Epithelial Cells: Unraveling Urine's Secret Agents
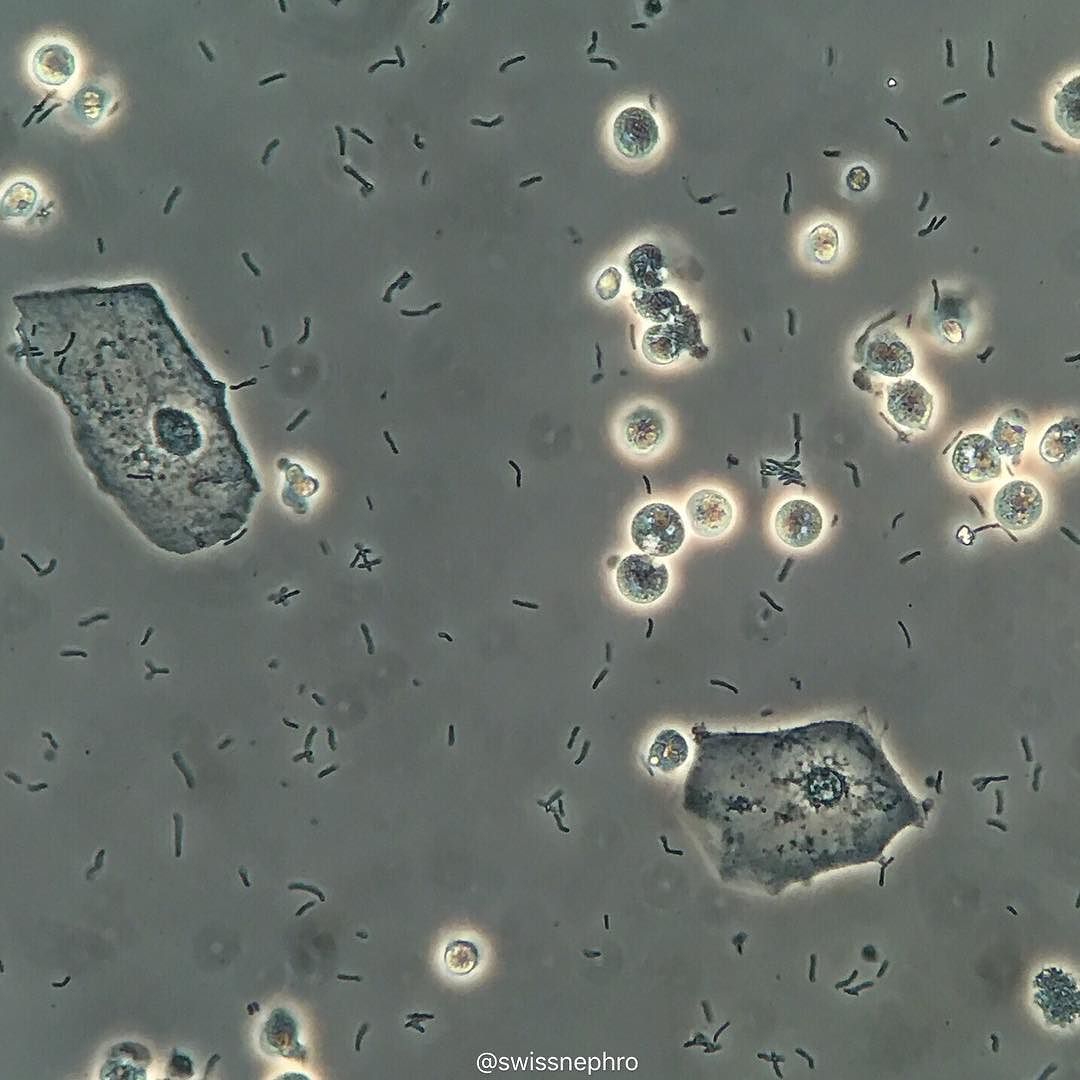
Epithelial cells are often overlooked in the grand scheme of our bodily functions, yet they play an essential role in maintaining our health and providing insights into various conditions. Among these unsung heroes, the epithelial cells in urine deserve special attention, as they reveal a wealth of information about our bodies. These cells, though tiny, are powerful messengers, carrying secrets that can unlock the mysteries of our well-being.
Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the remarkable role of epithelial cells in urine analysis and how they contribute to our understanding of health and disease.
The Urinary System: A Window to Our Vitality
Our urinary system is an intricate network of organs and structures, designed to filter and eliminate waste products from the body. At its core, urine is a liquid goldmine of data, containing a diverse array of cellular components, including epithelial cells. These cells, originating from the urinary tract, offer a unique glimpse into the health of our kidneys, bladder, and ureters.
The analysis of urine is not a new concept. For centuries, medical practitioners have relied on the visual and chemical examination of urine to diagnose various ailments. Today, with advanced technology and scientific understanding, we can delve deeper into the composition of urine, uncovering a wealth of information from its cellular components.
