Unraveling Graphing Data: Common Grouping Techniques
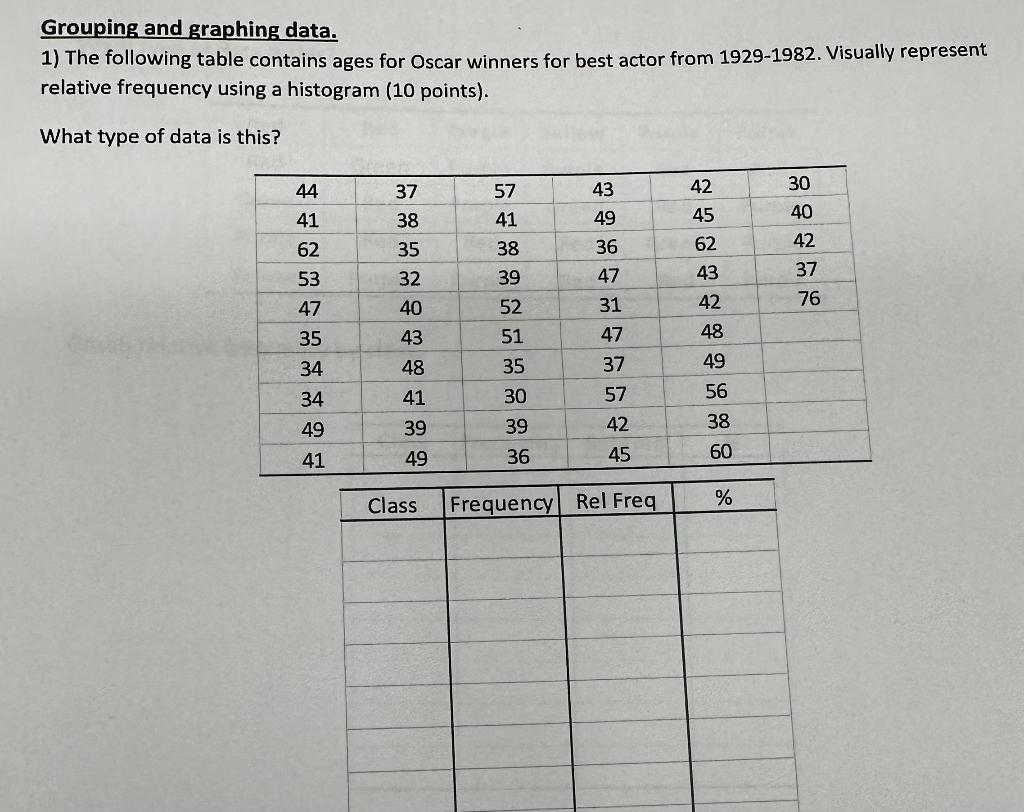
Graphing data is an essential aspect of data visualization, allowing us to gain insights, identify patterns, and communicate information effectively. One of the fundamental steps in creating meaningful graphs is grouping data. Grouping techniques play a pivotal role in organizing and presenting data in a way that highlights trends, outliers, and key relationships. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of graphing data, exploring various common grouping techniques and their applications.
The Significance of Grouping in Graphs

Grouping data in graphs serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it simplifies complex datasets, making them more manageable and easier to interpret. By categorizing data points into logical groups, we can reduce visual clutter and emphasize the underlying structure of the information. This simplification is crucial for effective communication, especially when presenting data to an audience that may not be familiar with intricate details.
Secondly, grouping enables us to uncover hidden patterns and correlations within the data. By organizing data points based on specific criteria, we can identify trends, outliers, and relationships that might not be immediately apparent when examining individual data points. This process is particularly valuable in fields such as market research, scientific analysis, and data-driven decision-making.
Common Grouping Techniques in Graphing

There are several grouping techniques commonly employed in graphing data, each suited to different types of data and analytical goals. Let’s explore some of these techniques and their applications.
Categorical Grouping
Categorical grouping involves dividing data points into distinct categories or groups based on qualitative characteristics. This technique is often used when dealing with nominal or ordinal data, where the order or magnitude of values is not relevant. Categorical grouping is particularly useful for analyzing demographic data, customer segments, or any other variable that can be categorized into discrete groups.
For instance, consider a dataset containing information about different types of fruits. Categorical grouping would involve creating groups such as "Citrus Fruits," "Stone Fruits," and "Berries," each containing fruits with similar characteristics. This grouping allows for a clear visual representation of the diversity of fruits and facilitates comparisons between different fruit categories.
| Fruit Type | Category |
|---|---|
| Apple | Pome Fruit |
| Orange | Citrus Fruit |
| Peach | Stone Fruit |
| Strawberry | Berry |

