Mastering Filter Pivot Table Techniques

Pivot tables are an indispensable tool for data analysis, especially when working with large datasets. Among the many features and functionalities they offer, filters play a crucial role in refining and extracting specific information. This article will delve into the world of filter pivot table techniques, exploring the various ways they can be utilized to enhance your data analysis skills and provide deeper insights.
Understanding Filter Pivot Tables
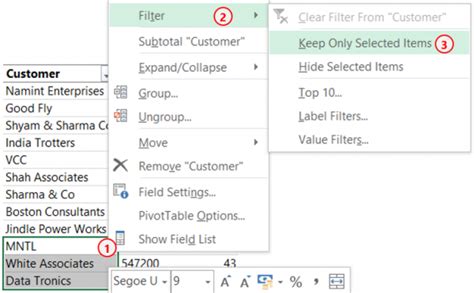
A filter pivot table is a powerful tool that allows users to narrow down and focus on specific subsets of data within a larger dataset. By applying filters, you can quickly isolate and analyze data that meets certain criteria, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
The beauty of filter pivot tables lies in their ability to provide dynamic and interactive data analysis. Unlike static tables, where data is presented in a fixed format, filter pivot tables enable users to explore and manipulate data on the fly, adjusting the filters to gain different perspectives and insights.
Key Benefits of Filter Pivot Tables
There are several advantages to incorporating filter pivot tables into your data analysis toolkit:
- Data Refinement: Filters allow you to select and display only the data that aligns with your specific criteria, making it easier to identify relevant information and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Dynamic Analysis: With filter pivot tables, you can quickly switch between different data subsets, enabling you to explore various scenarios and hypotheses without having to create multiple static tables.
- Visual Insights: By applying filters, you can create visually appealing and informative pivot tables, making it simpler to communicate complex data insights to stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Interactive Reports: Filter pivot tables can be integrated into interactive reports, allowing users to adjust filters and view real-time data updates, promoting data-driven decision-making.
Mastering Filter Techniques

Now that we understand the value of filter pivot tables, let’s explore some advanced techniques to unlock their full potential.
Customizing Filter Options
One of the first steps in mastering filter pivot tables is learning how to customize filter options to suit your analysis needs. By default, pivot tables offer a range of common filter types, such as date ranges, text filters, and number filters. However, you can further tailor these filters to align with your specific data requirements.
For instance, if you're working with a dataset containing customer information, you might want to create a custom filter for customer segments. This allows you to analyze data based on specific customer groups, such as "Gold Members" or "New Customers," providing valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Multiple Filters for Granular Analysis
A powerful technique when working with filter pivot tables is applying multiple filters simultaneously. By combining different filters, you can perform granular data analysis, identifying intersections and unique combinations of data points.
Imagine you have a dataset containing sales data for various products across different regions. By applying multiple filters, you can analyze sales performance for a specific product in a particular region, helping you identify regional trends and preferences for that product.
Dynamic Filter Ranges
Filter pivot tables offer the flexibility to define dynamic filter ranges, allowing you to analyze data that falls within specific ranges. This technique is particularly useful when dealing with numerical data, such as sales figures or customer ratings.
For example, you can create a dynamic filter range for sales data, specifying a minimum and maximum threshold. This enables you to focus on sales figures within a specific range, such as high-value sales or sales that fall within a particular target range.
Date-Based Filters for Time Series Analysis
Date-based filters are a powerful tool for analyzing time-series data. By applying filters based on specific date ranges or intervals, you can gain insights into data trends over time.
Consider a dataset containing monthly website traffic data. By applying date-based filters, you can analyze traffic patterns over different time periods, such as comparing monthly traffic trends or identifying peak traffic days.
Combining Filters with Slicers
Slicers are interactive filters that provide a visual interface for selecting and filtering data. By combining filters with slicers, you can create highly interactive and user-friendly pivot tables, allowing users to easily adjust filters and explore different data subsets.
Slicers can be particularly useful when presenting data to stakeholders or when creating interactive data dashboards. They provide a simple and intuitive way for users to manipulate data, promoting engagement and understanding.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
To ensure optimal performance and efficiency when working with filter pivot tables, it’s essential to follow some best practices.
