Excel's Powerful Search Function: A Guide
Microsoft Excel, the ubiquitous spreadsheet software, is an invaluable tool for data management and analysis. Among its vast array of features, the search function stands out as a powerful asset for users across various industries and skill levels. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Excel's search capabilities, offering expert insights and practical tips to unlock its full potential.
Mastering Excel’s Search: An Overview

Excel’s search function, often underutilized, is a versatile tool that can streamline data retrieval, manipulation, and analysis. By understanding and harnessing its capabilities, users can significantly enhance their productivity and data management efficiency.
The Basics: Finding Data in Excel
At its core, Excel’s search function allows users to locate specific values or strings of text within a worksheet. This fundamental capability is accessed through the Find feature, which can be triggered using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + F or by selecting the Find & Select option from the Home tab.
Upon activating the Find feature, a dialog box appears, offering various options to customize the search. Users can input the value or text they wish to locate and choose from additional settings to refine the search, such as matching case or searching within a specific range of cells.
| Find Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Find what | Enter the value or text to be searched. |
| Within | Select the range of cells to search within (e.g., Sheet, Selection, Formula, etc.). |
| Search | Choose between searching by Rows or Columns to determine the direction of the search. |
| Match case | Check this box to ensure that the search is case-sensitive. |
| Match entire cell contents | Enable this option to find cells that exactly match the search term. |
| Look in | Select whether to search within Formulas, Values, or Comments. |

Once the desired settings are selected, clicking Find Next initiates the search, and Excel highlights the first occurrence of the specified value or text. The user can then navigate to subsequent occurrences by clicking Find Next repeatedly or by selecting Find All to view a list of all matches.
Advanced Search Techniques
While the basic Find feature is a powerful tool, Excel offers a range of advanced search techniques to cater to more complex data scenarios.
Wildcard Searches
Wildcard searches enable users to find values or text that match a specific pattern. Excel supports two wildcard characters: asterisk (*) and question mark (?). The asterisk represents any number of characters, while the question mark stands for a single character.
For example, searching for "A*" will find values starting with the letter "A," such as "Apple," "Ant," or "Arizona." Similarly, searching for "C?" will locate values like "Cat," "Cap," or "Car," where the question mark matches any single character after the letter "C."
Regular Expressions
Excel also supports regular expressions, a powerful tool for pattern matching. Regular expressions allow users to define complex search patterns using special characters and sequences. While more advanced, regular expressions offer unparalleled flexibility in data retrieval.
For instance, the regular expression "[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{4}" will match phone numbers in the format "xxx-yy-zzzz," where "x," "y," and "z" are digits. This expression uses brackets, curly braces, and dashes to define the pattern.
Search and Replace
Excel’s Search and Replace feature allows users to not only locate specific values or text but also replace them with new ones. This tool is particularly useful for bulk data updates or error corrections.
To access Search and Replace, users can select the Replace option from the Home tab or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + H. The process is similar to the basic Find feature, but with an additional Replace with field where the new value or text can be entered.
Upon clicking Replace or Replace All, Excel performs the specified replacement, either one occurrence at a time or for all matches simultaneously.
Performance and Optimization