Quantitative Grouping
Quantitative grouping, on the other hand, involves dividing data points into groups based on numerical values or ranges. This technique is ideal for continuous or discrete numerical data, where the magnitude or order of values is significant. Quantitative grouping helps to identify patterns, trends, and outliers within numerical datasets.
Imagine a dataset containing information about the heights of individuals in a population. Quantitative grouping would involve creating height ranges, such as "Below 5 feet," "5-6 feet," and "Above 6 feet." This grouping allows for a visual representation of the distribution of heights and highlights any significant differences or trends within the population.
| Height Range | Number of Individuals |
|---|---|
| Below 5 feet | 120 |
| 5-6 feet | 350 |
| Above 6 feet | 50 |
Temporal Grouping
Temporal grouping is a technique specifically designed for time-series data, where data points are collected at regular intervals over time. This grouping involves organizing data points based on specific time periods or intervals, such as hours, days, weeks, months, or years. Temporal grouping is essential for analyzing trends, patterns, and seasonality in time-based data.
Consider a dataset tracking the daily sales of a retail store. Temporal grouping would involve creating groups such as "Morning Sales," "Afternoon Sales," and "Evening Sales," each representing different time periods within a day. This grouping allows for a comprehensive analysis of sales patterns throughout the day and highlights any peak or slow periods.
| Time Period | Sales Amount |
|---|---|
| Morning (9 AM - 12 PM) | $3,500 |
| Afternoon (12 PM - 4 PM) | $4,200 |
| Evening (4 PM - 8 PM) | $5,800 |
Geographical Grouping
Geographical grouping, as the name suggests, involves organizing data points based on geographical regions or locations. This technique is particularly useful when dealing with spatial data, such as sales data by region, population distribution, or climate patterns across different locations.
For instance, consider a dataset containing information about the population density of different cities. Geographical grouping would involve creating groups such as "Metropolitan Areas," "Rural Areas," and "Suburban Areas," each representing distinct geographical regions. This grouping allows for a comparative analysis of population density and helps identify areas with higher or lower concentrations of people.
| Geographical Region | Population Density (per sq. km) |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan Areas | 2,500 |
| Rural Areas | 50 |
| Suburban Areas | 1,200 |
Hierarchical Grouping
Hierarchical grouping is a powerful technique that organizes data points into a hierarchical structure, often represented as a tree-like diagram. This technique is particularly useful when dealing with data that has a natural hierarchical relationship, such as organizational structures, family trees, or product categories.
Imagine a dataset containing information about the sales performance of different product categories within a retail store. Hierarchical grouping would involve creating a structure where product categories are nested within broader categories. For example, "Electronics" might contain subcategories like "Smartphones" and "Laptops," each with further subcategories.
Choosing the Right Grouping Technique
Selecting the appropriate grouping technique depends on the nature of your data, the insights you aim to uncover, and the story you want to tell. Each technique has its strengths and is best suited to specific types of data and analytical goals.
Categorical grouping is ideal for qualitative data, allowing for a straightforward comparison of categories. Quantitative grouping is essential for analyzing numerical data and understanding distributions and outliers. Temporal grouping is crucial for time-series data, enabling the identification of trends and seasonality. Geographical grouping helps visualize spatial data, while hierarchical grouping is powerful for data with inherent hierarchical relationships.
Conclusion: Unlocking Insights through Grouping
Grouping data in graphs is a fundamental step in data visualization, enabling us to simplify complex datasets, uncover hidden patterns, and communicate information effectively. By employing the right grouping technique, we can transform raw data into powerful visual representations that drive insights and inform decision-making.
Whether it's categorical, quantitative, temporal, geographical, or hierarchical grouping, each technique has its unique strengths and applications. Understanding these techniques and their implications is crucial for any data analyst, researcher, or communicator aiming to unlock the full potential of their data. By mastering the art of grouping, we can unravel the stories hidden within our data and make informed decisions based on clear, compelling visualizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does grouping data in graphs benefit data analysis and communication?
+
Grouping data simplifies complex datasets, making them more manageable and easier to interpret. It highlights patterns, outliers, and relationships that might not be immediately apparent when examining individual data points. This simplification is crucial for effective communication, especially when presenting data to a diverse audience.
What are some common applications of categorical grouping?
+
Categorical grouping is commonly used in analyzing demographic data, customer segments, and any variable that can be categorized into discrete groups. It allows for straightforward comparisons of proportions or frequencies within each category.
How does quantitative grouping differ from categorical grouping?
+
Quantitative grouping is used for numerical data, where the magnitude or order of values is significant. It helps identify patterns, trends, and outliers within numerical datasets. Categorical grouping, on the other hand, is used for qualitative data, where the order or magnitude of values is not relevant.
What are some examples of temporal grouping in practice?
+
Temporal grouping is commonly used in analyzing time-series data, such as sales trends over different time periods (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly), website traffic patterns throughout the day, or temperature variations across seasons.



