Excel's BETWEEN Function Made Easy
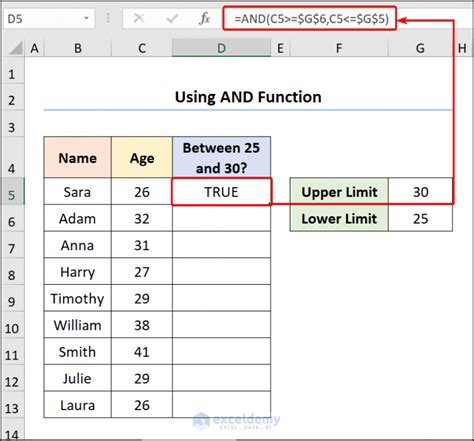
Excel's BETWEEN function, or more accurately the BETWEEN operator, is a powerful tool that allows users to perform complex conditional formatting and data analysis. This function is especially useful for identifying values that fall within a specified range, making it a valuable asset for various data-related tasks. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the BETWEEN function, exploring its syntax, real-world applications, and providing practical examples to enhance your understanding.
Understanding the BETWEEN Function

The BETWEEN function in Excel is not a standalone function but rather a conditional operator that compares a value against a specified range. It returns a logical value (TRUE or FALSE) based on whether the value being tested falls within the defined range. This function is particularly useful when you need to identify data points that satisfy specific criteria, making it an essential tool for data filtering and analysis.
Syntax and Usage
The syntax for the BETWEEN function is straightforward: =BETWEEN(value, range_start, range_end). Here’s a breakdown of the parameters:
- value: This is the value you want to test. It can be a cell reference, a formula result, or a literal value.
- range_start: The lower limit of the range. This can be a cell reference or a literal value.
- range_end: The upper limit of the range. Similar to range_start, it can be a cell reference or a literal value.
For example, if you want to check if the value in cell A1 is between 10 and 20, you would use the formula: =BETWEEN(A1, 10, 20). If the value in A1 is indeed between 10 and 20, the function will return TRUE; otherwise, it will return FALSE.
Real-World Applications
The BETWEEN function has numerous applications across various industries and data-related tasks. Here are a few practical examples:
- Financial Analysis: In finance, you can use the BETWEEN function to identify investments or transactions that fall within a specific price range or time frame.
- Sales and Marketing: This function is invaluable for segmenting customers based on their spending patterns or demographics. For instance, you can identify customers who have made purchases between certain dates or within a specific price range.
- Inventory Management: The BETWEEN function can help manage inventory by identifying items that need to be restocked or have exceeded their shelf life.
- Quality Control: In manufacturing, you can use this function to flag products that meet specific quality standards or fall within acceptable tolerance ranges.
- Data Visualization: When creating charts or graphs, the BETWEEN function can be used to highlight data points that fall within a particular range, making it easier to visualize and interpret data.
Practical Examples and Walkthroughs

Let’s explore some real-world scenarios and practical examples to deepen your understanding of the BETWEEN function.
Example 1: Financial Data Analysis
Imagine you have a dataset of stock prices, and you want to identify stocks that have experienced a price increase of 10% to 20% over the past year. You can use the BETWEEN function to achieve this. Here’s how:
- Create a new column in your dataset and label it “Price Increase.”
- In the first cell of this column, enter the formula: =BETWEEN(B2, 10%, 20%), where B2 represents the cell containing the stock’s current price.
- Drag the formula down to apply it to the entire dataset.
- The formula will return TRUE for stocks that meet the criteria and FALSE for those that don’t.
- You can then use this column to filter or analyze stocks that fall within the desired price increase range.
Example 2: Customer Segmentation
Suppose you manage a retail store, and you want to segment your customers based on their purchase amounts. You can use the BETWEEN function to identify customers who have spent between 50 and 100 in a single transaction.
- Create a new column in your customer dataset called “Purchase Amount.”
- In the first cell, enter the formula: =BETWEEN(C2, 50, 100), where C2 represents the cell containing the customer’s purchase amount.
- Drag the formula down to apply it to all customers.
- The formula will return TRUE for customers who meet the criteria, indicating they are in the desired spending range.
- You can now use this column to analyze and target these customers with specific marketing campaigns or loyalty programs.
Example 3: Quality Assurance
In a manufacturing setting, you might have a dataset of product measurements, and you want to identify products that meet your quality standards. You can use the BETWEEN function to achieve this. Let’s assume your quality standard requires products to have a measurement between 9.5 and 10.5.
- Create a new column in your dataset called “Quality Check.”
- In the first cell, enter the formula: =BETWEEN(D2, 9.5, 10.5), where D2 represents the cell containing the product’s measurement.
- Drag the formula down to apply it to all products.
- The formula will return TRUE for products that meet your quality standards.
- You can then use this column to quickly identify products that need further inspection or to make informed decisions about production processes.
Advanced Techniques and Tips
The BETWEEN function is a versatile tool, and by combining it with other Excel functions and techniques, you can unlock even more powerful capabilities.
Combining with Other Functions
You can use the BETWEEN function in conjunction with other Excel functions to create more complex conditional statements. For example, you can combine it with the IF function to perform different actions based on whether a value is within a specific range. Here’s an example:
=IF(BETWEEN(A2, 10, 20), “Within Range”, “Outside Range”)
In this formula, if the value in cell A2 is between 10 and 20, the cell will display “Within Range”; otherwise, it will display “Outside Range.”
Using Named Ranges
Excel allows you to create named ranges, which can make your formulas more readable and easier to manage. For instance, you can name a range of cells as “PriceRange” and then use it in your BETWEEN function like this: =BETWEEN(A2, PriceRange).
Data Filtering and Sorting
The BETWEEN function is an excellent tool for filtering and sorting data. You can use it with Excel’s built-in filtering and sorting features to quickly isolate and analyze data points that fall within specific ranges.
Error Handling
It’s essential to handle errors gracefully when using functions like BETWEEN. Excel’s ISERROR function can help you manage errors and prevent unexpected results. For example, you can use the formula: =IF(ISERROR(BETWEEN(A2, 10, 20)), “N/A”, BETWEEN(A2, 10, 20)) to display “N/A” if the BETWEEN function encounters an error.
Conclusion
The BETWEEN function in Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis and conditional formatting. By understanding its syntax and real-world applications, you can unlock a wide range of capabilities, from financial analysis to customer segmentation and quality assurance. Combine it with other Excel functions and techniques to create even more sophisticated data solutions. With practice and creativity, you’ll master this function and become an Excel power user.
Can I use the BETWEEN function with dates and times?
+Yes, the BETWEEN function works with dates and times. You can use it to identify dates or times that fall within a specified range. Just ensure that your date or time values are formatted correctly in Excel.
How can I use the BETWEEN function for dynamic ranges?
+You can use Excel’s OFFSET function to create dynamic ranges. For example, if you want to find values between two cells (e.g., A1 and B1), you can use the formula: =BETWEEN(value, OFFSET(A1, 0, 0), OFFSET(B1, 0, 0)). This allows the range to change based on the values in A1 and B1.
Is there a way to count the number of values within a specific range using the BETWEEN function?
+Yes, you can use the COUNTIF function along with the BETWEEN function to count the number of values within a specified range. For example, =COUNTIF(range, BETWEEN(range, range_start, range_end)) will count the number of values in the specified range that meet the criteria.