5 Common Diagnosis Codes for Lung Nodules
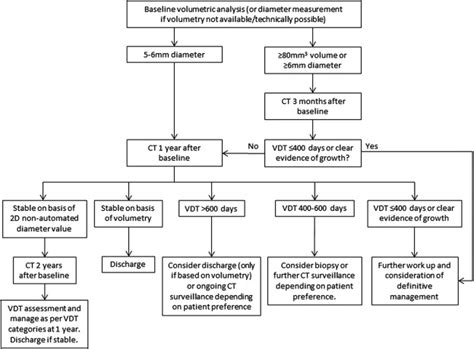
Lung nodules, often referred to as pulmonary nodules, are small, roundish growths that appear in the lungs. They can be a cause for concern as they might indicate various respiratory issues. Here, we explore the five most prevalent diagnosis codes associated with lung nodules, offering insight into their potential implications and the subsequent steps in medical management.
Diagnosis Code: J91.81

This code signifies the presence of solitary pulmonary nodules. Solitary nodules are singular, often round lesions found in the lung parenchyma. They can be discovered incidentally during imaging studies for unrelated reasons, or they may present with symptoms such as persistent coughing, chest pain, or unexplained weight loss.
The key challenge with solitary pulmonary nodules is determining their nature—benign or malignant. While many are benign and pose no immediate threat, some may be cancerous, particularly in individuals with a history of smoking or exposure to carcinogens. Further investigation, often through imaging and biopsy, is crucial to ascertain the nodule’s nature and guide treatment.
Diagnosis Code: J91.2

J91.2 is assigned to cases of multiple pulmonary nodules. Unlike solitary nodules, multiple nodules are characterized by the presence of several small lesions scattered throughout the lungs. These nodules can vary in size and number, and their appearance may suggest specific underlying conditions.
In some cases, multiple pulmonary nodules are indicative of metastatic cancer, where the disease has spread from its primary site to the lungs. Other potential causes include infectious diseases like tuberculosis or fungal infections, or inflammatory conditions such as sarcoidosis. The diagnosis and management of multiple pulmonary nodules heavily rely on understanding the patient’s medical history and the results of diagnostic tests.
Diagnosis Code: J91.89
This code is a catch-all for other specified pulmonary nodules. It encompasses a wide range of scenarios where the nodules do not fit into the above categories or where there is insufficient information to assign a more specific code. For instance, this code might be used when initial imaging suggests a nodule, but further testing is required to confirm its presence or nature.
In such cases, a thorough medical evaluation is necessary, often involving advanced imaging techniques and possibly biopsy procedures. The aim is to determine the exact nature of the nodule and its potential impact on the patient’s health, guiding subsequent treatment and management strategies.
Diagnosis Code: C34.90
When a lung nodule is identified as malignant, the diagnosis code C34.90 is applied. This code indicates that the nodule is cancerous and requires immediate attention. The specific type of cancer is often determined through biopsy, and further tests are conducted to assess the stage and extent of the disease.
The management of malignant lung nodules typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, with experts in oncology, surgery, and radiation therapy collaborating to develop an individualized treatment plan. This plan may include surgery to remove the nodule, chemotherapy to destroy cancer cells, or radiation therapy to shrink the nodule and prevent its spread.
Diagnosis Code: B99.2
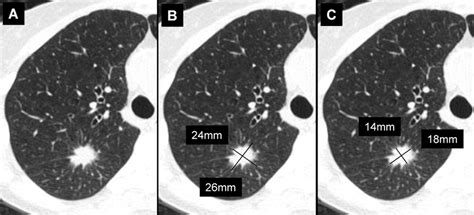
In the context of lung nodules, the diagnosis code B99.2 is assigned when the nodule is associated with an infectious disease. This code is broad and can cover a range of infections, from bacterial to viral and even fungal. The specific type of infection is often determined through laboratory testing of the nodule’s tissue or through analysis of the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
Treatment for infectious pulmonary nodules depends on the causative agent. Antibiotics, antifungal medications, or antiviral therapies may be prescribed, along with supportive care to manage symptoms and promote healing. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the nodule, especially if it is causing significant respiratory distress or if there is a risk of it spreading.
Conclusion
The diagnosis and management of lung nodules require a meticulous approach, involving a careful evaluation of the patient’s medical history, imaging studies, and, in some cases, invasive procedures like biopsies. While the presence of a lung nodule can be concerning, early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective management and the best possible outcomes.
By understanding the common diagnosis codes associated with lung nodules, healthcare professionals can navigate the complex path of investigation and treatment, offering patients the best chance at successful recovery and long-term health.