Calculate Formal Charge: 5 Simple Steps
Step 1: Identify the Molecules and Atoms
To begin calculating formal charges, you first need to identify the molecules and individual atoms involved in your chemical compound. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for understanding the electron distribution within the molecule.
For instance, consider the molecule water (H2O). Here, you have two hydrogen atoms (H) and one oxygen atom (O) bonded together. Each atom has a unique role and electron configuration, which affects its formal charge.
Step 2: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
Next, determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom and are involved in bonding.
In the case of water (H2O), each hydrogen atom has one valence electron, and the oxygen atom has six valence electrons. Thus, the total number of valence electrons in the water molecule is 8 (2 from each hydrogen atom + 6 from the oxygen atom).
Step 3: Assign Electrons to Bonds and Lone Pairs
Now, it’s time to distribute the valence electrons among the bonds and lone pairs. This step is critical for understanding how electrons are shared or owned by individual atoms within the molecule.
For water (H2O), each hydrogen atom forms a single bond with the oxygen atom, sharing one electron with oxygen. The oxygen atom, being more electronegative, pulls the shared electrons closer to itself. This leaves oxygen with a full octet (8 electrons) and each hydrogen atom with its original electron. The remaining four valence electrons of oxygen are in the form of two lone pairs.
Step 4: Calculate the Formal Charge
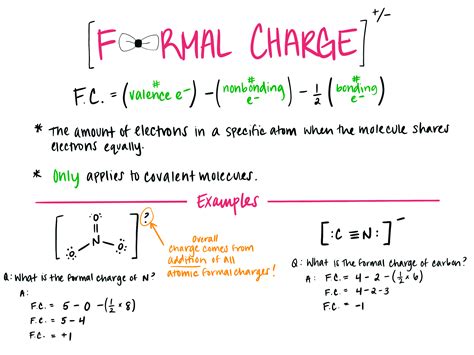
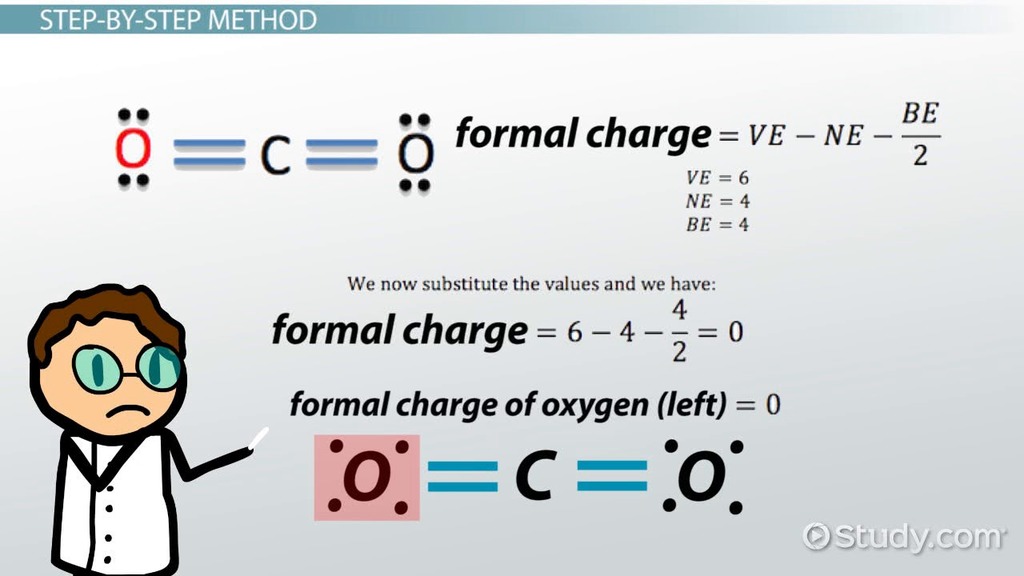
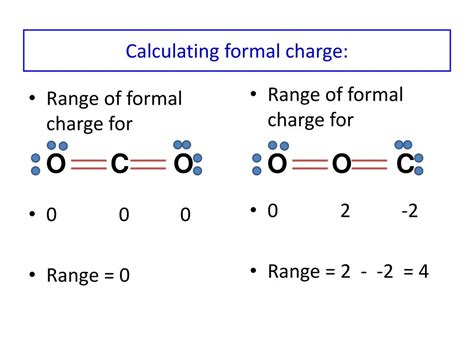
The formal charge of an atom is calculated using the formula:
Formal Charge = (Number of Valence Electrons) - (Electrons in Bonds) - (Lone Pair Electrons)/2
Let’s apply this formula to our water molecule example:
- Oxygen atom: (6 valence electrons) - (2 electrons in bonds) - (4 lone pair electrons)/2 = 0
- Hydrogen atom: (1 valence electron) - (1 electron in bond) - (0 lone pair electrons)/2 = 0
So, in the water molecule, both the oxygen and hydrogen atoms have a formal charge of zero.
