The Ultimate Guide: 2024 Bloom's Taxonomy Verbs
Unlocking the Power of Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs

In the realm of education, one tool has stood the test of time, offering a systematic approach to understanding and designing effective learning experiences. Bloom’s Taxonomy, a hierarchical framework, has been a cornerstone for educators, guiding them in creating engaging and impactful lessons. At the heart of this taxonomy are the verbs—powerful tools that define the actions and processes learners engage in during their educational journey.
As we step into 2024, it’s time to delve into an updated and comprehensive guide to Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs, exploring their role, application, and the transformative impact they can have on modern education. This guide aims to empower educators, providing them with the linguistic toolkit needed to craft extraordinary learning experiences.
The Historical Evolution of Bloom’s Taxonomy
To truly grasp the significance of Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs, we must first journey back to the origins of this influential framework. In the 1950s, a group of educational psychologists, led by Benjamin Bloom, set out to classify the different levels of intellectual behavior. Their work resulted in a hierarchical model, known as Bloom’s Taxonomy, which categorized cognitive objectives into six levels: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
Over the years, Bloom’s Taxonomy has undergone revisions and updates, keeping pace with the evolving landscape of education. In 2001, a group of cognitive psychologists, led by Lorin Anderson, introduced a revised version, which introduced a slightly different order of the cognitive processes and replaced the verb “synthesize” with “create.”
The Significance of Verbs in Bloom’s Taxonomy
Verbs are the active elements in Bloom’s Taxonomy, representing the actions and processes learners engage in as they progress through the levels of the taxonomy. These verbs provide a clear and actionable framework for educators, allowing them to design lessons and assessments that align with specific cognitive objectives.
For instance, at the lower levels of the taxonomy, verbs like “identify,” “describe,” and “define” focus on recalling and understanding basic information. As learners progress, verbs like “analyze,” “evaluate,” and “create” encourage higher-order thinking skills, fostering critical analysis, problem-solving, and creativity.
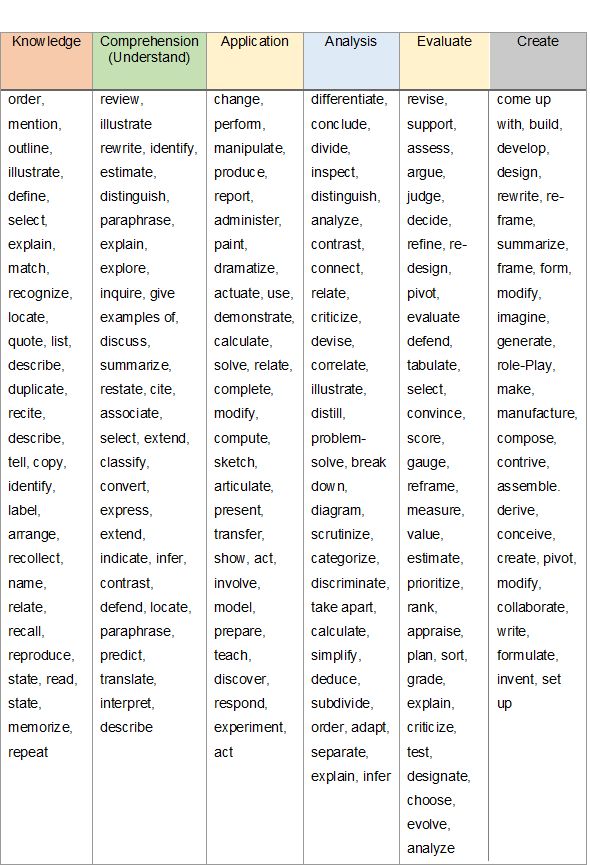
Exploring the 2024 Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs
As we embark on the year 2024, it’s essential to familiarize ourselves with the updated verbs that define the levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown:
Knowledge Level:
- Recognize: Learners identify and recall specific facts, terms, concepts, or principles.
- Recall: Retrieving information from memory, such as definitions, dates, or key concepts.
Comprehension Level:
- Explain: Providing a clear and concise account of a concept or process, demonstrating understanding.
- Paraphrase: Restating information in one’s own words, showing comprehension.
- Restate: Rewriting or summarizing key points, demonstrating understanding of the main idea.
Application Level:
- Apply: Using acquired knowledge in new situations or problems, demonstrating practical understanding.
- Implement: Putting theories, principles, or methods into practice.
