Understanding Dark Spots on Your Dog's Skin
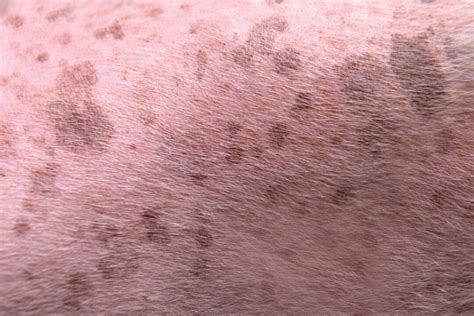
The appearance of dark spots on a dog’s skin can be a cause for concern for many pet owners, often leaving them with questions and uncertainties. These spots, known as hyperpigmentation, can vary in size, shape, and intensity, and understanding their nature and potential implications is crucial for maintaining your dog’s health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the world of canine hyperpigmentation, exploring its causes, characteristics, and the steps you can take to address it effectively.
Hyperpigmentation in dogs refers to the darkening of certain areas of the skin, typically resulting from an increase in melanin production. Melanin, a pigment responsible for the color of the skin, hair, and eyes, can become overproduced in response to various factors, leading to the development of dark spots. While these spots are generally benign, it’s essential to distinguish them from more serious conditions and understand their underlying causes.
Causes and Contributing Factors
There are several potential causes for the development of dark spots on a dog’s skin. Some of the most common factors include:
Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal fluctuations can trigger an increase in melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation. Conditions such as Cushing’s disease, hypothyroidism, or even certain medications can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to the formation of dark spots.
Allergies and Irritations: Allergic reactions, whether to food, environmental factors, or parasites, can cause inflammation and subsequent hyperpigmentation. Scratching, licking, or chewing due to irritation can also stimulate melanin production in the affected areas.
Sun Exposure: Just like humans, dogs can experience increased melanin production in response to sun exposure. Areas with less fur or thinner skin, such as the belly or nose, may develop dark spots as a protective response to UV radiation.
Infectious Diseases: Certain bacterial or fungal infections can result in skin inflammation and subsequent hyperpigmentation. Conditions like ringworm or bacterial folliculitis may cause dark spots to appear on the affected areas.
Age-Related Changes: As dogs age, their skin may undergo natural changes, including the development of dark spots. This is often a normal part of the aging process and may not indicate any underlying health issues.
Identifying Hyperpigmentation
Recognizing hyperpigmentation on your dog’s skin involves observing specific characteristics:
Appearance: Hyperpigmented spots typically appear as dark, well-defined areas on the skin. They can vary in size and shape, ranging from small, discrete patches to larger, more extensive regions.
Location: These spots can occur anywhere on a dog’s body, but they are often more noticeable on areas with lighter-colored skin, such as the belly, groin, or inside the legs.
Texture: The texture of hyperpigmented areas may vary. While some spots are smooth and flat, others may have a slightly raised or rough texture, depending on the underlying cause.
Symptoms: In some cases, hyperpigmentation may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as itching, redness, hair loss, or a foul odor. These additional signs can help differentiate hyperpigmentation from other skin conditions.
When to Seek Veterinary Care
While many cases of hyperpigmentation are benign and resolve on their own, there are instances where veterinary attention is necessary. Consider consulting your veterinarian if:
- The dark spots appear suddenly and rapidly increase in size or number.
- The hyperpigmented areas are accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as excessive itching, hair loss, or pain.
- Your dog has a history of hormonal imbalances or underlying health conditions that may contribute to hyperpigmentation.
- The dark spots do not resolve or improve despite implementing appropriate care measures.
Managing and Preventing Hyperpigmentation
There are several steps you can take to manage and prevent hyperpigmentation in your dog:
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Ensure your dog receives a balanced and nutritious diet, as nutritional deficiencies can contribute to skin issues. Consult your veterinarian for recommendations on appropriate food choices for your dog’s specific needs.
Provide Regular Grooming: Proper grooming practices, including regular brushing and bathing, can help maintain healthy skin and coat. This can also allow you to monitor your dog’s skin for any changes or abnormalities.
Protect from Sun Exposure: Limit your dog’s exposure to direct sunlight, especially during peak hours. Use pet-safe sunscreens on areas with less fur or thinner skin to prevent sunburn and reduce the risk of hyperpigmentation.
Manage Allergies: If your dog has known allergies, work closely with your veterinarian to manage them effectively. This may involve dietary adjustments, allergy testing, or medication to minimize allergic reactions and associated skin issues.
Address Underlying Conditions: If hyperpigmentation is linked to an underlying health issue, such as hormonal imbalances or infections, prompt veterinary care is essential. Treating the underlying condition can often lead to the resolution of hyperpigmentation.
The Role of Veterinary Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial when dealing with hyperpigmentation, as it can help differentiate between benign spots and more serious conditions. Your veterinarian may recommend various diagnostic tests, including:
Physical Examination: A thorough examination of your dog’s skin and overall health can provide valuable insights. Your veterinarian will assess the appearance, location, and characteristics of the dark spots to determine their nature.
Skin Scrapings and Cytology: Skin samples may be collected for microscopic examination to identify any underlying infections or parasites. This can help rule out certain conditions and guide appropriate treatment.
Blood Work and Hormone Testing: If hormonal imbalances are suspected, blood tests can be performed to assess hormone levels and identify any abnormalities.
Allergy Testing: In cases where allergies are suspected, your veterinarian may recommend allergy testing to identify specific triggers and develop an appropriate management plan.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for hyperpigmentation depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Some common treatment options include:
Medicated Shampoos and Topical Treatments: In cases of mild hyperpigmentation, medicated shampoos or topical treatments may be prescribed to soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
Oral Medications: If an underlying condition, such as a hormonal imbalance or infection, is identified, oral medications may be necessary to address the root cause.
Nutritional Supplements: Certain nutritional supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids or antioxidants, may be recommended to support skin health and promote the resolution of hyperpigmentation.
Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, surgical removal of hyperpigmented areas may be considered if they are causing discomfort or are suspected to be cancerous.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
The prognosis for hyperpigmentation varies depending on the underlying cause. In many cases, with proper care and management, hyperpigmentation can resolve or improve significantly. However, it’s important to note that some dogs may continue to experience periodic flare-ups or have persistent spots that require ongoing management.
Long-term management strategies may include:
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Schedule routine check-ups with your veterinarian to monitor your dog’s skin health and address any concerns promptly.
Consistent Care Practices: Maintain a consistent grooming routine, provide a balanced diet, and ensure your dog has adequate protection from sun exposure.
Ongoing Medication or Supplements: If your dog requires long-term medication or supplements, ensure you administer them as prescribed and consult your veterinarian for any necessary adjustments.
Allergy Management: If allergies are a contributing factor, work closely with your veterinarian to manage them effectively and minimize flare-ups.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and characteristics of dark spots on your dog’s skin is an essential aspect of responsible pet ownership. While hyperpigmentation is often a benign condition, it’s crucial to differentiate it from more serious issues and address any underlying causes promptly. By recognizing the signs, seeking veterinary care when necessary, and implementing appropriate management strategies, you can help your furry friend maintain healthy and vibrant skin. Remember, your veterinarian is your best resource for guidance and support in navigating your dog’s unique skin health needs.