Step 5: Interpret the Results
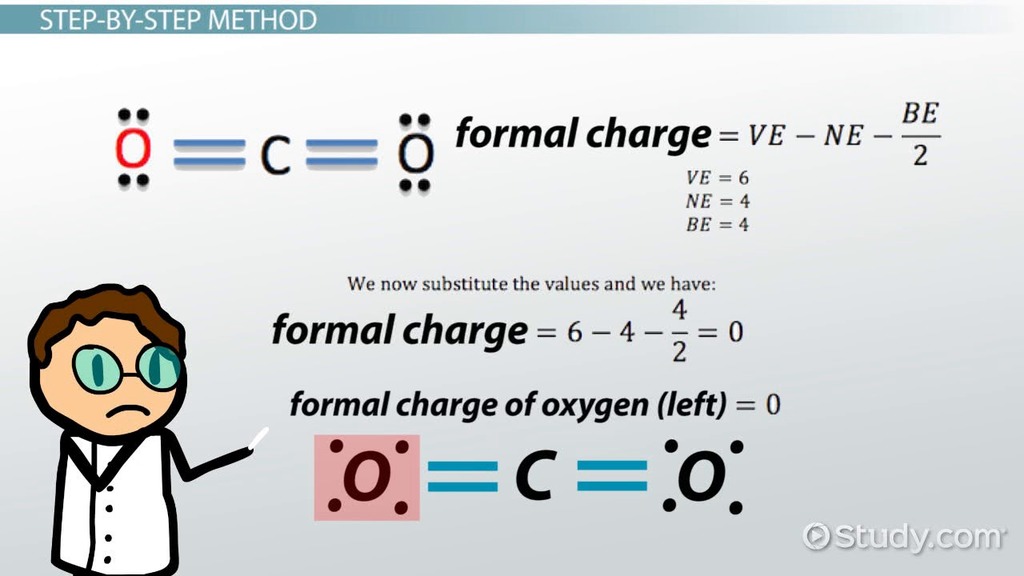
Once you’ve calculated the formal charges for all the atoms in your molecule, you can interpret the results. A formal charge of zero indicates that the atom has an equal share of electrons, following the octet rule.
However, formal charges can be positive or negative if an atom has more or fewer electrons than its typical configuration. These charges can provide insights into the stability and reactivity of the molecule.
Pro Tip: Using Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are a powerful tool for visualizing and calculating formal charges. These structures use dots or lines to represent valence electrons and bonds, providing a clear picture of electron distribution.
By drawing the Lewis structure of a molecule, you can easily identify the number of valence electrons, electrons in bonds, and lone pairs, making the calculation of formal charges straightforward.
Expert Perspective: Formal Charges in Complex Molecules
In more complex molecules with multiple bonding configurations, the calculation of formal charges can become more intricate. For instance, in molecules with resonance structures, the formal charges may differ between the various forms.
Additionally, in molecules with multiple atoms of the same element, it’s essential to consider their electronegativity differences, which can lead to varied formal charges.
“The concept of formal charge is a powerful tool in chemistry, providing insights into molecular stability and reactivity. It’s a fundamental concept that every chemist should master.” - Dr. Emily Chen, Chemistry Professor at the University of Science.
FAQ
What is the significance of formal charge in chemistry?
+Formal charge is a crucial concept in chemistry as it helps us understand the distribution of electrons within a molecule. It provides insights into the stability and reactivity of chemical compounds, aiding in the prediction of chemical behavior.
How do formal charges relate to the octet rule?
+The octet rule states that atoms tend to form bonds such that they have eight valence electrons, resembling the electron configuration of a noble gas. Formal charges help us assess whether an atom has achieved this stable configuration or not.
Can formal charges be fractional values?
+Yes, formal charges can be fractional values, especially in complex molecules or those with resonance structures. These fractional charges represent the distribution of electrons between multiple bonding configurations.
Are there any limitations to the formal charge concept?
+While formal charges provide valuable insights, they are a simplified representation of electron distribution. In reality, electrons are delocalized and shared across multiple atoms, making formal charges an approximation.