5 Creative Ways to Learn with Base 10 Blocks
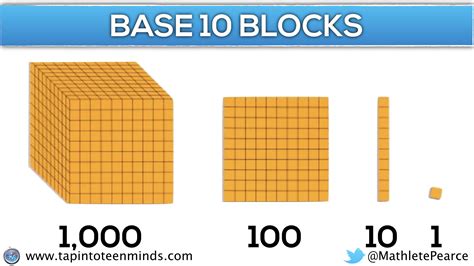
Base 10 blocks are a versatile and engaging tool for teaching mathematical concepts, especially in early education. These manipulatives offer a tactile and visual approach to understanding numbers, place value, and operations. Here are some innovative ways to incorporate base 10 blocks into your learning environment, ensuring an enjoyable and effective educational experience.
1. Building Block Stories
Storytelling is a powerful tool for engaging young minds, and when combined with base 10 blocks, it becomes a fun and educational activity. Create narratives that involve characters or scenarios where the blocks represent different quantities. For instance, imagine a story about a hungry caterpillar who loves eating apples. Each apple could be represented by a unit block, while a tens rod could symbolize a delicious apple pie. As the caterpillar eats more apples, children can physically add blocks to the caterpillar’s ‘food pile,’ helping them grasp the concept of addition and number sense.
2. Block Art with a Math Twist
Art and math can be beautifully intertwined using base 10 blocks. Encourage children to create unique patterns and designs using the blocks. This activity not only fosters creativity but also reinforces an understanding of symmetry, pattern recognition, and spatial reasoning. Moreover, by assigning specific values to each type of block, students can explore multiplication and division in a visual and hands-on way. For example, a flat of 100 blocks could represent a ‘hundreds’ square, and students can manipulate these to understand the multiplication of larger numbers.
3. Base 10 Block Games
Turning learning into a game is an effective way to keep students engaged. Design simple games that utilize base 10 blocks. For example, create a ‘Place Value Race’ game where students roll a die to determine which place value position to fill with a block. The first student to complete a number with the correct place value wins. Alternatively, a ‘Base 10 Bingo’ game could be played, where students mark off blocks on their bingo cards as they are called out, encouraging recognition of numbers and their representation with base 10 blocks.
4. Block-based Fraction Fun
Understanding fractions can be challenging for many students, but with base 10 blocks, this concept can become more tangible. Divide the unit blocks into halves, thirds, or quarters to visually represent different fractions. Students can then build and compare fractions, seeing firsthand how fractions relate to whole numbers. This tactile approach can make abstract concepts more understandable and memorable.
5. Real-world Connections
Base 10 blocks can be used to make connections between mathematical concepts and real-world scenarios. For instance, students can use the blocks to represent quantities of items they use daily, like pencils or erasers. This helps them relate abstract numbers to concrete objects, fostering a deeper understanding of quantity and measurement. Additionally, these blocks can be used to model and solve word problems, bringing mathematical operations to life.
"Base 10 blocks offer a tactile, kinesthetic approach to learning that engages multiple senses. This multi-modal learning can enhance comprehension and retention, making math more accessible and enjoyable for all learners."
- Dr. Sarah Thompson, Educational Psychologist
Conclusion
Base 10 blocks provide a wealth of opportunities for creative and effective learning. By integrating these blocks into various activities, educators can make math education fun, engaging, and tailored to different learning styles. These manipulatives not only help students grasp fundamental mathematical concepts but also foster a positive attitude towards learning, which is crucial for their overall academic development.
Can base 10 blocks be used for teaching older students or more advanced mathematical concepts?
+Absolutely! While base 10 blocks are commonly used in early education, they can be adapted for older students and more complex concepts. For instance, they can be used to visualize algebraic expressions, model decimal operations, or even demonstrate the concepts of exponents and scientific notation. The versatility of these blocks makes them a valuable tool throughout various stages of mathematical education.
Are there any specific benefits of using physical manipulatives like base 10 blocks over digital tools for learning math?
+Physical manipulatives like base 10 blocks offer a tangible, hands-on learning experience that can be especially beneficial for kinesthetic learners. They provide a concrete representation of abstract concepts, helping students to ‘see’ and ‘feel’ mathematical ideas. Digital tools, while also valuable, often rely more on visual and auditory learning styles. Combining both physical and digital resources can offer a well-rounded approach to math education.
How can I ensure that students don’t become overly reliant on base 10 blocks for problem-solving?
+It’s important to gradually transition students from using physical manipulatives to solving problems mentally or on paper. Start by having them explain their thinking process when using the blocks and then encourage them to apply that same process without the blocks. Gradually increase the difficulty of problems to challenge their understanding and ensure they’re not simply relying on the visual aids.



