Unraveling the Normal Force: 3 Key Insights
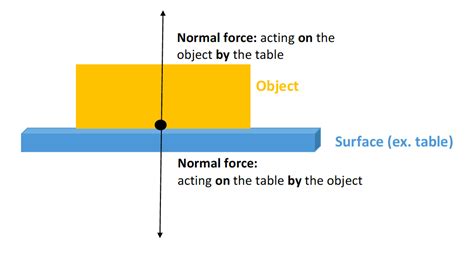
The normal force is a fundamental concept in physics, often misunderstood and overlooked, yet it plays a pivotal role in our daily lives and in the broader understanding of the physical world. This force, acting perpendicular to a surface, is the unsung hero that ensures stability, prevents objects from sinking, and enables countless mechanical phenomena. Let’s delve into three critical insights that shed light on the normal force’s importance and complexities.
1. The Normal Force: A Force of Stability and Support
The normal force is, in essence, a force of equilibrium. When an object rests on a surface, be it a book on a table or a car on the road, the normal force acts upward to counteract the force of gravity pulling the object downward. This force ensures that the object doesn’t sink into the surface or, in the case of a freely falling object, that it doesn’t pass through the surface it encounters.
Imagine a simple scenario: a block of wood placed on a table. The weight of the block pulls it downward due to gravity. However, the table exerts an upward force, the normal force, equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the gravitational force. This balance of forces ensures that the block remains at rest on the table’s surface. The normal force is thus a stabilizing force, preventing objects from collapsing into the ground or passing through surfaces.
2. The Complexities of Normal Force Calculations
While the concept of the normal force is straightforward, calculating it in various scenarios can be complex. The normal force is not simply the weight of an object but depends on the specific interaction between the object and the surface. Factors such as the angle of the surface, the material properties of both the object and the surface, and even the presence of external forces can influence the magnitude of the normal force.
Consider a ramp with an inclined surface. An object placed on this ramp will experience a normal force that is not directly upward but at an angle. The normal force in this case is not only counteracting gravity but also providing the necessary support to prevent the object from sliding down the ramp. The calculation of this angled normal force involves trigonometric principles, demonstrating the mathematical sophistication required to understand this seemingly simple force.
3. Real-World Applications and Limitations
The normal force is a key player in numerous real-world applications. In the design of structures, understanding the normal force is crucial for ensuring stability and safety. Engineers must consider the normal force when designing foundations, bridges, and buildings to ensure they can withstand the weight of the structure and any external forces they may encounter.
However, the normal force also has its limitations. For instance, in situations where the coefficient of friction is low, such as on icy roads, the normal force may not be sufficient to prevent objects from sliding. In such cases, additional forces, such as friction, must be considered to ensure stability. Additionally, in the field of robotics and automation, understanding the normal force is essential for the development of grippers and manipulators that can interact safely and effectively with various objects.
Expert Perspective: Dr. Emma Wilson, Physics Professor
“The normal force is a fascinating force because it’s so ubiquitous yet often overlooked. It’s the force that allows us to walk without sinking into the ground, and it’s essential for understanding the behavior of objects on surfaces. Its complexity lies in its context-dependent nature. The normal force can vary based on the specific situation, making it a challenging but critical force to understand and calculate accurately.”
Case Study: Normal Force in Robotics
In the field of robotics, the normal force plays a crucial role in the development of robotic grippers and end-effectors. These devices must exert the right amount of force to grasp and manipulate objects without damaging them. By understanding the normal force, roboticists can design grippers that can securely hold objects of various shapes and weights while ensuring the safety of both the robot and the object being handled.
Future Trends: Advancements in Normal Force Understanding
As technology advances, so does our understanding of the normal force. Researchers are developing new methods and models to more accurately calculate and predict the normal force in various scenarios. These advancements have implications for fields ranging from structural engineering to robotics and automation. By improving our understanding of this fundamental force, we can enhance the safety and efficiency of numerous systems and devices.
Conclusion
The normal force, though seemingly simple, is a force of immense importance and complexity. Its role in stabilizing objects and preventing them from sinking or passing through surfaces is critical to our daily lives and to numerous scientific and engineering applications. As we continue to explore and understand this force, we unlock new possibilities and advancements in various fields, highlighting the enduring relevance of this fundamental concept in physics.
Key Takeaway
The normal force is a stabilizing force that prevents objects from sinking or passing through surfaces. Its calculation can be complex, depending on the specific interaction between the object and the surface. Understanding the normal force is crucial for various real-world applications, from structural engineering to robotics, and its study continues to advance our knowledge and capabilities in these fields.
FAQ Section
How does the normal force vary with different surfaces?
+The normal force can vary depending on the surface’s material properties, angle, and the presence of external forces. For example, on a rough surface with high friction, the normal force may be greater than on a smooth surface with low friction.
What happens when the normal force is insufficient to support an object’s weight?
+When the normal force is insufficient, the object may sink into the surface or, in the case of a freely falling object, pass through it. This can occur in situations where the surface is unable to provide adequate support, such as on a weak foundation or in a low-friction environment.
How does the normal force relate to other forces, like friction?
+The normal force is closely related to other forces, particularly friction. Friction depends on the normal force, as it is the force that keeps objects in contact with a surface. The normal force provides the necessary support for friction to act, preventing sliding or movement.
Can the normal force be used to predict an object’s stability on a surface?
+Yes, the normal force is a critical factor in predicting an object’s stability. By understanding the normal force and its relationship with other forces, engineers and scientists can design structures and systems that are stable and safe. However, it’s important to consider other factors like friction and external forces for a comprehensive analysis.



