The Concave Curve: Understanding Its Meaning.

The Essence of Concavity

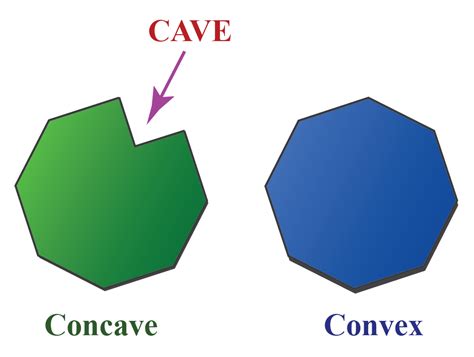
When we talk about concavity, we are referring to a specific curvature in a curve or shape. A concave curve, often referred to as a “concave-up” curve, possesses a unique property where it bends inward, forming a kind of bowl-like or cave-like structure. This inward curvature is a distinct feature that sets it apart from other curves.
The concave curve is a subtle yet powerful concept, influencing everything from the design of architectural structures to the intricate behavior of waves in physics.
Mathematical Perspective
In mathematics, the concave curve holds a special place. It is defined as a curve where, for any point on the curve, a line drawn through that point and the curve’s center of curvature will lie entirely on the same side of the curve. This definition, while precise, may seem abstract to those unfamiliar with geometric concepts.
Understanding Concavity Step by Step
- Imagine a circle with its center at a specific point. This point is known as the "center of curvature."
- Now, visualize a curve that, at every point, has a "radius of curvature" extending from the center. This radius essentially determines the curve's shape.
- A concave curve is one where, if you were to draw a tangent line at any point, the curve would lie entirely on one side of that tangent line.
- In simpler terms, a concave curve appears to "cave in" or "bow inward" at every point.
Beyond Mathematics: Real-World Applications

While the mathematical definition is crucial, the concave curve’s significance extends far beyond the confines of textbooks. Here are some intriguing ways in which the concave curve shapes our world:
Engineering Marvels
Nature's Mastery
The concave curve is not merely a human invention; it is a natural phenomenon that shapes our environment.
- In geology, concave curves can be observed in the formation of riverbeds, where the inward curvature guides the flow of water.
- Even in biology, concave curves play a role. For instance, the human eye's lens has a concave shape, allowing it to focus light onto the retina.
- The study of concavity in nature offers insights into the fundamental principles that govern our world.
The Physics of Concavity
In the realm of physics, the concave curve takes on a new dimension. Here, we explore its impact:
Optics and Light
Wave Phenomena
In the study of waves, whether it's water waves or electromagnetic waves, the concave curve plays a crucial role. When waves encounter a concave surface, they undergo interesting behaviors, such as diffraction and interference, which have significant implications in fields like acoustics and telecommunications.
Aesthetics and Art
The concave curve is not just a scientific concept; it is an artistic one too.
Artists and designers often utilize concave curves to evoke emotion and create visually captivating experiences. From the graceful lines of a violin to the sweeping curves of a sculpture, concavity adds depth and beauty to artistic creations.
Practical Applications in Everyday Life
- Concave curves are used in sports equipment, such as ski designs, to enhance performance and stability.
- In transportation, the design of aircraft wings often incorporates concave elements for aerodynamic efficiency.
- Even in everyday objects like spoons and ladles, the concave shape serves a functional purpose, aiding in scooping and pouring.
The Future of Concavity
As technology advances, so does our understanding and application of the concave curve.
Emerging Trends
- 3D printing technologies are enabling the creation of complex concave structures, opening new possibilities in design and manufacturing.
- In the field of robotics, concave curves are being explored for more efficient and flexible robotic arms, enhancing their capabilities.
Conclusion
The concave curve, with its subtle yet profound nature, continues to inspire and shape our world. From mathematics to art, and from architecture to physics, its influence is undeniable. As we continue to explore and understand the intricacies of concavity, we unlock new possibilities and deepen our appreciation for the elegance of geometry.
How is concavity different from convexity?
+Convexity refers to a curve that bends outward, forming a “hill-like” shape. In contrast, concavity is an inward curvature, creating a “valley-like” structure. These terms describe opposite geometric properties.
Can concavity be found in nature beyond human-made structures?
+Absolutely! Natural phenomena, from river bends to the shape of a bird’s wing, often exhibit concave curves. Understanding these natural occurrences adds to our appreciation of the world’s design.
What are some challenges in working with concave structures in architecture?
+Architects face challenges in ensuring structural integrity and stability when designing concave buildings. The inward curvature can introduce complex load-bearing considerations.
How do concave mirrors manipulate light, and what are their applications?
+Concave mirrors converge light rays, making them useful for focusing light in devices like telescopes and lasers. However, they can also create distorted images, which is a consideration in optical systems.



