5 Signs of Brain Tumors in Dogs
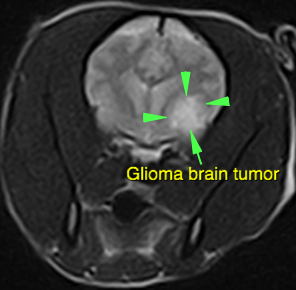
Understanding Brain Tumors in Dogs

Did you know that our furry companions, just like humans, can develop brain tumors? It’s a serious condition that often goes unnoticed until it progresses, but recognizing the early signs can be crucial for your dog’s health. Here, we’ll dive into the world of canine brain tumors, shedding light on the symptoms, potential causes, and the steps you can take to ensure your dog’s well-being.
Brain tumors in dogs are abnormal growths of cells within the brain or its surrounding structures. These tumors can be either primary, originating in the brain, or secondary, spreading to the brain from other parts of the body. While they can affect dogs of any age, certain breeds and older dogs are at a higher risk. Early detection is key, as it can significantly impact the treatment options and prognosis.
So, how can you spot the signs of a brain tumor in your canine friend? Let’s explore the five key indicators that should never be ignored.
1. Changes in Behavior and Personality
One of the earliest signs of a brain tumor in dogs is a noticeable shift in their behavior and personality. Your once-active dog might suddenly become lethargic, showing a lack of interest in their favorite activities. They might also exhibit unusual aggression or fear, even towards familiar people or objects.
Changes in sleep patterns are another red flag. Dogs with brain tumors may sleep more during the day and become restless at night. They might also display increased anxiety or become easily startled.
2. Neurological Symptoms
Brain tumors can affect the dog's nervous system, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. These may include seizures, which can be a frightening experience for both you and your pet. The seizures might be mild at first, but they can progress in frequency and severity over time.
Other neurological signs include head tilting, circling, or difficulty walking in a straight line. You might notice your dog stumbling, experiencing muscle weakness, or even having trouble with basic coordination tasks.
Brain tumors can cause a wide range of neurological symptoms, each depending on the tumor's location and size. It's crucial to seek veterinary advice at the earliest sign of any neurological issue.
3. Vision and Hearing Changes
Brain tumors often affect a dog's sensory functions, leading to noticeable changes in their vision and hearing. You might observe your dog bumping into objects, a sign of vision impairment. They might also seem disoriented or confused, especially in familiar surroundings.
Hearing loss is another potential symptom. Your dog might not respond to familiar sounds or commands, even when they're in the same room. This can be a subtle change, so pay close attention to their reactions and responses.
4. Appetite and Weight Changes
Brain tumors can impact a dog's appetite and metabolism, leading to noticeable changes in their eating habits. Some dogs may experience a sudden decrease in appetite, leading to weight loss. On the other hand, others might show an increased appetite, but still lose weight due to the tumor's metabolic effects.
It's important to monitor your dog's weight and any changes in their eating patterns. Significant and unexplained weight loss or gain should never be ignored.
While these symptoms can indicate a brain tumor, they can also be associated with other health issues. It's crucial to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and to rule out other potential causes.
5. Head and Facial Changes
Brain tumors can sometimes lead to physical changes in a dog's head and facial features. You might notice swelling or a visible mass on their head, especially if the tumor is located near the surface.
Additionally, changes in facial symmetry are common. For instance, one side of your dog's face might appear droopy or their eyes might be misaligned. These changes can be subtle, so close observation is key.
Other possible signs include a discharge from the eyes or nose, as well as changes in the position or movement of the eyes.
Early detection is critical for successful treatment. Don't hesitate to seek veterinary care if you notice any unusual changes in your dog's behavior, appearance, or health.
Treatment Options and Prognosis
The treatment for brain tumors in dogs depends on various factors, including the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the dog. Common treatment approaches include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In some cases, a combination of these treatments might be recommended.
The prognosis for dogs with brain tumors can vary greatly. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome. However, the survival rates and life expectancy depend on several factors, and it’s important to consult with a veterinary specialist for an accurate prognosis and treatment plan tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
FAQ
What are the most common types of brain tumors in dogs?
+The most common types of brain tumors in dogs include meningiomas, gliomas, and pituitary tumors. Meningiomas are typically benign and grow slowly, while gliomas are often more aggressive. Pituitary tumors can affect hormone production.
Can brain tumors in dogs be cured?
+The curability of brain tumors in dogs depends on various factors, including the type and location of the tumor. While some tumors can be completely removed through surgery, others might require a combination of treatments. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
What are the long-term effects of brain tumors on dogs?
+The long-term effects of brain tumors in dogs can vary. Some dogs might experience permanent neurological deficits, while others might have a full recovery. Ongoing veterinary care and monitoring are crucial to manage any potential complications and ensure the best quality of life.
Are certain dog breeds more prone to brain tumors?
+Yes, certain dog breeds are more predisposed to developing brain tumors. For instance, Boxers, Boston Terriers, and Golden Retrievers are among the breeds with a higher risk. However, any dog can develop a brain tumor, and regular veterinary check-ups are important for early detection.
How can I support my dog during and after brain tumor treatment?
+Providing a supportive and stress-free environment is crucial during and after brain tumor treatment. This includes ensuring a comfortable living space, offering a balanced diet, and providing regular opportunities for gentle exercise. Your veterinarian can guide you on specific care instructions tailored to your dog's needs.
Remember, early detection and prompt veterinary care are essential for managing brain tumors in dogs. By staying vigilant and aware of these signs, you can ensure your furry friend receives the best possible care and support.