While Excel’s search function is robust, its performance can be influenced by various factors, including worksheet size, data complexity, and search criteria. Understanding these factors and employing optimization techniques can significantly enhance search speed and efficiency.
Worksheet Size and Data Complexity
The size and complexity of a worksheet can impact search performance. Larger worksheets with extensive data may require more time for Excel to process search queries. Similarly, worksheets with nested formulas or complex data structures can also slow down search operations.
To mitigate these effects, users can consider breaking down large worksheets into smaller, more manageable sheets or utilizing Excel's powerful filtering and sorting tools to simplify data retrieval.
Optimizing Search Criteria
The choice of search criteria can also impact search performance. Broad or vague search terms may lead Excel to scan a larger portion of the worksheet, slowing down the process. Conversely, more specific and well-defined search criteria can expedite the search.
For instance, searching for an exact value or text string is generally faster than using wildcard characters or regular expressions, which require Excel to perform more complex pattern matching.
Utilizing Excel’s Built-in Functions
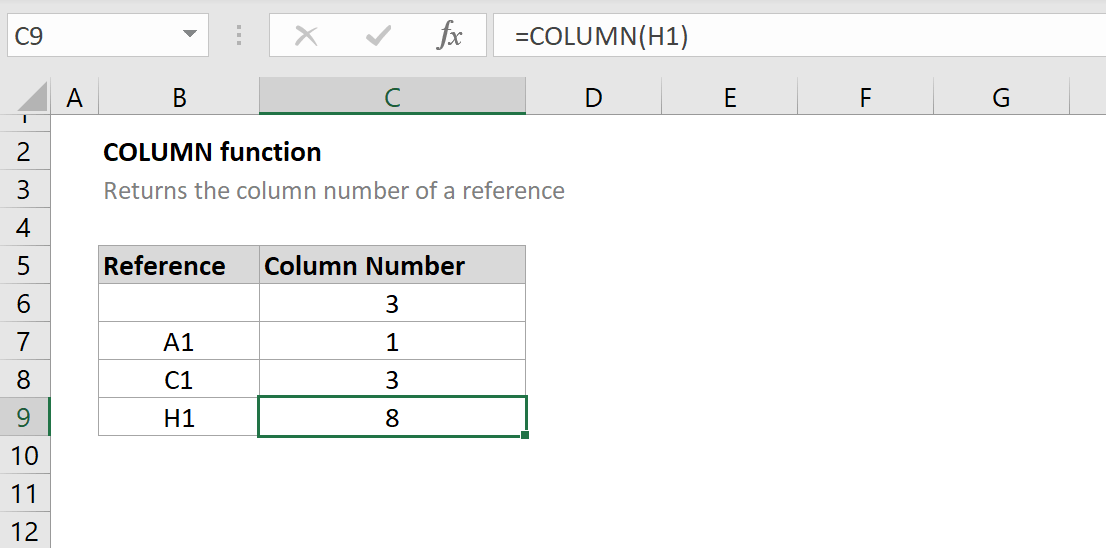
Excel offers a plethora of built-in functions that can enhance search capabilities and data management. Functions like VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, and INDEX/MATCH provide powerful tools for retrieving specific data points based on search criteria.
For example, the VLOOKUP function can be used to search for a value in the first column of a table array and return a corresponding value from another column in the same row. This function is particularly useful for cross-referencing data or performing complex data lookups.
Real-World Applications
Excel’s search function finds applications across a wide range of industries and use cases. From data analysis and reporting to financial modeling and inventory management, the ability to quickly and accurately retrieve specific data is invaluable.
Data Analysis and Reporting
In the realm of data analysis, Excel’s search function is a key tool for extracting specific data points from large datasets. Whether it’s identifying outliers, tracking trends, or performing complex calculations, the ability to locate and manipulate data efficiently is essential.
For instance, a financial analyst might use Excel's search function to locate specific transactions based on criteria such as date, amount, or category. This data can then be used to generate reports, analyze spending patterns, or identify areas for cost reduction.
Financial Modeling
Financial modeling often involves working with large, complex datasets. Excel’s search function is a powerful tool for navigating these datasets, locating specific financial metrics, or identifying key assumptions and inputs.
In a financial model, a user might employ Excel's search capabilities to locate specific assumptions, such as growth rates or discount rates, and update them based on new information. This ensures that the model remains accurate and reflects the latest market conditions.
Inventory Management
Excel is a popular tool for managing inventory, especially in small to medium-sized businesses. The search function plays a vital role in this context, allowing users to quickly locate specific inventory items, check stock levels, or identify items that need to be reordered.
For example, a retail store owner might use Excel's search function to find items with low stock levels, ensuring that popular products are restocked before they run out. This proactive approach helps maintain customer satisfaction and reduces the risk of lost sales.
Future Implications and Innovations
As Excel continues to evolve, its search function is likely to see further enhancements and innovations. Microsoft’s ongoing commitment to improving Excel’s capabilities suggests that future versions will offer even more powerful and intuitive search tools.
Enhanced Search Algorithms
Excel’s search algorithms may undergo refinement to improve speed and accuracy. Advanced search techniques, such as fuzzy matching or natural language processing, could be integrated to enhance Excel’s ability to understand and interpret user queries.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning technologies could revolutionize Excel’s search capabilities. By leveraging these technologies, Excel could offer predictive search suggestions, intelligent data retrieval, and even automated data analysis.
For instance, Excel might suggest relevant search terms based on a user's historical search patterns or provide intelligent data summaries and insights based on complex data searches.
User Experience Improvements
Excel’s user interface, including its search functionality, could be enhanced to provide a more intuitive and user-friendly experience. Visual search tools, improved search result presentation, and enhanced keyboard shortcuts could make Excel’s search function more accessible and efficient for users of all skill levels.
Conclusion
Excel’s search function is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance a user’s productivity and data management capabilities. By understanding its features, optimizing search performance, and applying it to real-world scenarios, users can unlock Excel’s full potential as a versatile and indispensable data management solution.
As Excel continues to evolve, its search function is poised to become even more sophisticated, offering users an even more powerful tool for data retrieval and analysis. The future of Excel's search capabilities promises to be exciting, with potential advancements in search algorithms, AI integration, and user experience enhancements.
Can Excel’s search function handle large datasets efficiently?
+Yes, Excel’s search function is designed to handle large datasets efficiently. However, performance can be impacted by factors such as worksheet size, data complexity, and search criteria. Optimizing search criteria and utilizing Excel’s built-in functions can significantly enhance search speed and efficiency.
What are some best practices for using Excel’s search function effectively?
+To use Excel’s search function effectively, consider the following best practices: Define specific and well-defined search criteria, utilize wildcard searches or regular expressions for complex pattern matching, and employ Excel’s built-in functions like VLOOKUP or INDEX/MATCH for advanced data retrieval.
How can I improve the performance of Excel’s search function?
+To improve Excel’s search performance, consider optimizing your worksheet by reducing its size or complexity. Additionally, refining your search criteria and utilizing Excel’s built-in functions can enhance search speed and efficiency.