Heat Pump Size: The Ultimate Guide

Welcome to the comprehensive guide on heat pump sizing, an essential aspect of ensuring optimal heating and cooling efficiency in your home. As we delve into this topic, we'll uncover the intricate process of selecting the right-sized heat pump, a critical decision that significantly impacts your comfort and energy savings. With the increasing popularity of heat pumps as an energy-efficient alternative to traditional HVAC systems, understanding their sizing requirements is more important than ever.
Heat pumps are a vital component of any home's heating and cooling system, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution. However, the size of the heat pump you choose can make or break the efficiency and comfort of your indoor environment. In this guide, we'll explore the factors that influence heat pump sizing, provide detailed calculations and considerations, and offer expert advice to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Heat Pump Sizing

Heat pump sizing is a complex process that requires careful consideration of various factors. The size of a heat pump is typically measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) or tons, with one ton of cooling capacity equating to approximately 12,000 BTUs. This measurement refers to the amount of heat the pump can remove from your home in an hour.
The goal of proper heat pump sizing is to ensure that the system can effectively and efficiently heat or cool your home without overworking itself. An oversized heat pump may short-cycle, leading to inefficient operation and increased energy costs. On the other hand, an undersized heat pump will struggle to maintain the desired temperature, resulting in discomfort and potentially damaging your system.
Key Factors Influencing Heat Pump Sizing

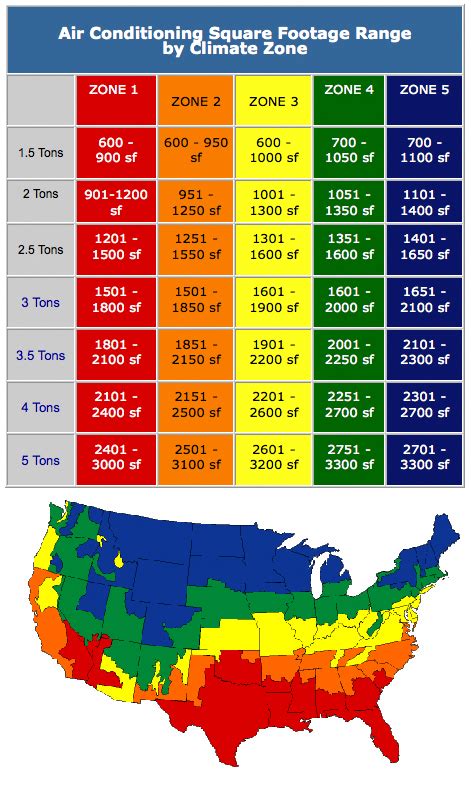
Climate and Weather Conditions
One of the primary factors influencing heat pump sizing is the climate and weather conditions in your region. Heat pumps are highly adaptable, but they perform differently in various climates. For instance, in extremely cold regions, heat pumps may need to work harder to extract heat from the outdoor air, affecting their sizing requirements.
It's crucial to consider the lowest and highest temperatures your area experiences. Heat pumps are generally designed to operate efficiently within a specific temperature range. If your region experiences extreme cold or hot temperatures, you may need a heat pump with a higher capacity to ensure it can handle these conditions effectively.
| Climate Zone | Temperature Range (°F) |
|---|---|
| Zone 1: Mild | 40°F - 60°F |
| Zone 2: Moderate | 30°F - 50°F |
| Zone 3: Cold | 20°F - 40°F |
| Zone 4: Extreme Cold | Below 20°F |

Home Size and Insulation
The size of your home and its insulation play a significant role in heat pump sizing. A larger home will generally require a higher-capacity heat pump to adequately heat or cool the entire space. Similarly, a well-insulated home may need a smaller heat pump since it can retain heat more effectively.
When considering home size, it's essential to assess the total square footage and the layout. A home with multiple stories or an open floor plan may require a different sizing approach than a single-story home with separate rooms. Additionally, factors like ceiling height, window size, and the number of occupants can influence the heat pump's capacity needs.
Heating and Cooling Loads
Heating and cooling loads refer to the amount of heat that needs to be added or removed from your home to maintain a comfortable temperature. These loads are calculated based on various factors, including the home's insulation, the number of windows, the orientation of the house, and the climate.
