications as the original to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Conclusion

The motherboard battery, though small, plays a critical role in the overall functionality and longevity of your computer system. Understanding its types, functions, and lifespan is essential for effective system management and maintenance. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this guide, you can ensure your motherboard battery performs optimally and extends its lifespan, contributing to a smoother and more reliable computing experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I replace my motherboard battery?
+As a general guideline, it’s recommended to replace your motherboard battery every 3 to 5 years. However, this timeframe can vary based on factors like temperature, usage patterns, and the overall health of your motherboard. Regularly monitoring your system’s date and time settings can help you identify when a battery replacement is necessary.
Can I use any battery for my motherboard, or does it have to be a specific type?
+While it’s possible to use batteries of similar specifications, it’s best to use a battery of the same type and capacity as the original. Using a different battery type may not provide the same level of performance or could even lead to compatibility issues. Always refer to your motherboard’s manual or consult with the manufacturer for the recommended battery type.
What happens if I don’t replace a failing motherboard battery?
+If you ignore a failing motherboard battery, it can lead to various issues. Your system may encounter boot problems, lose its custom BIOS settings, or even become non-functional. Additionally, a completely discharged battery can cause data corruption or loss, especially if your system relies on time-sensitive operations.
Are there any safety precautions I should take when replacing the motherboard battery?
+Yes, safety should always be a priority. Ensure your system is powered off and unplugged before attempting any replacement. Be cautious when handling the battery, as some types can leak or release harmful substances if damaged. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the process, it’s best to seek professional assistance.
Can a failing motherboard battery affect other components in my system?
+While a failing motherboard battery primarily impacts the system’s date, time, and BIOS settings, it can indirectly affect other components. For instance, if the battery is drawing excessive power due to a fault, it could lead to instability or even damage to other components. Regularly monitoring and replacing the battery can help prevent such issues.



