Embed Excel Magic: 3 Simple Steps
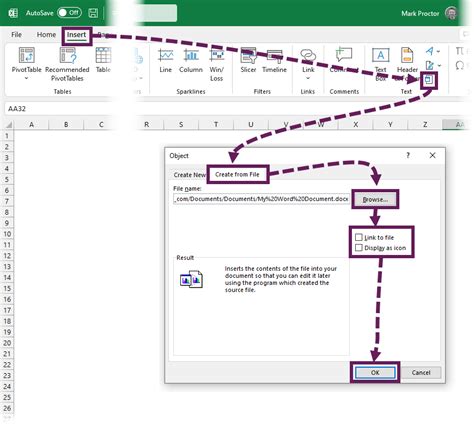
Welcome to the world of Excel, where data comes to life and magic happens with just a few clicks! Excel, the powerful spreadsheet software, is not just a tool for data entry; it's a versatile platform that can transform your data into meaningful insights and automate complex tasks. In this article, we will guide you through a simple yet effective process to unleash the magic of Excel and elevate your data analysis skills.
Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, these three steps will help you master the art of embedding Excel magic into your workflows. Get ready to discover the power of dynamic charts, automated calculations, and efficient data management that will revolutionize the way you work with data.
Step 1: Dynamic Charts - Visualize Your Data with Impact

Excel offers a wide range of chart types, each designed to showcase different aspects of your data. From simple bar graphs to intricate scatter plots, the choice is yours. By selecting the appropriate chart type, you can visualize your data in a way that tells a compelling story.
Step 1.1: Choosing the Right Chart Type
The first step in creating a dynamic chart is selecting the right chart type for your data. Consider the nature of your data and the story you want to tell. Here are some common chart types and their ideal use cases:
- Bar Chart: Great for comparing different categories or tracking trends over time.
- Line Chart: Ideal for showing trends and patterns in data over a continuous scale.
- Pie Chart: Perfect for illustrating the proportion of each category in a whole.
- Scatter Plot: Used to display the relationship between two sets of data points.
- Area Chart: Effective for emphasizing the magnitude of change over time.
For example, let's say you have sales data for different regions over a year. A line chart would be an excellent choice to visualize the sales trend for each region over time. By selecting the appropriate chart type, you set the foundation for a visually appealing and informative representation of your data.
Step 1.2: Customizing Your Chart
Once you’ve selected the chart type, it’s time to customize it to perfection. Excel provides a wealth of customization options to ensure your chart aligns with your preferences and requirements.
Start by adjusting the chart title, axis labels, and legend to ensure they accurately represent your data. You can also experiment with different color schemes, data labels, and gridlines to enhance the visual appeal and clarity of your chart.
For instance, you might want to highlight a particular region's sales performance by using a distinct color for its data points. Excel's customization options allow you to emphasize specific aspects of your data, making your chart more engaging and informative.
Step 1.3: Making Your Chart Dynamic
The true magic of Excel charts lies in their dynamic nature. By linking your chart to your data, any changes in the underlying data will automatically update the chart, ensuring it always reflects the latest information.
To make your chart dynamic, ensure that the data you wish to visualize is linked to the chart. As you update your data, the chart will automatically adjust, providing an up-to-date visual representation without the need for manual intervention.
For example, if you add a new data point to your sales dataset, the line chart will seamlessly incorporate the new data point, updating the visual representation without any additional effort on your part. This dynamic feature saves time and ensures your charts always present accurate and relevant information.
| Chart Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Visualizes categorical data, comparing values across different categories. |
| Line Chart | Displays trends and patterns in data over a continuous scale, ideal for time-series data. |
| Pie Chart | Shows the proportion of each category in a whole, perfect for illustrating percentages. |
| Scatter Plot | Plots data points on a coordinate system, revealing relationships between variables. |
| Area Chart | Emphasizes the magnitude of change over time, often used for cumulative data. |
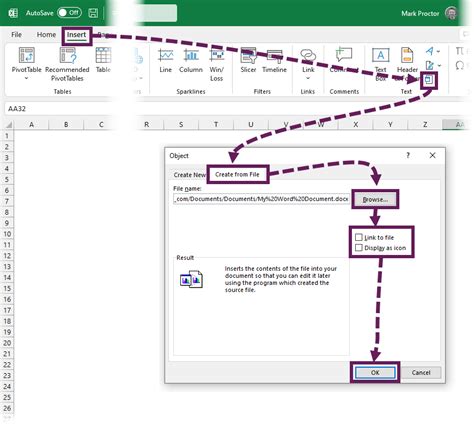
Step 2: Automated Calculations - Unleash Excel’s Power

Excel is renowned for its ability to perform complex calculations with ease. By leveraging Excel’s built-in functions and formulas, you can automate repetitive tasks and save valuable time.
Step 2.1: Understanding Excel Functions
Excel functions are predefined formulas that perform specific calculations. From simple arithmetic operations to advanced statistical analyses, Excel functions cover a wide range of use cases.