Optimize Data Structure
Before creating a pivot table, ensure your data is structured in a way that aligns with your analysis goals. Organize your data into columns and rows, with clear labels and consistent formatting. This simplifies the process of creating and applying filters.
Utilize Filter Cache
To enhance performance, especially with large datasets, consider utilizing the filter cache feature. This feature allows you to store filtered data in memory, enabling faster access and analysis. It’s particularly useful when working with complex filters or frequently adjusting filter settings.
Limit Filter Options
While filter pivot tables offer extensive customization, it’s important not to overwhelm users with an excessive number of filter options. Limit the number of filters to those that are most relevant and frequently used, ensuring a streamlined and user-friendly experience.
Utilize Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting is a powerful tool for highlighting specific data points or patterns within your pivot table. By applying conditional formatting rules, you can visually emphasize important data, making it easier to identify trends and anomalies.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Filter pivot tables find applications across various industries and domains. Let’s explore some real-world examples of how these techniques are utilized in practice.
Marketing Analytics
In the marketing domain, filter pivot tables are invaluable for analyzing campaign performance. By applying filters, marketers can segment data based on campaign types, target audiences, or specific time periods, enabling them to identify successful strategies and optimize future campaigns.
For instance, a marketing team can use filter pivot tables to analyze the performance of different email campaigns, comparing open rates, click-through rates, and conversion metrics across various customer segments.
Financial Analysis
Filter pivot tables are extensively used in financial analysis to gain insights into financial performance and trends. By applying filters, financial analysts can segment data based on specific criteria, such as revenue sources, expense categories, or time periods, enabling them to identify areas of strength and weakness.
A financial analyst might use filter pivot tables to analyze quarterly revenue performance, comparing revenue figures across different product lines or geographic regions, to identify high-performing areas and opportunities for growth.
Healthcare Data Analysis
In the healthcare industry, filter pivot tables are employed to analyze patient data, clinical trials, and treatment outcomes. By applying filters, healthcare professionals can segment data based on patient demographics, medical conditions, or treatment protocols, facilitating more effective patient care and research.
For example, a healthcare researcher can use filter pivot tables to analyze the effectiveness of a new treatment regimen, comparing outcomes across different patient groups or treatment durations.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of data analysis is continuously evolving, and filter pivot tables are no exception. As technology advances, we can expect to see new features and enhancements that further streamline and enhance data analysis processes.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into data analysis tools, including filter pivot tables. These technologies can automate data analysis processes, identify patterns and anomalies, and provide intelligent recommendations based on historical data.
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies are being leveraged to enable users to interact with pivot tables using natural language queries. This innovation will make data analysis more accessible and intuitive, allowing users to ask questions and receive insights in a conversational manner.
Visual Analytics Enhancements
Visual analytics, which involves the use of interactive charts and graphs, is expected to become even more advanced. Future filter pivot tables may offer enhanced visual representations, enabling users to explore data through immersive and interactive visualizations, promoting deeper understanding and insights.
Conclusion
Filter pivot tables are a powerful tool for data analysis, offering a dynamic and interactive approach to exploring and understanding complex datasets. By mastering filter techniques and incorporating best practices, you can unlock valuable insights and drive data-informed decision-making.
As technology advances, the future of filter pivot tables looks promising, with AI, NLP, and visual analytics enhancements set to revolutionize the way we analyze and interpret data. Stay tuned for exciting developments in this field and continue to leverage the power of filter pivot tables to gain deeper insights into your data.
How can I customize filter options in pivot tables to align with my specific analysis needs?
+
To customize filter options, you can modify the default filter types by creating custom filters based on your data requirements. This allows you to apply filters that align with specific criteria, such as customer segments or product categories.
What are some best practices for optimizing the performance of filter pivot tables, especially with large datasets?
+
To optimize performance, ensure your data is well-structured and organized. Utilize the filter cache feature to store filtered data in memory, enabling faster access. Additionally, limit the number of filter options to those most relevant, and consider applying conditional formatting to visually emphasize important data.
How can filter pivot tables be integrated into interactive data dashboards for stakeholder engagement and understanding?
+
Filter pivot tables can be integrated into interactive data dashboards by combining filters with slicers. Slicers provide a visual interface for selecting and filtering data, allowing users to easily adjust filters and explore different data subsets. This promotes engagement and understanding, as users can manipulate data to gain insights relevant to their specific interests.



