Cranial Nerves Label Challenge
Cranial Nerves: An Essential Guide to Their Functions and Fascinating Facts

The cranial nerves, a remarkable set of twelve pairs, play an integral role in our sensory and motor functions. Understanding their intricacies is crucial for anyone interested in neuroscience or the human body. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of cranial nerves, exploring their unique characteristics and the vital roles they play in our daily lives.
The Benefits of Cranial Nerve Knowledge
Grasping the functions of these nerves is not just for medical professionals. It can provide fascinating insights into our sensory experiences, control over body movements, and even offer clues to potential health issues. By recognizing the symptoms associated with cranial nerve dysfunctions, we can promote early detection and timely treatment.
The Challenges
However, the world of cranial nerves is complex, with each nerve having distinct functions and pathways. Memorizing their names, functions, and associated conditions can be a daunting task. But fear not, for we are here to demystify this challenge and make it an engaging journey.
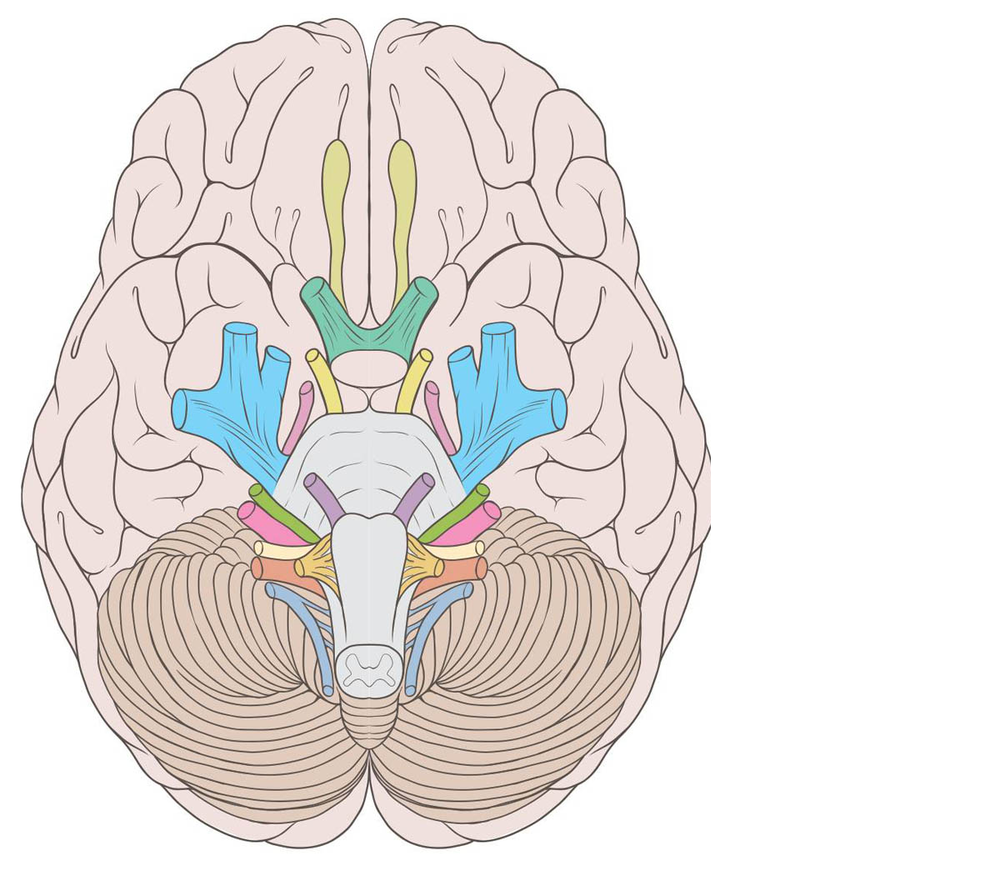
Unraveling the Cranial Nerve Mystery

Let's embark on a journey through the twelve cranial nerves, each with its unique story and significance.
Key Takeaway: The cranial nerves are numbered and named based on their functions and historical discoveries. Understanding their names provides a glimpse into their diverse roles in our bodies.
The First Cranial Nerve: Olfactory
Our sense of smell is an intricate process, and the olfactory nerve (CN I) is the star of this sensory show. It carries signals from the olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity to the brain, allowing us to perceive and distinguish a myriad of scents.
Optic Nerve (CN II): The Visual Pathway
The optic nerve is a critical component of our visual system. It transmits visual information from the retina to the brain, enabling us to see the world around us. Any disruption to this nerve can result in visual disturbances or even blindness.
Oculomotor, Trochlear, and Abducens Nerves (CN III, IV, and VI): Eye Movement Masters
These nerves work in harmony to control the intricate movements of our eyes. The oculomotor nerve (CN III) is responsible for most eye movements, while the trochlear nerve (CN IV) and abducens nerve (CN VI) each play specific roles in eye rotation, ensuring we can scan our environment with precision.