Some commonly used functions include:
- SUM: Adds up a range of cells.
- AVERAGE: Calculates the average of a set of values.
- MAX and MIN: Find the highest and lowest values, respectively.
- COUNT: Counts the number of cells containing numbers.
- IF: Performs a logical test and returns one value if the test is true and another if it's false.
For example, the SUM function is incredibly useful for calculating totals in financial spreadsheets, while the IF function can automate decision-making processes based on specific conditions.
Step 2.2: Creating Custom Formulas
While Excel provides a vast library of built-in functions, there may be times when you need a formula tailored to your specific requirements. Excel allows you to create custom formulas by combining functions and operators.
For instance, if you need to calculate the average of a range of cells and then multiply it by a certain factor, you can create a custom formula using the AVERAGE and MULTIPLY functions. Excel's formula builder assists you in constructing complex formulas with ease.
Step 2.3: Automating Your Calculations
The real power of Excel lies in its ability to automate calculations. By linking your formulas to specific cells, any changes in the input data will automatically update the calculated results.
For example, if you have a sales spreadsheet with a formula that calculates the total revenue, and you update the sales data, the formula will automatically recalculate the total revenue, ensuring accuracy and saving time.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| SUM | Adds up a range of cells. |
| AVERAGE | Calculates the average of a set of values. |
| MAX | Finds the highest value in a range. |
| MIN | Finds the lowest value in a range. |
| COUNT | Counts the number of cells containing numbers. |
| IF | Performs a logical test and returns one value if true, another if false. |
Step 3: Efficient Data Management - Streamline Your Workflow
Efficient data management is crucial for effective data analysis. Excel provides various tools and techniques to help you organize, manipulate, and analyze your data with ease.
Step 3.1: Data Cleaning and Preparation
Before diving into analysis, it’s essential to ensure your data is clean and organized. Excel offers a range of tools to help you identify and remove duplicates, fill in missing values, and standardize data formats.
For example, you can use Excel's Remove Duplicates feature to eliminate redundant data, ensuring your analysis is based on unique records. Additionally, tools like Flash Fill and Text to Columns assist in transforming data into a usable format.
Step 3.2: Data Sorting and Filtering
Excel’s sorting and filtering capabilities enable you to quickly organize and analyze your data. You can sort data based on specific criteria, such as highest to lowest or alphabetically, and filter data to display only the information you need.
For instance, if you have a large dataset of customer information, you can sort it by sales amount to identify your top customers. Filtering allows you to focus on specific subsets of data, making it easier to analyze and draw insights.
Step 3.3: Data Analysis with PivotTables
PivotTables are a powerful feature in Excel that allows you to summarize and analyze large datasets quickly. With PivotTables, you can easily aggregate, group, and calculate data, providing valuable insights in a matter of seconds.
For example, you can use a PivotTable to analyze sales data by region, product category, and time period, helping you identify trends and make data-driven decisions.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Remove Duplicates | Identifies and eliminates duplicate records in a dataset. |
| Flash Fill | Automatically fills in data based on a pattern detected in existing data. |
| Text to Columns | Splits text data into separate columns based on specified delimiters. |
| Sort | Organizes data based on specific criteria, such as highest to lowest or alphabetically. |
| Filter | Displays only the data that meets specific criteria, allowing for focused analysis. |
| PivotTable | Summarizes and analyzes large datasets, providing valuable insights through aggregation and grouping. |
Conclusion
By following these three simple steps, you can unlock the full potential of Excel and transform your data into powerful insights. From dynamic charts that visualize your data with impact to automated calculations that save time and reduce errors, Excel is a versatile tool that empowers you to analyze and present data effectively.
Efficient data management streamlines your workflow, ensuring your data is organized and ready for analysis. With Excel's powerful features, you can make informed decisions, identify trends, and communicate your findings with clarity and confidence.
So, embrace the magic of Excel, and let your data shine! Whether you're a student, a professional, or a business owner, Excel is a valuable asset that can enhance your data analysis skills and elevate your productivity.
FAQ
How do I create a dynamic chart in Excel?
+To create a dynamic chart, start by selecting the data you want to visualize. Choose the appropriate chart type and customize it to your preferences. Ensure that the chart is linked to the data range, so any changes in the data will automatically update the chart.
What are some commonly used Excel functions for data analysis?
+Excel offers a wide range of functions for data analysis. Some commonly used functions include SUM, AVERAGE, MAX, MIN, COUNT, and IF. These functions can be used to calculate totals, averages, identify the highest and lowest values, count occurrences, and perform logical tests.
How can I efficiently manage large datasets in Excel?
+Efficient data management is crucial for large datasets. Start by cleaning and organizing your data using tools like Remove Duplicates, Flash Fill, and Text to Columns. Utilize sorting and filtering to focus on specific subsets of data. PivotTables are powerful tools for summarizing and analyzing large datasets quickly.

