Excel Bar Charts: Customize with Value-Based Colors
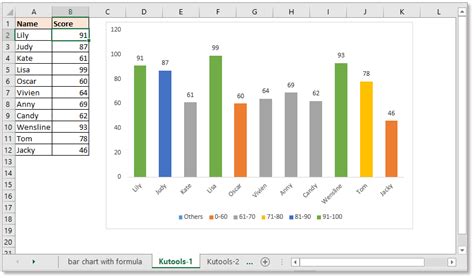
Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis and visualization, offering a wide range of chart types to help users communicate their findings effectively. Among these, bar charts are a popular choice for comparing values and presenting data in a clear and concise manner. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the process of customizing bar charts in Excel, specifically focusing on a unique and dynamic approach: value-based color customization.
Value-based color customization allows you to assign specific colors to your data points based on their values. This technique adds a layer of visual information to your bar chart, making it more engaging and informative. By understanding and implementing this feature, you can create bar charts that not only showcase data but also tell a story, highlighting key trends and insights.
Setting the Stage: Preparing Your Data

Before we dive into the customization process, it's essential to ensure your data is organized and structured appropriately. Here's a step-by-step guide to preparing your data for value-based color customization:
- Define Categories and Values: Ensure your data is organized into distinct categories, with corresponding numerical values. For instance, you might have a dataset with categories such as "Product A," "Product B," and "Product C," each with a sales value associated.
- Format Values: Verify that your values are in a consistent format. Excel often interprets values differently based on their formatting, so it's crucial to ensure numbers are recognized as such. A common pitfall is using commas as thousands separators, which can lead to Excel treating your values as text.
- Consider Data Range: Identify the range of values in your dataset. This range will play a crucial role in determining the color scale for your bar chart. A wide range of values may require a different color scheme than a dataset with values closer together.
- Categorical Data: If your data is categorical (e.g., "High," "Medium," "Low"), you might consider using a different chart type, such as a column chart with data labels, to avoid potential misinterpretation of the value-based colors.
By taking these preparatory steps, you ensure that your data is ready for effective visualization and that your bar chart will accurately represent the information you wish to convey.
Customizing Bar Charts: A Step-by-Step Guide

Now that your data is prepared, let's explore the process of customizing your bar chart with value-based colors. Follow these steps to create a dynamic and informative visualization:
- Insert a Bar Chart: Begin by selecting your data range, including both categories and values. Navigate to the "Insert" tab in Excel's ribbon and choose the "Bar" chart type. Various options are available, including 2-D and 3-D variations. Select the one that best suits your data and presentation needs.
- Format Data Series: With your bar chart inserted, select the data series (the bars themselves) by clicking on them. This will activate the "Format Data Series" pane, which offers a wide range of customization options.
- Apply Value-Based Colors: In the "Format Data Series" pane, locate the "Fill & Line" section. Click on the "Fill" option, and then select "Series Color." Here, you will find the "Color by Point" option, which allows you to assign colors based on the values of your data series.
- Choose Color Scale: Excel provides a variety of color scales to choose from. Select the one that best represents your data. For instance, a "Red-Yellow-Green" scale might be ideal for highlighting positive and negative trends, with green representing success and red indicating areas of concern.
- Customize Color Scale: To further refine your color scale, you can adjust the minimum and maximum values associated with each color. This allows you to fine-tune the representation of your data and ensure that specific values are highlighted as desired.
- Add Data Labels: Consider adding data labels to your bar chart to provide a clear indication of the values represented by each bar. This can be done by selecting the "Data Labels" option in the "Format Data Series" pane. Choose the label position and format that best suits your chart's layout and design.
- Enhance Chart Aesthetics: Excel offers a wide range of chart styles and color themes to enhance the visual appeal of your bar chart. Experiment with different styles and themes to find the one that aligns with your presentation goals and ensures that your chart is not only informative but also aesthetically pleasing.
Best Practices and Considerations
When customizing bar charts with value-based colors, it's essential to keep certain best practices in mind to ensure the effectiveness and clarity of your visualization:
- Color Contrast: Ensure that your color scale provides sufficient contrast between adjacent colors. This is crucial for viewers to easily distinguish between different values, especially when presenting to a diverse audience with varying visual abilities.
- Color Blindness Awareness: Consider the potential impact of color blindness on your audience. While Excel offers a variety of color scales, some may be less effective for individuals with color vision deficiencies. Aim for color combinations that remain discernible to a broad range of viewers.
- Legend and Key: If your color scale is complex or contains many colors, consider adding a legend or key to your chart. This provides a clear reference for viewers to understand the meaning behind each color.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in your color scheme throughout your presentation or report. Avoid using different color scales for similar types of data, as this can confuse your audience and undermine the impact of your visualizations.
- Data Interpretation: Remember that value-based colors are a powerful tool for data interpretation. Ensure that your color choices align with the message you wish to convey. For instance, a red-green scale might be ideal for indicating profit and loss, with green representing financial gains.
By adhering to these best practices, you can create bar charts that not only showcase your data but also tell a compelling story, guiding your audience to the key insights you wish to highlight.
Real-World Applications
Value-based color customization in bar charts finds applications in various fields and industries. Here are some real-world scenarios where this technique proves invaluable:
Market Analysis
In the world of business and marketing, value-based color customization can be a game-changer. Imagine a scenario where a marketing team is analyzing the performance of different ad campaigns. By assigning colors to each campaign based on their return on investment (ROI), the team can quickly identify the most successful and least successful campaigns at a glance.
| Campaign | ROI | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media Campaign | $15,000 | Green |
| Email Marketing | $8,000 | Orange |
| Print Advertising | $3,000 | Red |

