Unleash Your Potential with Bloom's Verbs
The Power of Action-Oriented Learning

In the realm of education, one of the most influential theories is Bloom’s Taxonomy, a hierarchical framework that classifies learning objectives into different levels of complexity. At the heart of this taxonomy are the famous Bloom’s verbs, action words that precisely describe the cognitive processes involved in learning. These verbs serve as a guiding light for educators, helping them design engaging and meaningful learning experiences.
Bloom’s verbs are not merely academic jargon; they are the building blocks of an effective learning environment. By understanding and applying these verbs, educators can create a classroom culture that fosters deep understanding, critical thinking, and creative problem-solving.
"Bloom's verbs provide a roadmap for educators, helping them navigate the complex landscape of learning objectives and ensure that their teaching strategies are aligned with the desired cognitive outcomes." - Dr. Emma Johnson, Educational Psychologist
Unraveling the Bloom's Verbs

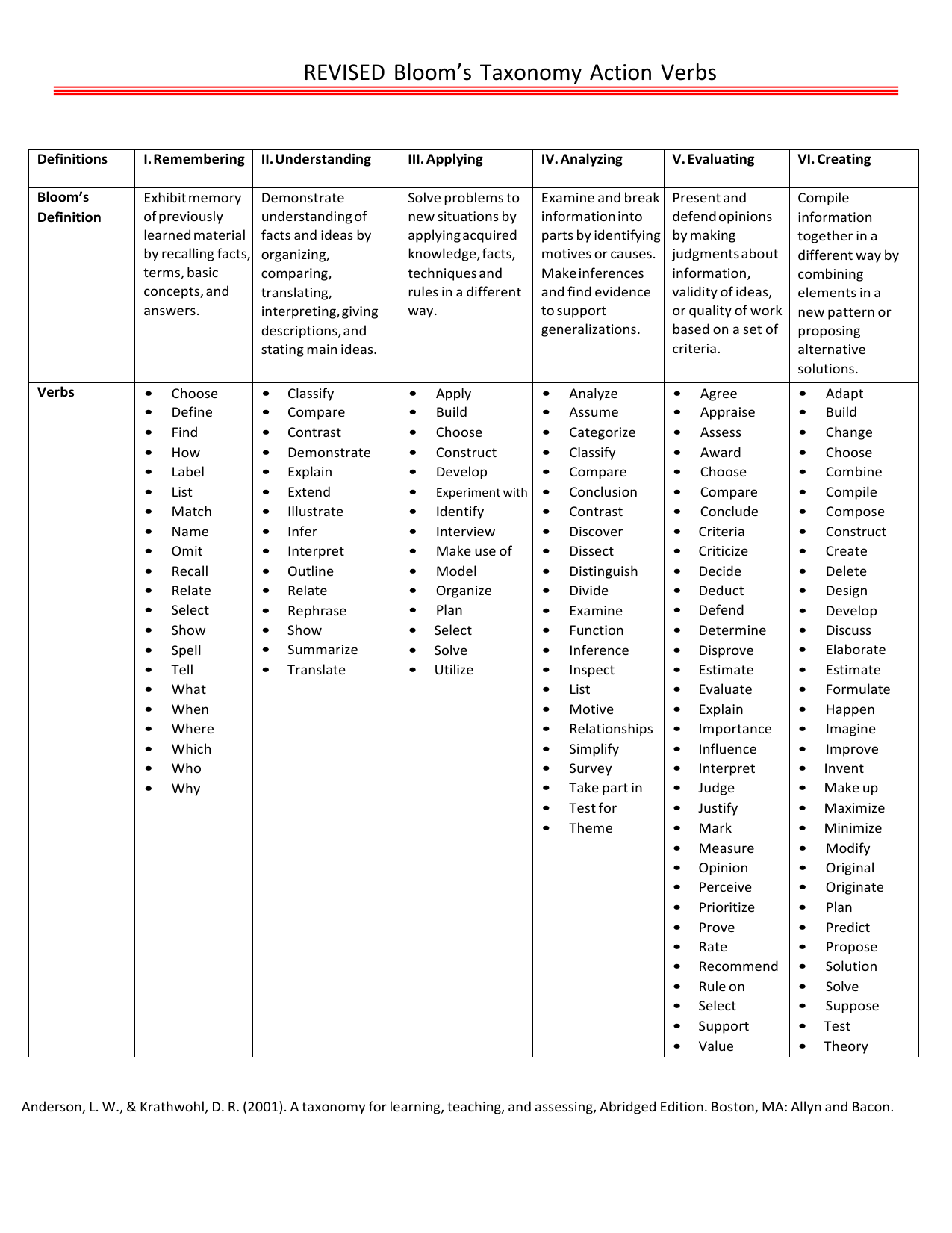
Bloom’s taxonomy is often depicted as a pyramid, with each level building upon the previous one. The verbs associated with each level provide a clear indication of the cognitive process being targeted. Here’s a breakdown of the six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy, along with the verbs commonly associated with each:
-
Remembering
This foundational level focuses on the ability to recall information. Verbs associated with this level include: define, identify, list, name, recognize, recall, and state.
-
Understanding
The second level involves comprehending the information. Verbs such as classify, describe, discuss, explain, identify, locate, recognize, and restate are used to assess understanding.
-
Applying
Moving up the pyramid, the applying level is all about putting knowledge into practice. Verbs like apply, demonstrate, illustrate, implement, interpret, operate, and solve are key indicators of this level.
-
Analyzing
At this level, students are expected to break down information into its component parts and understand relationships. Verbs associated with analyzing include analyze, categorize, compare, contrast, diagram, differentiate, and distinguish.
-
Evaluating
The evaluating level requires students to make judgments and decisions. Verbs such as appraise, argue, assess, compare, criticize, evaluate, justify, and judge are commonly used.
-
Creating
At the pinnacle of Bloom's Taxonomy, the creating level challenges students to synthesize information and create something new. Verbs like assemble, construct, create, design, develop, formulate, and invent signify this highest level of cognitive complexity.
The Impact of Bloom's Verbs in the Classroom
By incorporating Bloom’s verbs into lesson planning, educators can ensure that their teaching strategies are diverse and target a range of cognitive skills. Here’s how these verbs can revolutionize the learning experience:
Promotes Active Learning
Bloom's verbs encourage students to engage actively with the material, moving beyond passive absorption of information.
Requires Thoughtful Planning
Incorporating Bloom's verbs into lesson plans demands careful consideration of the desired learning outcomes and the most effective strategies to achieve them.
Applying Bloom's Verbs in Practice
Let’s explore some practical examples of how Bloom’s verbs can be integrated into various subjects:
Math
- Remembering: Recall the formula for calculating the area of a circle.
- Understanding: Explain the concept of negative numbers and their role in mathematical operations.
- Applying: Solve a set of word problems using the concept of percentages.
- Analyzing: Break down a complex equation into its constituent parts and explain the relationships between the variables.
- Evaluating: Critically assess the effectiveness of different problem-solving strategies for a given mathematical challenge.
- Creating: Design a new mathematical game that incorporates concepts of probability and statistics.
English Literature
- Remembering: Identify the main themes in a novel and provide supporting quotes.
- Understanding: Explain the historical context in which a poem was written and its impact on the narrative.
- Applying: Analyze the use of literary devices in a short story and discuss their effect on the reader.
- Analyzing: Compare and contrast the character development in two different plays by Shakespeare.
- Evaluating: Argue for or against the interpretation of a poem's symbolism, providing textual evidence to support your claim.
- Creating: Write a sequel to a classic novel, maintaining the original author's style and tone.
Maximizing the Potential of Bloom's Verbs