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V): The Three-Branched Sensation
As the largest of the cranial nerves, the trigeminal nerve has a three-branched structure. It provides sensory information from the face and head, and also plays a role in motor functions, such as biting and chewing.
Facial Nerve (CN VII): Beyond Facial Expressions
While the facial nerve is famous for controlling our facial muscles, allowing us to smile, frown, and express emotions, it also has a crucial sensory function. It carries taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and plays a role in tear and saliva production.
Acoustic (Vestibulocochlear) Nerve (CN VIII): Hearing and Balance Experts
The acoustic nerve is vital for both hearing and balance. It carries auditory information from the inner ear to the brain, enabling us to perceive sound. Additionally, it helps maintain our sense of balance and spatial orientation.
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX): Swallowing and More
This nerve is involved in a range of functions, including taste sensation from the posterior one-third of the tongue, swallowing, and controlling the muscles of the throat and neck. It also plays a role in regulating blood pressure and heart rate.
Vagus Nerve (CN X): The Wanderlust Nerve
Known as the wanderer or the wanderlust nerve, the vagus nerve has an extensive reach. It plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including heart rate regulation, digestion, and speech. It also has a significant impact on our emotional well-being, earning it the nickname "the mood nerve."
Accessory Nerve (CN XI): Head and Neck Support
The accessory nerve is responsible for the motor control of certain neck and shoulder muscles, allowing us to move our heads and shoulders with ease. It works in conjunction with the spinal accessory nerve to ensure smooth movements.
Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII): Tongue Movement Master
As the name suggests, the hypoglossal nerve is crucial for tongue movements. It controls the muscles of the tongue, enabling us to speak, swallow, and move our tongues in various directions. Dysfunction of this nerve can lead to slurred speech and difficulty swallowing.
Cranial Nerve Disorders: Recognizing the Symptoms
Understanding the functions of cranial nerves is not just an academic exercise. It can be a life-saving endeavor. Being aware of the symptoms associated with cranial nerve disorders can lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Expert Insight: Early detection of cranial nerve disorders is crucial. Many of these conditions are treatable, and early intervention can prevent further complications and improve long-term outcomes.
Common Cranial Nerve Disorders and Their Symptoms
-
Bell's Palsy (Facial Nerve Palsy): Sudden weakness or paralysis on one side of the face, affecting facial expressions and causing drooping of the mouth and eyelid. It can also lead to difficulty eating and speaking.
-
Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannoma): A benign tumor on the acoustic nerve, causing hearing loss, tinnitus, and balance issues. In severe cases, it can lead to facial paralysis.
-
Trigeminal Neuralgia: A condition characterized by intense, shooting facial pain, often triggered by mundane activities like chewing, speaking, or even brushing teeth. It can be debilitating and affect daily life.
-
Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia: Similar to trigeminal neuralgia, but affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve. It causes severe pain in the throat, neck, and ear, often triggered by swallowing or coughing.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of Cranial Nerves
The cranial nerves are a fascinating and intricate part of our neurological system. Their diverse functions and pathways showcase the complexity and beauty of the human body. By understanding their roles and potential disorders, we can appreciate the delicate balance that keeps us healthy and functioning optimally.
As we conclude our journey through the world of cranial nerves, we hope you have gained a deeper understanding and appreciation for these essential components of our sensory and motor systems. Remember, knowledge is power, and when it comes to our health, it can be a life-changing force.
How many cranial nerves are there, and what are their main functions?
+There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves, each with distinct functions. These nerves play crucial roles in sensory perception, motor control, and various physiological processes. From enabling us to see and hear to controlling our facial expressions and regulating vital functions like heart rate and digestion, the cranial nerves are an essential part of our daily lives.
What are some common disorders associated with cranial nerves, and what are the symptoms to look out for?
+Common disorders associated with cranial nerves include Bell’s Palsy, acoustic neuroma, trigeminal neuralgia, and glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Symptoms vary depending on the nerve involved but can include facial weakness or paralysis, hearing loss, tinnitus, balance issues, and severe facial or throat pain. Prompt medical attention is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
How can understanding cranial nerves benefit non-medical professionals?
+Understanding cranial nerves provides valuable insights into our sensory experiences and body functions. It can enhance our awareness of potential health issues, enable early detection of disorders, and promote overall well-being. Knowledge of cranial nerves is not just for medical professionals; it’s a powerful tool for anyone interested in the human body and its incredible capabilities.
What are some ways to maintain the health and optimal functioning of cranial nerves?
+Maintaining cranial nerve health involves adopting a holistic approach to well-being. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Additionally, practices like yoga and meditation can promote overall neurological health and well-being.
Are there any emerging treatments or technologies for cranial nerve disorders?
+Yes, there are exciting advancements in the treatment of cranial nerve disorders. These include targeted drug therapies, innovative surgical techniques, and cutting-edge technologies like deep brain stimulation and stem cell therapies. These developments offer new hope and improved outcomes for individuals affected by cranial nerve disorders.



