CPK Formula: 5 Excel Tips

In the world of data analysis and financial modeling, understanding the ins and outs of Excel formulas is crucial. Among these, the CPK Formula stands out as a powerful tool for process improvement and quality control. This formula, often used in conjunction with the Six Sigma methodology, provides a comprehensive measure of process capability. In this article, we will delve into the CPK Formula and explore five essential Excel tips to help you master its application.
Understanding the CPK Formula

The CPK Formula, also known as the Process Capability Index, is a statistical measure used to evaluate how well a process meets its specifications. It considers both the process capability (CP) and the process performance (PP) to provide a single index that indicates the process’s ability to produce consistent and high-quality outputs. The CPK Formula is particularly valuable in industries where precision and quality are paramount, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and financial services.
The formula is calculated as follows:
CPK = min(CPU, CPL)
where:
- CPU is the upper process capability index
- CPL is the lower process capability index
The CPK Formula takes into account the process's ability to meet both upper and lower specifications, ensuring that it remains within acceptable limits. A higher CPK value indicates a more capable process, while a value closer to 1 suggests that the process is just meeting the minimum requirements.
Excel Tips for Mastering the CPK Formula
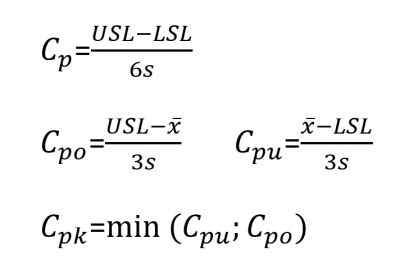
Now, let’s explore five practical Excel tips to enhance your understanding and application of the CPK Formula:
1. Data Preparation
Before diving into the CPK Formula, ensure your data is properly organized and cleaned. Excel’s data sorting and filtering features can help you identify and remove any outliers or errors. Accurate data is crucial for obtaining reliable CPK values.
2. Utilizing Built-in Functions
Excel offers a range of built-in functions that can streamline your CPK calculations. Functions like AVERAGE, STDEV, and MAX can be used to calculate key parameters needed for the CPK Formula. By leveraging these functions, you can automate your calculations and reduce the risk of errors.
3. Visualizing Process Capability
Excel’s charting capabilities allow you to visualize your process capability. Create a histogram or a box plot to visually represent your data and its distribution. This can help you identify any potential issues or outliers, making it easier to interpret your CPK results.
| Histogram | Box Plot |
|---|---|
| A histogram provides a visual representation of the frequency distribution of your data, allowing you to assess its spread and shape. | A box plot, or box-and-whisker plot, displays the distribution of your data in a concise manner, highlighting the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. |

4. Sensitivity Analysis
Performing sensitivity analysis can help you understand how changes in your data impact the CPK value. By using Excel’s data table or scenario manager features, you can analyze the effect of varying input parameters on your CPK calculations. This is particularly useful for assessing the robustness of your process.
5. Custom CPK Formulas
In some cases, you may need to customize the CPK Formula to align with specific industry standards or requirements. Excel’s formula builder and custom functions allow you to create your own CPK calculations tailored to your unique needs. This flexibility ensures that you can adapt the formula to any situation.
Real-World Application: Case Study
To illustrate the power of the CPK Formula and its Excel implementation, let’s consider a case study from the manufacturing industry. A company producing electronic components aims to improve the quality of its products by implementing Six Sigma principles. By using the CPK Formula in Excel, they can analyze their process capability and make data-driven decisions to enhance their production line.
The company collects data on the dimensions of its components, specifically focusing on a critical parameter, X, which must fall within the range of 5.00 to 5.50 mm. They measure a sample of 50 components and calculate the following parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean (X-bar) | 5.25 mm |
| Standard Deviation (s) | 0.12 mm |
| Upper Specification Limit (USL) | 5.50 mm |
| Lower Specification Limit (LSL) | 5.00 mm |
Using these values, the CPK Formula can be calculated as follows:
CPK = min(CPU, CPL)
where:
- CPU = (USL - X-bar) / (3 * s) = (5.50 - 5.25) / (3 * 0.12) ≈ 0.79
- CPL = (X-bar - LSL) / (3 * s) = (5.25 - 5.00) / (3 * 0.12) ≈ 1.25
CPK = min(0.79, 1.25) = 0.79
The CPK value of 0.79 indicates that the process is capable but could benefit from further improvements. The company can now use this insight to optimize their production process and ensure consistent quality.
Conclusion
The CPK Formula is a valuable tool for process improvement and quality control, and Excel offers a user-friendly platform to harness its power. By following the tips outlined in this article and applying them to real-world scenarios, you can become an expert in using the CPK Formula to drive process excellence. Remember, a well-understood and properly implemented CPK analysis can lead to significant improvements in any industry.
How does the CPK Formula differ from other process capability indices like Cpk and Pp?
+The CPK Formula, CPK, and Pp are all process capability indices, but they differ in their focus and calculation. CPK (Process Capability Index) considers both the upper and lower specifications, providing a single index that represents the overall process capability. Cpk, on the other hand, focuses on the process’s ability to meet the upper and lower specifications separately. Pp (Process Performance) measures the process’s short-term variability, often used for real-time monitoring. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right index for specific process evaluation needs.
Can the CPK Formula be used for non-manufacturing processes?
+Absolutely! While the CPK Formula is commonly used in manufacturing, its principles can be applied to various industries. For example, in healthcare, it can assess the quality of patient care processes. In finance, it can evaluate the performance of investment strategies. The key is to identify the critical parameters and specifications relevant to your specific process, allowing you to apply the CPK Formula effectively.
What are some common challenges when implementing the CPK Formula in Excel?
+Implementing the CPK Formula in Excel may present challenges such as handling large datasets efficiently, ensuring data integrity, and interpreting the results accurately. Additionally, creating custom formulas and functions can be complex, especially when dealing with multiple scenarios. However, with practice and a solid understanding of Excel’s capabilities, these challenges can be overcome, leading to successful CPK analyses.