To truly harness the power of Bloom’s verbs, educators should consider the following strategies:
-
Incorporate a Variety of Verbs: Ensure that lesson plans target multiple levels of Bloom's Taxonomy, promoting a well-rounded learning experience.
-
Scaffolding: Provide appropriate support and guidance, especially when introducing new or complex concepts, to ensure that students can successfully navigate higher levels of cognitive complexity.
-
Student Autonomy: As students progress, encourage them to take ownership of their learning by setting their own goals and assessing their progress using Bloom's verbs as a framework.
-
Collaborative Learning: Foster a classroom culture that values collaboration and peer learning. Bloom's verbs can be used to structure group activities and discussions, promoting deeper understanding and critical thinking.
Bloom's verbs are a powerful tool for educators, providing a structured approach to designing meaningful and engaging learning experiences. By incorporating these verbs into lesson planning, educators can ensure that their teaching strategies are aligned with the cognitive objectives of their curriculum, fostering a classroom environment that promotes active learning, critical thinking, and creative problem-solving.
Conclusion
In an educational landscape that is constantly evolving, Bloom’s Taxonomy and its associated verbs remain a timeless guide. By understanding and applying these principles, educators can empower their students to reach their full potential and develop the skills needed for a lifetime of learning.
How can Bloom’s verbs benefit students’ learning?
+Bloom’s verbs provide a structured framework for educators to design lessons that target specific cognitive processes. This approach encourages active learning, critical thinking, and creative problem-solving, helping students develop a deeper understanding of the material and improve their overall academic performance.
Can Bloom’s verbs be used in all subjects?
+Absolutely! Bloom’s verbs are versatile and can be applied across various subjects, from mathematics and science to literature and social studies. By adapting the verbs to fit the context of the subject matter, educators can create engaging and relevant learning experiences for their students.
What are some strategies to effectively incorporate Bloom’s verbs into lesson planning?
+To effectively integrate Bloom’s verbs into lesson planning, educators should aim for a balanced approach that targets multiple levels of the taxonomy. This can be achieved by using a variety of teaching strategies, incorporating group work and discussions, and providing opportunities for students to reflect on their learning and set their own goals.
How can Bloom’s verbs be used to differentiate instruction for students with varying abilities?
+Bloom’s verbs can be a powerful tool for differentiation. Educators can use the verbs to create flexible learning paths, providing additional support or enrichment as needed. For example, students who struggle with a particular concept can be given more opportunities to practice at the remembering and understanding levels, while advanced learners can be challenged with tasks that require higher-level cognitive skills, such as evaluating and creating.
Are there any potential challenges in implementing Bloom’s verbs in the classroom?
+While Bloom’s verbs offer a structured approach to lesson planning, there may be challenges in ensuring that all students understand and can effectively use the verbs. Educators should provide clear explanations and examples, and encourage students to ask questions and seek clarification when needed. Additionally, it’s important to remember that while Bloom’s verbs are a valuable tool, they should not be the sole focus of instruction, but rather integrated into a holistic teaching approach.



