How to Distinguish Common and Proper Nouns

When it comes to the English language, understanding the difference between common and proper nouns is essential for accurate grammar usage and clear communication. This distinction is crucial for both written and spoken language, as it helps convey meaning and avoid ambiguity. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the nuances of common and proper nouns, providing you with the tools to identify and employ them correctly.
Understanding the Basics: Common and Proper Nouns

Nouns are fundamental parts of speech, serving as the names or labels for people, places, things, and abstract concepts. They form the backbone of our language, providing the building blocks for constructing sentences and expressing ideas. Within the vast realm of nouns, we find two distinct categories: common nouns and proper nouns.
Common Nouns: The Everyday Names
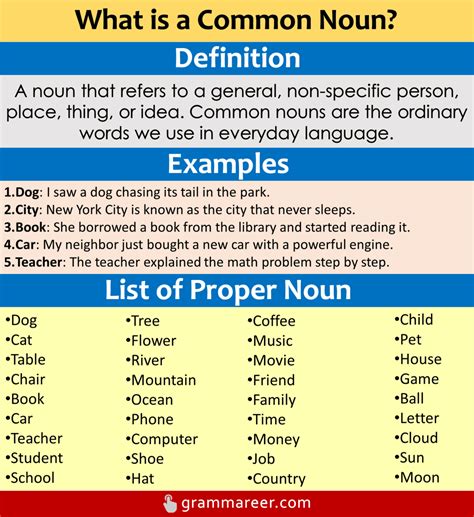
Common nouns are the workhorses of our language, referring to general categories or types of things. They do not represent a specific instance but rather a broader class or group. For example, words like “tree,” “book,” “city,” and “idea” are all common nouns. These nouns can be further classified into countable and uncountable categories, depending on whether they can be counted or not.
Proper Nouns: The Specific Identifiers
In contrast, proper nouns are the nouns that represent specific, unique entities. They are the names given to individual people, places, organizations, or things, setting them apart from the general category. Proper nouns are always capitalized to emphasize their specificity and to distinguish them from common nouns. Some examples of proper nouns include “John,” “Mount Everest,” “Apple Inc.,” and “Tuesday.”
Identifying Common Nouns

Identifying common nouns is a crucial skill for any language user. Here are some key characteristics and strategies to help you recognize them:
General Reference: Common nouns typically refer to a general category or class, rather than a specific instance. For instance, “dog” is a common noun, as it refers to any member of the canine species, not a particular dog.
Countability: Common nouns can be either countable or uncountable. Countable common nouns, like “book” or “chair,” can be used with determiners like “a,” “an,” or “the,” and they can be pluralized. Uncountable common nouns, such as “water” or “happiness,” do not have a plural form and cannot be preceded by determiners like “a” or “an.”
Contextual Clues: Pay attention to the context in which a noun is used. If it is accompanied by descriptive adjectives or used in a general sense, it is likely a common noun. For example, “The beautiful tree stood tall in the garden” indicates that “tree” is a common noun, referring to any tree that is beautiful.
Recognizing Proper Nouns
Proper nouns, with their specific and unique nature, have distinct characteristics that set them apart:
Capitalization: Proper nouns are always capitalized, regardless of their position in a sentence. This capitalization serves as a visual cue, alerting readers to the fact that the word represents a specific entity.
Individuality: Proper nouns represent specific, individual entities. They could be the names of people, places, brands, organizations, or even events. For example, “Microsoft” is a proper noun, referring to the specific technology company, not just any software company.
Cultural and Social Significance: Proper nouns often carry cultural or social significance. They may represent iconic landmarks, historical figures, or well-known brands that have become deeply embedded in our collective consciousness.
Examples and Practice
Let’s dive into some examples to reinforce your understanding:
“The boy kicked the ball.” In this sentence, “boy” and “ball” are common nouns, referring to any boy and any ball.
“Mount Everest is the tallest mountain on Earth.” Here, “Mount Everest” is a proper noun, referring to the specific mountain, while “mountain” is a common noun, representing any mountain.
“The Amazon rainforest is a unique ecosystem.” “Amazon rainforest” is a proper noun, denoting a specific rainforest, while “rainforest” is a common noun, referring to any rainforest.
“I love the way she plays the piano.” In this case, “she” is a common noun, referring to any female person, while “piano” is a common noun representing a musical instrument.
Practical Tips for Distinguishing Nouns
Here are some practical tips to help you distinguish between common and proper nouns:
Ask for Specificity: When in doubt, ask yourself if the noun refers to a specific, unique entity. If it does, it is likely a proper noun. For example, “London” is a proper noun, referring to a specific city, while “city” is a common noun, referring to any city.
Consider Capitalization: Proper nouns are always capitalized, so if you see a noun starting with a capital letter, it is a strong indicator that it is a proper noun.
Look for Contextual Clues: The context in which a noun is used can provide valuable insights. If the noun is accompanied by adjectives or used in a general sense, it is more likely to be a common noun.
Conclusion: The Art of Precision
Distinguishing between common and proper nouns is an essential skill for precise communication. By understanding the characteristics and contexts in which these nouns are used, you can ensure your language usage is accurate and clear. Remember, common nouns refer to general categories, while proper nouns represent specific, unique entities. With practice and awareness, you’ll become adept at identifying and employing these nouns correctly, elevating your language skills to new heights.
Mastering the distinction between common and proper nouns is a powerful tool for effective communication, enabling you to express ideas with precision and clarity.



