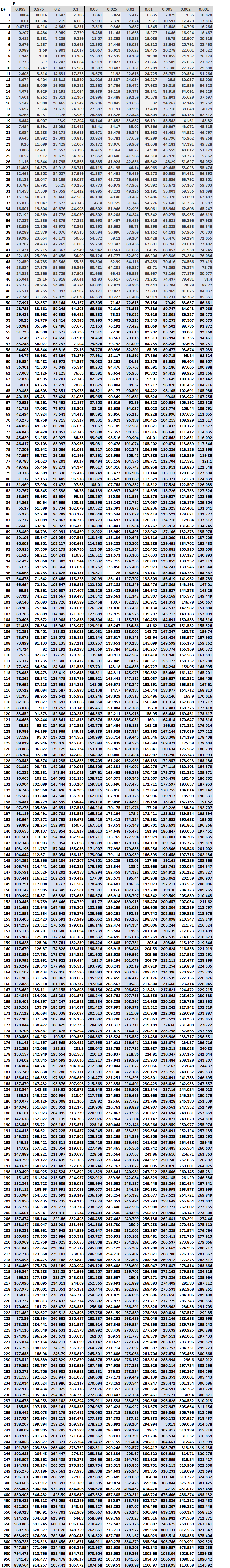
Master Google Sheets: Sumif Checkboxes

In the ever-evolving landscape of data management and analysis, Google Sheets has emerged as a powerful tool for both personal and professional use. With its intuitive interface and extensive functionality, Google Sheets allows users to perform complex calculations, create dynamic visualizations, and automate repetitive tasks. Among the myriad of features offered by this spreadsheet software, the SUMIF function stands out as a versatile and indispensable tool for handling conditional summation.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of the SUMIF function in Google Sheets, focusing on its integration with checkboxes to create dynamic and interactive data analysis tools. By the end of this article, you will have a deep understanding of how to leverage the SUMIF function, enhance your data management skills, and unlock the full potential of Google Sheets for your projects.
Understanding the SUMIF Function
The SUMIF function in Google Sheets is a versatile formula designed to calculate the sum of values in a range that meet specific criteria. It is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets, allowing you to quickly aggregate data based on specified conditions. The function takes three main arguments: a range, a criterion, and a sum_range. Here’s a breakdown of each component:
Range
The range argument specifies the cells or data range that you want to evaluate. It can be a single column, a row, or even a multi-dimensional range of cells. For instance, if you have a dataset in column A and you want to sum the values based on a criterion, you would specify A1:A100 as the range.
Criterion
The criterion argument defines the condition that must be met for a cell to be included in the sum. It can be a number, a text string, a cell reference, or a logical expression. For example, if you want to sum values greater than 100, your criterion would be >100. Alternatively, if you want to sum cells containing the text “Apple”, your criterion would be “Apple”.
Sum_range
The sum_range argument specifies the cells whose values will be summed if the criterion is met. By default, if you omit this argument, the SUMIF function will sum the values in the range specified by the first argument. However, you can provide a separate range to sum. For instance, if your data is in column B, you might specify B1:B100 as the sum_range.
Let's illustrate the SUMIF function with a simple example. Suppose you have a dataset in cells A1:A10 with various values, and you want to sum the values greater than 50. Your formula would look like this:
=SUMIF(A1:A10,">50",A1:A10)
This formula would sum all the values in the range A1:A10 that are greater than 50. The result would be displayed in the cell where you entered the formula.
Enhancing SUMIF with Checkboxes
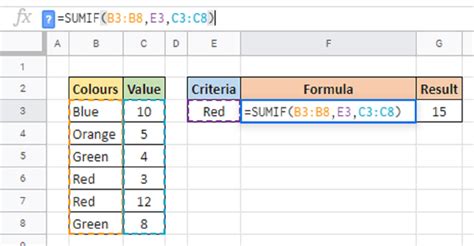
While the SUMIF function is powerful on its own, combining it with checkboxes in Google Sheets adds a layer of interactivity and dynamic functionality to your data analysis. Checkboxes are graphical controls that allow users to select or deselect options, providing a visual representation of data states.
Adding Checkboxes to Your Sheet
To begin, ensure you have a dataset with a column or row of cells where you want to add checkboxes. These cells will serve as the criteria for your SUMIF calculations. To add checkboxes, follow these steps:
- Select the cells where you want the checkboxes to appear.
- Go to the Insert menu in the Google Sheets toolbar.
- Click on Checkbox from the drop-down menu.
- Checkboxes will appear in the selected cells.
Now, you can use these checkboxes as criteria for your SUMIF calculations.