Accurate calculation of heating and cooling loads is critical for proper heat pump sizing. This process involves a detailed analysis of your home's characteristics and the use of specialized software or tools. By understanding your specific heating and cooling needs, you can ensure that the heat pump's capacity matches these requirements precisely.
Efficiency Ratings
Heat pumps are rated for their energy efficiency using the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF). These ratings indicate how effectively the heat pump can convert energy into heating or cooling output.
When selecting a heat pump, it's essential to consider its efficiency ratings. A higher SEER and HSPF indicate a more energy-efficient model, which can result in significant cost savings over the life of the system. However, it's important to strike a balance between efficiency and capacity. A highly efficient heat pump may be oversized for your home, leading to inefficiencies and increased initial costs.
Calculating Heat Pump Size
Manual J Calculation
One of the most accurate methods for determining the correct heat pump size is the Manual J calculation. This comprehensive process involves assessing various factors specific to your home, including insulation levels, window size and orientation, and the number of occupants. By considering these factors, a Manual J calculation can provide an accurate heating and cooling load for your home.
While you can perform a Manual J calculation yourself using online tools and guides, it's recommended to seek professional assistance. HVAC contractors or energy auditors can conduct these calculations accurately, ensuring that your heat pump is properly sized for your unique home environment.
Load Calculation Considerations
When calculating the heating and cooling loads for your home, several key considerations come into play:
- Insulation Levels: The level of insulation in your home directly impacts the heat pump's sizing. Well-insulated homes can retain heat more effectively, reducing the load on the heat pump.
- Window Orientation and Size: Windows can be a significant source of heat loss or gain. South-facing windows may provide passive solar heating, while north-facing windows tend to lose more heat. The size and orientation of windows can influence the heat pump's capacity requirements.
- Ductwork Efficiency: If your home has ductwork, its efficiency is crucial. Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can result in heat loss, increasing the heat pump's load.
- Occupancy and Lifestyle: The number of occupants in your home and their lifestyle habits can affect the heating and cooling loads. For example, a home with multiple occupants who are often home may require a larger heat pump to accommodate the increased heat gain.
Selecting the Right Heat Pump Size
Matching Capacity to Heating and Cooling Loads
Once you have determined your home's heating and cooling loads, the next step is to select a heat pump with an appropriate capacity. It's crucial to find a balance between the heat pump's capacity and your home's needs. An oversized heat pump may be more efficient in certain conditions, but it can lead to short-cycling, which reduces overall efficiency and lifespan.
By matching the heat pump's capacity to your home's heating and cooling loads, you ensure that the system operates at its peak efficiency. This balance can result in optimal comfort and significant energy savings over time.
Considering Heat Pump Efficiency
When selecting a heat pump, it's essential to consider its efficiency ratings. While a more efficient heat pump may have a higher upfront cost, it can lead to substantial long-term savings on energy bills. Here's a breakdown of the key efficiency ratings to consider:
- SEER Rating: The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) measures the heat pump's cooling efficiency. A higher SEER rating indicates a more energy-efficient cooling performance.
- HSPF Rating: The Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) measures the heat pump's heating efficiency. A higher HSPF rating means the heat pump is more efficient at heating your home.
Expert Tips for Optimal Sizing
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting with an experienced HVAC contractor or energy auditor can provide valuable insights into your home's specific needs. They can perform detailed calculations and offer expert advice on the most suitable heat pump size and model.
- Consider Zone Heating and Cooling: If your home has multiple zones with different heating and cooling requirements, you may benefit from a zoned heat pump system. This approach allows for precise temperature control in each zone, optimizing comfort and efficiency.
- Factor in Future Expansion: If you have plans to expand your home in the future, consider the potential impact on heating and cooling loads. Sizing the heat pump with some capacity to spare can accommodate future additions without requiring a complete system overhaul.
Heat Pump Performance Analysis
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the primary benefits of properly sized heat pumps is their energy efficiency. By matching the heat pump's capacity to your home's heating and cooling needs, you can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower your utility bills. Heat pumps are known for their ability to provide efficient heating and cooling, especially when compared to traditional HVAC systems.
A well-sized heat pump can achieve up to 300% efficiency, meaning it can produce three units of energy for every unit of electricity it consumes. This level of efficiency translates into substantial cost savings over the life of the system. Additionally, many heat pumps qualify for energy efficiency rebates and tax incentives, further reducing the overall cost of ownership.
