5 Common Hawthorn Tree Diseases

Hawthorn Diseases: Understanding and Managing the Challenges

The hawthorn tree, with its graceful form and delicate blossoms, is a beloved addition to many landscapes. However, like all living organisms, it is susceptible to a range of diseases that can impact its health and aesthetic appeal. In this article, we delve into the five most common diseases affecting hawthorn trees, offering insights into their causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies. By arming ourselves with knowledge, we can better protect these beautiful trees and ensure their longevity.
1. Fire Blight
Fire blight, caused by the bacterium Erwinia amylovora, is a devastating disease that affects not only hawthorns but also other members of the Rosaceae family, such as apples and pears. The name “fire blight” originates from the scorched appearance of infected plant parts, which can turn black and shrivelled, resembling fire damage. This disease primarily targets young, actively growing tissues, including shoots, flowers, and fruits.
Symptoms and Identification: - Wilting and blackening of flowers and young shoots. - Cankers on branches that ooze a bacterial exudate, especially during warm, wet weather. - Infected leaves may remain attached to the tree, appearing scorched and giving the canopy a charred look. - In severe cases, the entire tree can be affected, leading to a decline in health and potential death.
Management Strategies: - Prune affected branches during dry weather, cutting at least 12 inches below the visible symptoms. Disinfect pruning tools between cuts to prevent spreading the bacteria. - Avoid excessive nitrogen fertilization, as it promotes susceptible growth. - Apply copper-based bactericides during bloom to reduce infection. - Plant resistant varieties when possible.
2. Cedar-Hawthorn Rust
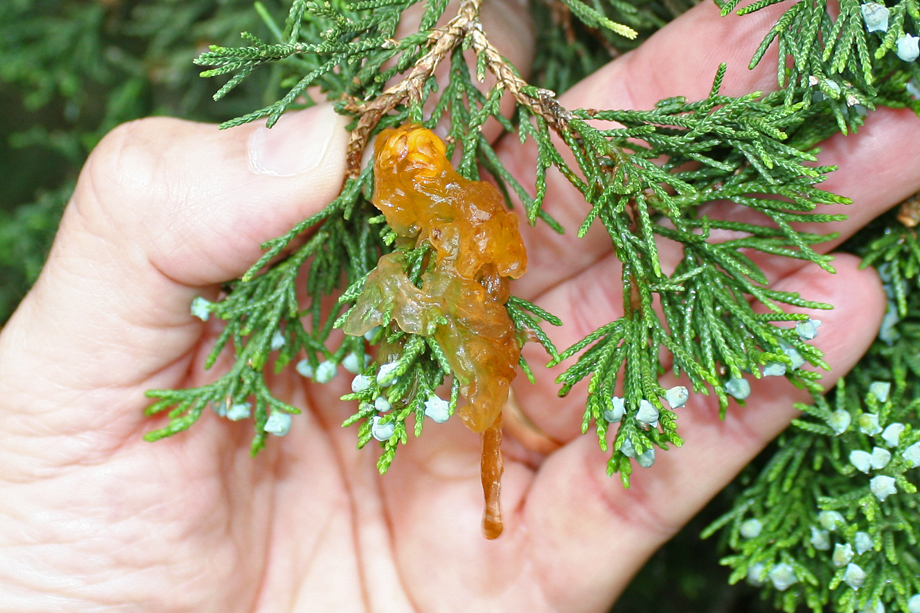
Cedar-hawthorn rust is a fungal disease caused by the pathogen Gymnosporangium globosum. It requires two different host plants to complete its life cycle: hawthorn trees and junipers. The disease gets its name from its ability to infect both hawthorns and various species of junipers.
Symptoms and Identification: - Yellow-orange spots on hawthorn leaves, which may turn into raised, corky growths. - Infected leaves often drop prematurely. - Hawthorn fruits may develop galls. - On junipers, the fungus produces bright orange, gelatinous masses on branches and needles.
