Excel Template: 5 Ways to Price Compare

In the competitive world of business, understanding the pricing landscape is crucial for success. Price comparison is an essential tool that enables businesses to stay ahead of the curve, make informed decisions, and ultimately thrive in the market. This comprehensive guide will delve into the realm of price comparison, offering five effective ways to utilize an Excel template for this purpose.
The Significance of Price Comparison

Price comparison is a fundamental strategy for businesses, providing a bird’s-eye view of the market dynamics. It empowers organizations to identify their competitive advantage, recognize pricing trends, and make strategic pricing adjustments. By analyzing competitors’ pricing strategies, businesses can optimize their own pricing models, enhance profitability, and deliver value to customers.
In this article, we will explore practical methods to leverage an Excel template for price comparison, ensuring that businesses can effectively gather, organize, and analyze pricing data. Let's dive into the first strategy.
Method 1: Competitive Analysis through Excel
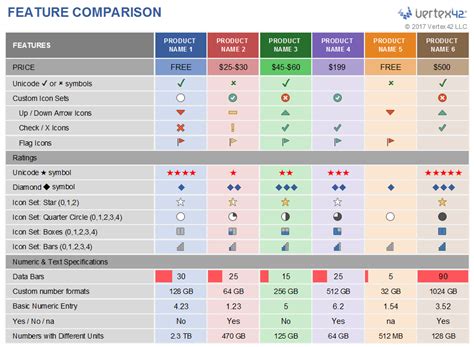
Competitive analysis is a critical aspect of price comparison. It involves understanding the pricing strategies of direct competitors and industry leaders. By analyzing their pricing models, promotions, and value propositions, businesses can pinpoint their unique selling points and make informed decisions.
To begin, create a comprehensive list of competitors within your industry. Identify their core products or services and the respective prices. This data can be gathered through online research, industry reports, or direct interactions with competitors. Ensure that the data is accurate and up-to-date.
Building the Excel Template
Once you have collected the necessary information, it’s time to construct an Excel template. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
-
Define the Template Structure: Create a table with columns for competitor names, products or services, and their corresponding prices. Include additional columns for any relevant factors, such as discounts, promotions, or unique features.
-
Data Entry: Populate the template with the collected data. Ensure that the information is organized consistently across competitors.
-
Calculate Average Prices: Use Excel's built-in functions to calculate the average price for each product or service. This provides a quick snapshot of the industry's average pricing.
-
Identify Outliers: Analyze the data to identify any significant outliers. These could be competitors with exceptionally high or low prices. Understanding the reasons behind these outliers can offer valuable insights.
-
Visualize the Data: Create charts or graphs to visually represent the pricing data. This can help identify patterns, trends, and areas where your business can differentiate itself.
Analysis and Insights
After constructing the Excel template, the real power lies in the analysis. Here are some key insights you can derive:
- Competitive Pricing Strategy: Determine whether your competitors primarily use cost-based pricing, value-based pricing, or a combination of both. This understanding can guide your own pricing strategy.
- Pricing Trends: Identify any pricing trends or patterns within your industry. Are prices generally increasing, decreasing, or stable? Understanding these trends can help forecast future market movements.
- Competitive Advantage: Highlight areas where your business excels in terms of pricing. Perhaps you offer a unique value proposition at a competitive price, or your pricing structure is more flexible and appealing to customers.
- Pricing Gaps: Identify gaps in the market where your business can thrive. Are there specific products or services that are underpriced or overpriced? These insights can guide your product positioning and pricing strategy.
Method 2: Cost-Based Pricing Analysis
Cost-based pricing is a fundamental approach where businesses set prices based on their production costs and desired profit margins. Understanding your costs and margins is crucial for sustainable business operations.
Calculating Costs and Margins
To perform a cost-based pricing analysis, you need to calculate your production costs and desired profit margins. Here’s a simplified example:
| Cost Category | Cost |
|---|---|
| Production Costs | $100 per unit |
| Overhead Costs | $50 per unit |
| Marketing and Sales | $20 per unit |
| Total Costs | $170 per unit |

In this example, the total costs amount to $170 per unit. To determine the price, you need to add the desired profit margin.
Setting Prices
Let’s assume you want a profit margin of 20% on each unit sold. Here’s how you can calculate the price using Excel:
-
Desired Profit Margin: $170 x 0.20 = $34
-
Price per Unit: $170 + $34 = $204
Therefore, to achieve a 20% profit margin, you would set the price at $204 per unit.
Advantages and Considerations
Cost-based pricing offers several advantages. It ensures that your business covers its costs and generates a profit. However, it’s essential to consider the following:
- Market Dynamics: Cost-based pricing may not always align with market demands. If your competitors offer lower prices, you might need to adjust your strategy to remain competitive.
- Cost Efficiency: Regularly review your production and overhead costs to identify areas for cost reduction. This can improve your margins and competitiveness.
- Profitability Analysis: Use Excel to analyze your profit margins over time. This helps identify trends and areas for improvement.
Method 3: Value-Based Pricing Strategy
Value-based pricing is a powerful approach where businesses set prices based on the perceived value of their products or services to customers. This strategy focuses on delivering exceptional value and justifying higher prices.
Understanding Customer Perceived Value
To implement a value-based pricing strategy, you need to understand the perceived value of your offerings from the customer’s perspective. This involves:
- Customer Research: Conduct surveys, focus groups, or interviews to understand customer preferences, needs, and perceptions.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze competitors' pricing and value propositions. Identify areas where your business can offer unique value.
- Feature Analysis: Break down your products or services into features and benefits. Highlight the unique value each feature brings to customers.
Setting Value-Based Prices
Once you have a clear understanding of the perceived value, you can set prices accordingly. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
-
Identify Core Value Propositions: Determine the key features or benefits that drive the most value for your customers.
-
Assign Value to Each Proposition: Quantify the value of each proposition in terms of customer savings, time saved, or other benefits.
-
Set Prices Based on Value: Establish prices that reflect the value delivered to customers. This may involve premium pricing for unique features or value-added services.
-
Bundle Options: Consider offering bundled packages or subscription models to provide additional value and flexibility to customers.
Advantages and Considerations
Value-based pricing offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Customer Perceived Value: By focusing on value, you can deliver a superior customer experience and build brand loyalty.
- Price Differentiation: Value-based pricing allows you to differentiate your offerings from competitors and command higher prices.
- Profitability: With a strong value proposition, you can justify higher prices and improve profitability.
- Customer Education: Value-based pricing requires effective communication to educate customers about the benefits they receive.
Method 4: Dynamic Pricing Strategies