Comfort and Indoor Air Quality
Proper heat pump sizing is not just about energy efficiency; it's also about ensuring optimal comfort and indoor air quality. An appropriately sized heat pump can maintain a consistent and comfortable temperature throughout your home, eliminating hot or cold spots.
Furthermore, heat pumps can improve indoor air quality by filtering and dehumidifying the air. They can remove allergens, dust, and pollutants, providing a healthier indoor environment for you and your family. By maintaining a comfortable and clean indoor climate, a well-sized heat pump contributes to improved overall well-being.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Heat pumps, like any mechanical system, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper heat pump sizing can play a significant role in reducing maintenance needs and extending the system's lifespan.
An oversized heat pump may short-cycle frequently, leading to increased wear and tear on its components. Short-cycling can cause premature failure of the compressor and other critical parts. On the other hand, an undersized heat pump may struggle to maintain the desired temperature, leading to excessive strain on the system.
By selecting the right-sized heat pump, you can ensure that it operates within its designed parameters, reducing the risk of breakdowns and extending its lifespan. Regular maintenance, including cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting the outdoor unit, can further enhance the heat pump's performance and durability.
Future Implications and Innovations
Advancements in Heat Pump Technology
The heat pump industry is constantly evolving, with ongoing advancements in technology that enhance efficiency and performance. Here are some of the latest innovations in heat pump technology:
- Variable Speed Compressors: Heat pumps with variable speed compressors can adjust their output based on the heating or cooling load, optimizing efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
- Inverter Technology: Inverter-driven heat pumps use variable-frequency drives to control the speed of the compressor, allowing for precise temperature control and reduced energy use.
- Hybrid Systems: Hybrid heat pump systems combine the benefits of both air-source and ground-source heat pumps, providing efficient heating and cooling in a wide range of climates.
- Smart Controls: Heat pumps with smart controls and connectivity can adjust their operation based on real-time data, weather conditions, and occupant preferences, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the integration of heat pumps with renewable energy sources is gaining traction. Heat pumps can be effectively paired with solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy systems to create a highly efficient and environmentally friendly heating and cooling solution.
By harnessing the power of renewable energy, heat pumps can further reduce their environmental impact and lower operating costs. This integration is particularly beneficial in off-grid or remote locations where traditional power sources may be unreliable or expensive.
Heat Pump Sizing in Commercial Buildings
While this guide primarily focuses on residential heat pump sizing, the principles apply to commercial buildings as well. Commercial heat pump systems are designed to meet the unique needs of larger spaces, often with multiple zones and specific temperature requirements.
Proper sizing of commercial heat pumps is critical to ensure optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and cost savings for businesses. The process involves detailed load calculations and considerations specific to the building's size, layout, and usage patterns. By investing in properly sized commercial heat pumps, businesses can create comfortable indoor environments while reducing their carbon footprint and operating costs.
Conclusion
Heat pump sizing is a critical decision that impacts your home's comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term savings. By understanding the key factors influencing heat pump sizing, performing accurate load calculations, and selecting the right-sized heat pump, you can ensure a comfortable and energy-efficient indoor environment.
As heat pump technology continues to advance and integrate with renewable energy sources, the future of heating and cooling looks promising. With the right heat pump sizing and maintenance, you can enjoy a sustainable and comfortable home for years to come.
How do I know if my heat pump is the right size for my home?
+To determine if your heat pump is properly sized, you can look for signs such as frequent short-cycling (turning on and off rapidly), inconsistent temperatures throughout your home, and high energy bills. It’s best to consult an HVAC professional who can perform a load calculation to confirm the right size.
Can I install a heat pump myself, or do I need a professional?
+While some DIY enthusiasts may attempt to install a heat pump, it is highly recommended to hire a professional HVAC contractor. Heat pump installation requires specialized knowledge, and improper installation can lead to inefficiencies, safety hazards, and voided warranties.
Are there any tax incentives or rebates available for heat pump installations?
+Yes, there are often tax incentives and rebates available for heat pump installations, especially if you choose an energy-efficient model. These incentives can significantly offset the initial cost of the heat pump. Check with your local utility company and government agencies for the latest incentives in your area.