- Demonstrate: Showing how to use a skill or concept in a real-world context.
Analysis Level:
- Analyze: Breaking down information into parts to understand the relationships between the parts and the whole.
- Categorize: Grouping information based on shared characteristics or properties.
- Evaluate Criteria: Judging the value or importance of information based on established criteria.
Synthesis Level:
- Create: Generating new ideas, products, or solutions by combining existing elements in novel ways.
- Design: Developing plans or proposals for new systems, structures, or processes.
- Innovate: Introducing new ideas, methods, or products that challenge existing norms.
Evaluation Level:
- Judge: Making informed decisions or judgments based on criteria and evidence.
- Critique: Providing a detailed analysis and evaluation of a work, idea, or concept.
- Recommend: Providing suggestions or proposals based on informed judgment and evaluation.
Practical Application: Integrating Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs in Education
So, how can educators leverage Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs to create engaging and impactful learning experiences? Here are some practical strategies:
Lesson Planning:
- Begin by identifying the desired learning outcome and the level of Bloom’s Taxonomy it aligns with.
- Select verbs that accurately reflect the actions learners will engage in to achieve that outcome.
- Design activities, assignments, and assessments that require learners to demonstrate their understanding through these verbs.
Assessment Design:
- Use Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs to create a balanced assessment plan that covers various cognitive levels.
- Create rubrics or scoring guides that align with the chosen verbs, providing clear expectations for learners.
- Encourage learners to self-assess and reflect on their performance, fostering metacognitive skills.
Differentiated Instruction:
- Recognize that learners may have different starting points and progress at varying rates.
- Offer a range of tasks or activities that cater to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy, allowing learners to work at their own pace.
- Provide opportunities for learners to move up the taxonomy levels as they demonstrate mastery.
Future Trends and Implications
As we look ahead, it’s evident that Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping educational practices. With the increasing focus on 21st-century skills, such as critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving, educators will leverage these verbs to foster these essential skills.
Moreover, the integration of technology in education opens up new possibilities. Educators can utilize digital tools to create interactive and engaging learning experiences, aligning with the verbs of Bloom’s Taxonomy. From virtual simulations to collaborative online platforms, the potential for innovation is vast.
Conclusion: Empowering Educators, Transforming Learning
In a rapidly changing educational landscape, Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs provide a timeless and versatile framework. By understanding and effectively applying these verbs, educators can design lessons that engage learners, challenge their thinking, and foster a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
As we move forward into 2024, let us embrace the power of Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs, unlocking the full potential of learning and empowering our students to become critical thinkers, problem solvers, and creative innovators.
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy, and why is it important in education?
+Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical framework that categorizes cognitive objectives into six levels: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation. It provides educators with a structured approach to designing lessons and assessments, ensuring a balanced focus on various cognitive skills. By understanding Bloom’s Taxonomy, educators can create engaging and effective learning experiences, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity.
How can educators effectively integrate Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs into their teaching practice?
+Educators can start by identifying the desired learning outcome and selecting verbs that align with the corresponding level of Bloom’s Taxonomy. They can then design activities, assignments, and assessments that require learners to demonstrate their understanding through these verbs. Additionally, creating rubrics or scoring guides based on the chosen verbs can provide clear expectations for learners, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Are there any resources available to help educators implement Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs in their lessons?
+Absolutely! There are numerous resources available online, including verb lists, lesson planning guides, and assessment templates. These resources can help educators navigate the complexities of Bloom’s Taxonomy and provide practical strategies for integrating verbs into their teaching practice. Additionally, professional development workshops and online communities can offer further support and guidance.
How can Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs be used to foster 21st-century skills, such as critical thinking and creativity?
+Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs, particularly those at the higher levels (Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation), are particularly effective in fostering critical thinking and creativity. By encouraging learners to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information, educators can challenge their thinking, promote problem-solving skills, and nurture creative thinking. Additionally, providing opportunities for open-ended exploration and project-based learning can further enhance the development of these essential 21st-century skills.
What role does technology play in implementing Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs in the classroom?
+Technology can be a powerful tool in implementing Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs, providing opportunities for interactive and engaging learning experiences. Educators can utilize digital platforms, simulations, and collaborative tools to create activities and assessments that align with the chosen verbs. Additionally, technology can facilitate differentiated instruction, allowing learners to work at their own pace and providing personalized learning experiences.