With this color-coded bar chart, the team can make informed decisions about future marketing strategies, allocating resources to the most successful channels and improving underperforming campaigns.
Sales Performance
Value-based color customization is equally valuable in sales performance analysis. Consider a sales team tracking the monthly sales of their top products. By assigning colors based on sales volume, the team can visually identify which products are performing exceptionally well and which might need additional attention or marketing efforts.
| Product | Sales Volume | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Widget A | 1200 units | Green |
| Widget B | 850 units | Orange |
| Widget C | 400 units | Red |
This color-coded bar chart provides a clear visual representation of product performance, helping the sales team focus their efforts and strategies on maximizing sales for each product.
Environmental Monitoring
Value-based color customization extends beyond business applications. In environmental science, researchers often track and visualize data related to air or water quality. By assigning colors to pollution levels or environmental parameters, they can create visually striking charts that communicate the severity of environmental issues to a wide audience.
| Parameter | Value | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Level | 8.5 mg/L | Green |
| Nitrate Level | 15 mg/L | Orange |
| Phosphate Level | 3.2 mg/L | Red |
Such color-coded bar charts can raise awareness and provide a compelling visual representation of environmental data, driving home the importance of sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
Conclusion: Empowering Data Visualization
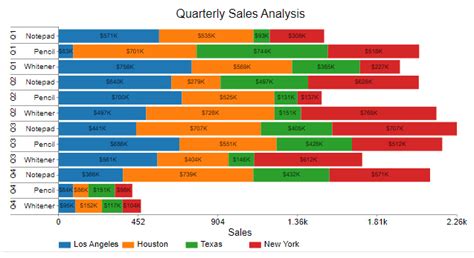
Value-based color customization in Excel bar charts is a powerful tool that enhances the visual appeal and informational value of your data. By following the step-by-step guide and considering the best practices outlined in this article, you can create bar charts that not only showcase your data but also tell a compelling story, guiding your audience to key insights and trends.
Remember, effective data visualization is a powerful means of communication, and with the right tools and techniques, you can transform your Excel bar charts into dynamic and informative visuals that resonate with your audience.
How do I choose the right color scale for my data?
+The choice of color scale depends on the nature of your data and the message you wish to convey. For instance, a “Red-Yellow-Green” scale is often used for indicating performance, with green representing success and red indicating areas of concern. Consider the context and the story you want your chart to tell when selecting a color scale.
Can I customize the color scale further?
+Absolutely! Excel allows you to fine-tune the color scale by adjusting the minimum and maximum values associated with each color. This customization ensures that specific values are highlighted as desired and that the color scale accurately represents your data range.
What if my data has negative values?
+Excel handles negative values gracefully in value-based color customization. The colors assigned to negative values will typically be on the opposite side of the color scale, providing a clear visual distinction between positive and negative trends. This makes it easy to identify areas of concern or success in your data.