Management Strategies: - Remove nearby juniper plants if possible to break the disease cycle. - Prune infected hawthorn branches to improve air circulation and reduce humidity, which can inhibit fungal growth. - Apply fungicides during the spring to protect new growth. - Plant rust-resistant hawthorn varieties when available.
3. Hawthorn Leaf Spot
Hawthorn leaf spot, caused by the fungus Diplocarpon mespili, is a common disease that primarily affects the foliage of hawthorn trees. While it rarely kills the tree, it can cause significant defoliation, impacting the tree’s overall health and appearance.
Symptoms and Identification: - Small, purple spots with a yellow halo appear on the upper surface of leaves. - As the disease progresses, the spots enlarge and may coalesce, causing the leaves to turn brown and fall prematurely. - In severe cases, the tree may experience twig dieback.
Management Strategies: - Rake and destroy fallen leaves to reduce the spread of spores. - Prune to improve air circulation, reducing the moist conditions that favor fungal growth. - Apply fungicides containing chlorothalonil or mancozeb in the spring before bud break. - Avoid overhead irrigation, as wet foliage can promote disease development.
4. Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants, including hawthorn trees. It is characterized by a white, powdery growth on leaves, buds, and young shoots, giving the tree an unsightly appearance. While it rarely kills the tree, it can weaken it and make it more susceptible to other diseases and pests.
Symptoms and Identification: - White, powdery patches on leaves, stems, and buds. - Infected leaves may curl, distort, or turn yellow. - In severe cases, the tree may experience stunted growth and reduced flowering.
Management Strategies: - Prune to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration, as powdery mildew thrives in shaded, humid conditions. - Apply fungicides containing sulfur or neem oil in the early stages of infection. - Avoid excessive nitrogen fertilization, as it promotes susceptible growth. - Remove and destroy heavily infected plant parts.
5. Root and Crown Rot
Root and crown rot are caused by various fungal pathogens, including Phytophthora and Armillaria. These diseases primarily affect the roots and lower trunk of hawthorn trees, compromising their ability to absorb water and nutrients. As a result, the entire tree can suffer from water stress and nutrient deficiencies.
Symptoms and Identification: - Wilting of leaves, even when the soil is moist. - Discolored, soft, or decaying roots. - Darkened and discolored bark at the base of the trunk. - In advanced stages, the tree may exhibit canopy dieback and overall decline.
Management Strategies: - Improve soil drainage to prevent waterlogging, which favors fungal growth. - Avoid planting hawthorns in poorly drained soils or low-lying areas. - Apply fungicides containing mefenoxam or fosetyl-aluminum as a preventative measure. - Remove and destroy severely infected trees to prevent the spread of the disease.
Early detection and prompt action are crucial in managing hawthorn diseases. By understanding the unique challenges posed by each disease and implementing targeted management strategies, we can help ensure the long-term health and beauty of these cherished trees.
FAQs
What are the visible signs of fire blight on hawthorn trees?
+Fire blight causes flowers and young shoots to wilt and turn black. Cankers on branches may ooze a bacterial exudate, especially during warm, wet weather. Infected leaves may remain attached, giving the canopy a scorched appearance.
How can I prevent cedar-hawthorn rust on my hawthorn trees?
+To prevent cedar-hawthorn rust, consider removing nearby juniper plants to break the disease cycle. Improve air circulation and apply fungicides during the spring to protect new growth.
What are the early symptoms of hawthorn leaf spot?
+Hawthorn leaf spot initially presents as small, purple spots with a yellow halo on the upper surface of leaves. These spots may enlarge and coalesce, leading to premature leaf drop.
Can powdery mildew on hawthorn trees be treated organically?
+Yes, powdery mildew can be treated organically by applying fungicides containing sulfur or neem oil. Improving air circulation and sunlight penetration can also help control the disease.
What are the best practices for managing root and crown rot in hawthorns?
+To manage root and crown rot, improve soil drainage to prevent waterlogging. Apply fungicides containing mefenoxam or fosetyl-aluminum as a preventative measure, and remove severely infected trees to prevent the spread of the disease.