Epithelial Cells: Sentinels of the Urinary Tract
Epithelial cells are the guardians of the urinary tract, lining the surfaces and forming a protective barrier. These cells are specialized to perform various functions, from filtering waste products to regulating fluid balance. In urine analysis, epithelial cells provide crucial insights into the health of the urinary system.
There are several types of epithelial cells found in urine, each with its unique characteristics and functions:
Transitional Epithelial Cells: These cells are highly adaptable, capable of changing shape and size to accommodate the varying volume of urine. They line the inner surfaces of the bladder and ureters, providing a smooth passage for urine flow.
Squamous Epithelial Cells: Often present in trace amounts, these cells originate from the vagina or urethra in females, and the prostate gland in males. Their presence in urine can indicate potential issues in these organs.
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells: Derived from the kidneys, these cells are responsible for reabsorbing essential nutrients and maintaining the balance of electrolytes in the body. Their appearance in urine can signal kidney damage or dysfunction.
Urothelial Cells: These cells form a protective layer in the urinary tract, preventing toxins and pathogens from entering the bloodstream. Their presence in urine can indicate inflammation or infection in the urinary system.
Unveiling Health Conditions through Urine Analysis
The analysis of epithelial cells in urine is a powerful tool in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. Here’s how these cells can provide critical insights:
Kidney Function: The presence of renal tubular epithelial cells in urine can indicate kidney damage or disease. This can help diagnose conditions like acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, or glomerulonephritis.
Bladder Health: Transitional epithelial cells, when present in large numbers or showing abnormal characteristics, can indicate bladder inflammation, infection, or even cancer.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Epithelial cells, especially those with signs of inflammation or damage, can be a strong indicator of UTIs. The presence of white blood cells and bacteria further confirms the diagnosis.
Prostate Health: In males, the appearance of squamous epithelial cells from the prostate gland can signal potential issues like prostatitis or prostate cancer.
Vaginal Health: In females, the presence of vaginal squamous epithelial cells in urine can indicate vaginal infections or inflammation.
Advanced Techniques for Epithelial Cell Analysis
With advancements in laboratory technology, the analysis of epithelial cells in urine has become more precise and informative. Here are some of the cutting-edge techniques used:
Cytology: Traditional microscopic examination of urine samples can reveal the presence and characteristics of epithelial cells. Experienced cytotechnologists can identify abnormalities and provide valuable insights.
Immunocytochemistry: This technique uses specific antibodies to detect and visualize epithelial cells and their components. It helps in identifying the origin and type of epithelial cells, aiding in accurate diagnosis.
Flow Cytometry: This advanced method allows for the rapid analysis of large numbers of cells, providing detailed information on cell size, shape, and complexity. It can help distinguish between different types of epithelial cells and detect abnormalities.
Genetic Analysis: By analyzing the genetic material of epithelial cells, scientists can identify mutations and genetic markers associated with specific diseases. This approach is particularly useful in diagnosing and monitoring cancer.
The Future of Urine Analysis: Personalized Medicine
The study of epithelial cells in urine is not just about diagnosis; it’s also about personalized medicine and preventive care. By analyzing these cells, healthcare professionals can gain insights into an individual’s unique health profile, allowing for tailored treatment plans and proactive interventions.
In the future, urine analysis may become a routine part of regular health check-ups, providing an early warning system for various conditions. With further research and development, we can expect more accurate and accessible tests, empowering individuals to take control of their health.
Conclusion: The Unseen Power of Epithelial Cells
Epithelial cells in urine are more than just passive components; they are dynamic messengers, carrying crucial information about our health. Through their analysis, we can unlock the secrets of the urinary system, diagnose diseases, and monitor our well-being.
As we continue to explore the potential of urine analysis, we unlock a world of possibilities for early detection, personalized treatment, and improved health outcomes. The humble epithelial cell, once overlooked, is now recognized as a powerful ally in the quest for better health.
What is the role of epithelial cells in urine analysis?
+Epithelial cells in urine provide valuable insights into the health of the urinary system. They can indicate kidney function, bladder health, urinary tract infections, prostate issues, and vaginal infections. Their analysis helps in diagnosing and monitoring various conditions.
How are epithelial cells analyzed in urine samples?
+Epithelial cells in urine can be analyzed through various techniques, including traditional cytology, immunocytochemistry, flow cytometry, and genetic analysis. These methods provide detailed information on cell characteristics, origin, and potential abnormalities.
Can epithelial cells in urine indicate cancer?
+Yes, the presence of certain epithelial cells, such as transitional or squamous cells, with abnormal characteristics can be an early indicator of bladder, prostate, or vaginal cancer. Genetic analysis of these cells can further confirm the diagnosis.
How does urine analysis contribute to personalized medicine?
+Urine analysis, including the study of epithelial cells, provides a unique health profile for each individual. This information can be used to tailor treatment plans, predict disease risks, and develop personalized preventive strategies, leading to better health outcomes.