Dynamic pricing, also known as demand-based pricing, is a strategy where businesses adjust prices based on market demand, customer segments, and other variables. It involves real-time adjustments to optimize revenue and profitability.
Understanding Demand and Customer Segments
Dynamic pricing relies on a deep understanding of market demand and customer segments. Here’s how to approach it:
- Demand Analysis: Analyze historical sales data and market trends to identify periods of high and low demand. Use Excel to calculate average sales per period and identify peak seasons.
- Customer Segmentation: Divide your customer base into segments based on demographics, purchasing behavior, or loyalty. Understand the price sensitivity and preferences of each segment.
- Price Elasticity: Assess the price elasticity of your products or services. Determine how price changes affect demand. This information is crucial for dynamic pricing strategies.
Implementing Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing can be implemented in various ways. Here are some common approaches:
- Seasonal Pricing: Adjust prices based on seasonal demand. Offer discounts during off-peak seasons and increase prices during peak seasons.
- Time-Based Pricing: Implement time-based pricing, such as happy hours or early bird discounts, to attract customers during specific time slots.
- Personalized Pricing: Use customer segmentation to offer personalized pricing based on individual preferences and purchase history. This can be done through loyalty programs or customized pricing plans.
- Event-Based Pricing: Adjust prices for special events, promotions, or limited-time offers. Create a sense of urgency and attract customers with dynamic pricing strategies.
Advantages and Considerations
Dynamic pricing offers several advantages, including:
- Revenue Optimization: By adjusting prices based on demand, you can maximize revenue during peak seasons and manage costs during off-peak periods.
- Customer Engagement: Dynamic pricing strategies can attract new customers and engage existing ones with personalized offers.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Dynamic pricing relies on data analysis. Excel can help you track and analyze sales data, customer behavior, and pricing trends to make informed decisions.
- Competition Response: Dynamic pricing allows you to respond quickly to competitive pricing strategies and market changes.
Method 5: Price Comparison with Industry Leaders
Comparing your pricing with industry leaders is a valuable strategy to benchmark your performance and identify areas for improvement. It allows you to learn from the best practices of established companies and adapt your pricing strategy accordingly.
Identifying Industry Leaders
Start by identifying the top players in your industry. These are the companies that have established a strong market presence, brand recognition, and a track record of success. Research their pricing strategies, value propositions, and market positioning.
Excel Template for Price Comparison
Create an Excel template to compare your pricing with industry leaders. Here’s a suggested structure:
| Industry Leader | Product/Service | Price | Value Proposition | Pricing Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leader A | Product X | $150 | High-quality materials, excellent customer support | Value-based pricing |
| Leader B | Service Y | $250 | Customized solutions, 24/7 support | Premium pricing |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Your Business | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Analysis and Insights
After comparing your pricing with industry leaders, analyze the findings to gain valuable insights:
- Value Proposition Alignment: Assess whether your value proposition aligns with industry leaders. Identify areas where you can enhance your offerings to match or exceed their standards.
- Pricing Strategy Comparison: Compare your pricing strategy with industry leaders. Determine if you are underpricing or overpricing your products or services. Adjust your strategy accordingly to stay competitive.
- Market Positioning: Understand how your business positions itself in the market relative to industry leaders. Identify unique selling points and areas where you can differentiate yourself.
- Customer Perception: Analyze customer feedback and reviews to understand how your pricing and value proposition are perceived by your target audience. Make adjustments to align with customer expectations.
Conclusion
Price comparison is a powerful tool for businesses to stay competitive and make informed pricing decisions. By leveraging an Excel template, you can efficiently gather, organize, and analyze pricing data. The methods outlined in this article - competitive analysis, cost-based pricing, value-based pricing, dynamic pricing, and industry leader comparison - provide a comprehensive framework for effective price comparison.
Remember, pricing is a dynamic process, and regular analysis and adjustments are essential. Stay attuned to market trends, customer feedback, and competitor strategies to continuously optimize your pricing model. With the right tools and strategies, your business can thrive in a competitive market.
How often should I update my Excel template for price comparison?
+It is recommended to update your Excel template regularly, ideally on a quarterly basis or whenever significant market changes occur. Regular updates ensure that your pricing data remains accurate and reflects the current market conditions.
Can I use Excel to analyze pricing trends over time?
+Absolutely! Excel provides powerful tools for trend analysis. You can use charts, graphs, and formulas to visualize pricing trends over time. This helps identify patterns, seasonality, and long-term pricing strategies.
What are some best practices for dynamic pricing strategies?
+Best practices for dynamic pricing include thorough market research, understanding customer segments, and data-driven decision-making. Regularly analyze sales data, customer feedback, and competitor pricing to optimize your dynamic pricing strategy.



