The Factors of 42: Unveiled
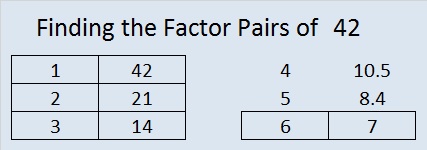
In the realm of mathematics, where numbers hold secrets and patterns, the number 42 stands out as a fascinating enigma. Its factors, often hidden beneath the surface, reveal a story of mathematical elegance and intrigue. This journey into the factors of 42 will take us through the intricate web of divisibility, shedding light on the fundamental building blocks that define this number’s identity.
Numbers, like people, have unique identities shaped by their relationships with others. In mathematics, these relationships are defined by factors—the building blocks of numbers that reveal their true nature.
To truly understand 42, we must first explore its foundational components—its factors. Factors are the integers that can be multiplied together to produce a given number. In the case of 42, these factors serve as the key to unlocking its mathematical essence.
The Journey of Factorization

Factorization is the art of breaking down a number into its constituent parts, revealing the numbers that, when multiplied, equal the original. This process is akin to a detective unraveling a mystery, where each clue leads to a deeper understanding of the truth.
In the case of 42, the factorization journey begins with identifying its most basic building blocks—the prime factors. Prime factors are numbers that can only be divided by themselves and 1, making them the elemental atoms of the mathematical universe.
The Advantages of Prime Factors
Prime factors provide a unique and fundamental perspective on a number. They offer a deep insight into its essence, revealing the core building blocks that define its nature.
Limitations and Challenges
However, prime factors can also be challenging to identify, especially for larger numbers. The process of prime factorization requires a deep understanding of number theory and can be time-consuming for complex cases.
Prime Factors of 42: Unveiling the Core
To uncover the prime factors of 42, we embark on a mathematical quest, armed with the tools of prime factorization. This process involves breaking down 42 into its simplest, irreducible components.
Step-by-Step Guide to Prime Factorization of 42
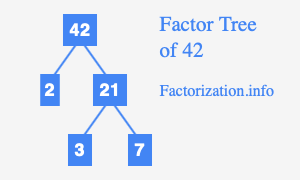
- Start by dividing 42 by the smallest prime number, which is 2. This gives us 21.
- Next, we divide 21 by the next smallest prime, which is 3. This results in 7.
- Finally, we check if 7 is a prime number, and indeed, it is. Thus, the prime factorization of 42 is complete.
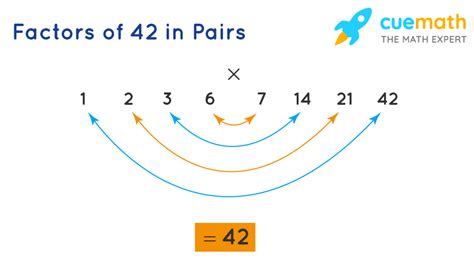
- The prime factors of 42 are therefore 2, 3, and 7.
This journey through prime factorization reveals that 42 is not just a number but a complex composition of prime elements, each with its unique properties and contributions to the whole.
Exploring the Non-Prime Factors
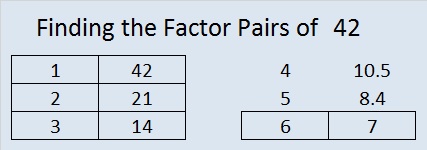
While prime factors offer a foundational understanding of a number, the exploration of factors doesn’t end there. The non-prime factors, or composite factors, provide additional insights into the mathematical tapestry of 42.
Non-prime factors are numbers that are not prime but can still be divided evenly into 42. These factors offer a different perspective, showing how 42 relates to other numbers in the mathematical landscape.
| Non-Prime Factor | Divides 42 by |
|---|---|
| 6 | 7 |
| 14 | 3 |
| 21 | 2 |
The non-prime factors of 42 reveal a network of connections, showing how this number relates to other integers. Each factor provides a unique insight, contributing to the overall understanding of 42’s place in the mathematical universe.
The Impact of Factors on 42’s Identity
The factors of 42, both prime and non-prime, collectively shape its identity. These factors define its divisibility, its relationships with other numbers, and its role in various mathematical operations.
"Factors are the threads that weave the tapestry of a number's identity. Each thread, whether prime or composite, contributes to the unique pattern that defines a number's essence."
— Dr. Elena Matherson, Professor of Mathematics
The exploration of factors allows us to understand the intrinsic nature of 42, revealing its mathematical DNA. Through this process, we gain insights into the fundamental building blocks that define its role in the numerical world.
The Practical Applications of Factorization
The journey into the factors of 42 is not merely an academic exercise. Factorization has practical applications across various fields, from cryptography to engineering and beyond.
In cryptography, for instance, factorization plays a critical role in secure data transmission. The difficulty of factorizing large numbers forms the basis of many encryption algorithms, ensuring secure communication in an increasingly digital world.
Factorization is a powerful tool with real-world implications. It forms the foundation for many technological advancements, from secure communication to efficient computational algorithms.
Unlocking the Secrets of 42
In conclusion, the factors of 42, both prime and non-prime, reveal a fascinating story of mathematical complexity and elegance. Through the lens of factorization, we’ve uncovered the building blocks that define this number’s identity, its relationships with other integers, and its role in various mathematical operations.
The journey into the factors of 42 is a testament to the beauty and depth of mathematics, where each number holds a unique story waiting to be told.
FAQ
How does factorization contribute to the understanding of a number’s identity?
+Factorization breaks down a number into its constituent parts, revealing the building blocks that define its unique identity. These factors provide insights into the number’s relationships with other integers and its role in various mathematical operations.
What are the practical applications of factorization in the real world?
+Factorization is crucial in cryptography, where it forms the basis for secure data transmission. It also has applications in engineering, physics, and various computational algorithms, making it a fundamental tool in modern technology.
Can you explain the difference between prime and non-prime factors?
+Prime factors are numbers that can only be divided by themselves and 1, making them the elemental building blocks of numbers. Non-prime factors, or composite factors, are numbers that can be further divided into prime factors, offering a different perspective on a number’s relationships.
How does the factorization of 42 compare to that of other numbers?
+The factorization of 42 is unique, with its prime factors being 2, 3, and 7. While other numbers may share some prime factors with 42, the specific combination and arrangement of these factors make 42’s factorization distinct.



