Powerful Lookup Functions: HLOOKUP Meets VLOOKUP

In the realm of data manipulation and analysis, lookup functions are indispensable tools that enable users to retrieve specific information from large datasets efficiently. While the VLOOKUP function has long been a staple in the Excel user's toolkit, its horizontal counterpart, the HLOOKUP, often remains underutilized. This article aims to explore the strengths and applications of the HLOOKUP function, showcasing how it complements and expands the capabilities of VLOOKUP.
Understanding the VLOOKUP Function
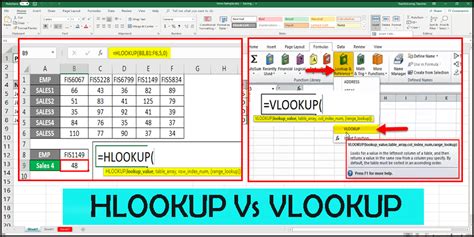
The VLOOKUP function is a versatile tool that searches for a value in the leftmost column of a table and returns the corresponding value from a specified column to the right. It is particularly useful when dealing with vertical data structures, where the lookup value is in a column on the left side of the table and the desired result is in a column on the right side.
The function’s syntax is straightforward: =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]). Here, lookup_value is the value you want to find, table_array is the range of cells containing the data, col_index_num specifies the column from which the result should be returned, and range_lookup is an optional argument that determines whether an exact or approximate match is sought.
Exploring the Power of HLOOKUP

While VLOOKUP excels in vertical data scenarios, the HLOOKUP function shines when data is arranged horizontally. It searches for a value in the top row of a table and returns the corresponding value from a specified row below. This makes it ideal for situations where the lookup value is in a row at the top of the table, and the desired result is in a row below it.
The syntax for HLOOKUP is similar to VLOOKUP: =HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num, [range_lookup]). The main difference lies in the interpretation of the table_array and row_index_num arguments. Here, table_array refers to the range of cells containing the data, and row_index_num specifies the row from which the result should be returned.
Comparative Analysis: VLOOKUP vs. HLOOKUP
Both VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP have their unique strengths and applications. VLOOKUP is perfect for scenarios where data is arranged vertically, making it easy to find and retrieve information from a column. On the other hand, HLOOKUP excels when data is presented horizontally, allowing users to efficiently extract information from rows.
Consider a scenario where you have a database of employee information with their names, IDs, and departments listed horizontally. In this case, HLOOKUP would be the ideal choice to quickly find an employee’s department based on their ID or name. Conversely, if the data were structured vertically with employee IDs listed in a column, VLOOKUP would be the go-to function.
The choice between VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP often depends on the orientation of your data. If your data is structured vertically, VLOOKUP is your friend. However, if your data is arranged horizontally, HLOOKUP is the tool you need to efficiently retrieve the desired information.
Advanced Techniques with HLOOKUP
The power of HLOOKUP extends beyond basic lookups. Here are some advanced techniques to enhance your data manipulation skills:
Multiple Lookup Values
HLOOKUP allows you to perform lookups for multiple values simultaneously. By combining HLOOKUP with other functions like INDEX and MATCH, you can create powerful formulas to retrieve data for multiple lookup values in a single formula.
For instance, imagine you have a table with student names and their corresponding exam scores. You can use HLOOKUP with INDEX and MATCH to find the average score for a group of students. This technique can be especially useful when dealing with large datasets.
Error Handling with IFERROR
To enhance the reliability of your formulas, you can combine HLOOKUP with the IFERROR function. This combination ensures that your formula returns a specified value or performs an alternative action when the HLOOKUP function cannot find a match.
For example, if you’re looking up values in a large table and expect some values to be missing, you can use IFERROR to return a default value or a custom message, preventing errors from propagating throughout your spreadsheet.
Dynamic Range Lookup
HLOOKUP’s ability to handle dynamic ranges can be a game-changer. By using the OFFSET function in conjunction with HLOOKUP, you can create formulas that automatically adjust to changing data ranges, making your spreadsheets more robust and adaptable.
Imagine you have a table that is regularly updated with new data. By using OFFSET with HLOOKUP, you can ensure that your formula always references the correct range of cells, even if the table expands or contracts.
Real-World Applications
The versatility of HLOOKUP makes it applicable in various real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples:
Product Pricing in E-commerce
In an e-commerce setting, HLOOKUP can be used to retrieve product prices based on their IDs. By maintaining a pricing table with product IDs in the top row and corresponding prices in the rows below, you can efficiently update and display prices for a large catalog of products.
Financial Analysis
HLOOKUP is invaluable in financial analysis, especially when dealing with horizontal data structures. For instance, when analyzing a company’s financial statements, you can use HLOOKUP to quickly find and compare financial metrics like revenue, expenses, or profit margins across different years or reporting periods.
Data Consolidation
When consolidating data from multiple sources, HLOOKUP can be a lifesaver. By using HLOOKUP with INDEX and MATCH, you can merge data from different tables based on common keys, ensuring accurate and efficient data consolidation.
Conclusion

The HLOOKUP function, though often overshadowed by its vertical counterpart VLOOKUP, is a powerful tool in the Excel user’s arsenal. Its ability to handle horizontal data structures and perform advanced lookups makes it an essential skill for data analysts and spreadsheet enthusiasts alike. By mastering HLOOKUP and its advanced techniques, you can streamline your data manipulation processes and unlock new levels of efficiency in your work.
What is the main difference between VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP?
+VLOOKUP searches for a value in the leftmost column of a table and returns the corresponding value from a specified column to the right, while HLOOKUP searches for a value in the top row of a table and returns the corresponding value from a specified row below.
When should I use HLOOKUP instead of VLOOKUP?
+HLOOKUP is ideal when your data is arranged horizontally, such as when you have lookup values in a row at the top of the table and the desired result is in a row below it. In contrast, VLOOKUP is best suited for vertical data structures where the lookup value is in a column on the left side of the table.
Can I combine HLOOKUP with other functions for more complex lookups?
+Absolutely! HLOOKUP can be combined with functions like INDEX and MATCH to perform more complex lookups. This allows you to retrieve data for multiple lookup values in a single formula, enhancing your data manipulation capabilities.