Creating a Dynamic SUMIF Formula with Checkboxes
To create a dynamic SUMIF formula that responds to checkbox states, you’ll use a combination of the SUMIF function and the ISCHECKBOX function. The ISCHECKBOX function evaluates whether a cell contains a checkbox, returning TRUE if it does and FALSE otherwise.
Here's the formula structure:
=SUMIF(range, ISCHECKBOX(criterion_range), sum_range)
In this formula, range refers to the cells you want to sum, criterion_range is the cells containing the checkboxes, and sum_range is the range of cells whose values will be summed if the checkboxes are checked.
Let's break down an example. Suppose you have a dataset in cells A1:A10 with various values, and you want to sum the values where the corresponding checkbox in cells B1:B10 is checked. Your formula would look like this:
=SUMIF(A1:A10, ISCHECKBOX(B1:B10), A1:A10)
This formula will sum the values in the range A1:A10 where the checkboxes in the corresponding cells in B1:B10 are checked. The result will be dynamically updated as you check or uncheck the checkboxes.
Advanced SUMIF Techniques with Checkboxes
The combination of SUMIF and checkboxes opens up a world of advanced data analysis possibilities. Here are some techniques to enhance your data management skills:
Multiple Criteria with AND and OR
You can combine multiple criteria using the AND and OR functions within the SUMIF formula. For example, to sum values where both checkboxes in cells B1 and C1 are checked, you would use the following formula:
=SUMIF(A1:A10, AND(ISCHECKBOX(B1), ISCHECKBOX(C1)), A1:A10)
Similarly, to sum values where either checkbox in cells B1 or C1 is checked, you would use the following formula:
=SUMIF(A1:A10, OR(ISCHECKBOX(B1), ISCHECKBOX(C1)), A1:A10)
Customizing Checkbox Labels
By default, checkboxes in Google Sheets have a generic label. However, you can customize these labels to better represent your data. To do this, simply enter the desired label in the cell next to the checkbox. For example, if you want the checkbox in cell B1 to have the label “Apple,” you would enter “Apple” in cell C1. This label will be displayed next to the checkbox.
Using Checkboxes for Data Validation
Checkboxes can also be used for data validation, ensuring that specific conditions are met before data is entered or modified. For instance, you can create a checkbox that must be checked before a user can input data in a particular cell. This can be especially useful for controlling data entry and maintaining data integrity.
Best Practices and Troubleshooting
When working with SUMIF and checkboxes, it’s essential to keep a few best practices in mind:
- Consistency: Ensure that your data is consistently formatted and that the checkboxes are aligned with the correct data range.
- Avoid Overlapping Criteria: When using multiple criteria, be cautious not to create overlapping conditions that could lead to inaccurate results.
- Test and Verify: Always test your formulas with sample data to ensure they are functioning as intended.
- Utilize Conditional Formatting: Conditional formatting can enhance the visual representation of your data, making it easier to identify patterns and trends.
If you encounter issues with your SUMIF calculations or checkboxes, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check Formula Syntax: Ensure that your formula is correctly structured and that all arguments are properly referenced.
- Verify Data Range: Confirm that the ranges specified in your formula match the intended data range.
- Refresh Formulas: Sometimes, formulas may not update dynamically. In such cases, manually refreshing the formulas by pressing F9 or selecting Data > Refresh may resolve the issue.
- Seek Online Resources: The Google Sheets community is vast and supportive. If you encounter a complex issue, searching online forums or documentation can often provide solutions.
Conclusion: Mastering Data Analysis with SUMIF and Checkboxes

The SUMIF function, when combined with checkboxes, offers a powerful toolkit for data analysis and management in Google Sheets. By leveraging these features, you can create dynamic, interactive spreadsheets that respond to user input and provide real-time data insights. Whether you’re a data analyst, a project manager, or simply a user looking to enhance your spreadsheet skills, the SUMIF function with checkboxes is a valuable asset.
As you continue to explore the capabilities of Google Sheets, remember that practice and experimentation are key to mastering these tools. With time and dedication, you'll be able to tackle increasingly complex data analysis tasks and make informed decisions based on your data.
FAQ
Can I use checkboxes with other Google Sheets functions besides SUMIF?
+
Yes, checkboxes can be used with various other Google Sheets functions. For example, you can use them with COUNTIF, AVERAGEIF, or even custom functions to create dynamic calculations and analyses.
How can I remove checkboxes from my sheet?
+
To remove checkboxes, simply select the cells containing the checkboxes and click on the “Checkbox” option in the Insert menu again. This will remove the checkboxes from the selected cells.
Can I use checkboxes to filter data in Google Sheets?
+
Yes, checkboxes can be used for data filtering. You can create a custom filter using checkboxes, allowing users to select which data they want to display based on the checked options.