Mastering Excel: Average with Multiple Criteria
Excel, the powerful spreadsheet software, offers an array of functions and tools to enhance data analysis and manipulation. Among these, the AVERAGE function stands out as a fundamental tool for calculating the average value of a dataset. However, what if you need to calculate the average based on specific criteria or conditions? This is where the art of mastering Excel's AVERAGE function with multiple criteria comes into play, opening up a world of possibilities for advanced data analysis.
Understanding the Need for Average with Multiple Criteria

In the realm of data analysis, often we encounter situations where a simple average isn’t sufficient. Consider a scenario where you manage a sales team, and you want to calculate the average sales for a specific product across different regions, while also considering various sales channels. In such a case, a straightforward AVERAGE function won’t provide the desired result. This is where the power of criteria-based averaging comes into play, allowing you to slice and dice your data to extract meaningful insights.
Imagine you have a sales dataset with columns for product, region, channel, and sales amount. To calculate the average sales for a specific product, say "Widget A," across all regions and channels, you'd need to apply multiple criteria. This is where the AVERAGE function, coupled with other functions like SUMIFS or SUMPRODUCT, becomes a powerhouse for data manipulation.
The Art of Average with Multiple Criteria

Mastering the AVERAGE function with multiple criteria involves a combination of Excel functions and logical thinking. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this powerful feature:
Step 1: Identify Your Criteria
The first step in calculating the average with multiple criteria is to clearly define your criteria. In our sales example, the criteria could be the product name, region, and sales channel. These criteria will determine the scope of your average calculation.
Step 2: Choose the Right Function
Excel offers several functions that can handle multiple criteria. The most common ones are SUMIFS and SUMPRODUCT. These functions allow you to specify multiple conditions and then perform a calculation on the values that meet all the conditions. In our case, we’ll use SUMIFS to calculate the sum of sales that meet our criteria, and then we’ll divide it by the count of those values to get the average.
Step 3: Construct the Formula
The formula for calculating the average with multiple criteria using SUMIFS can be structured as follows:
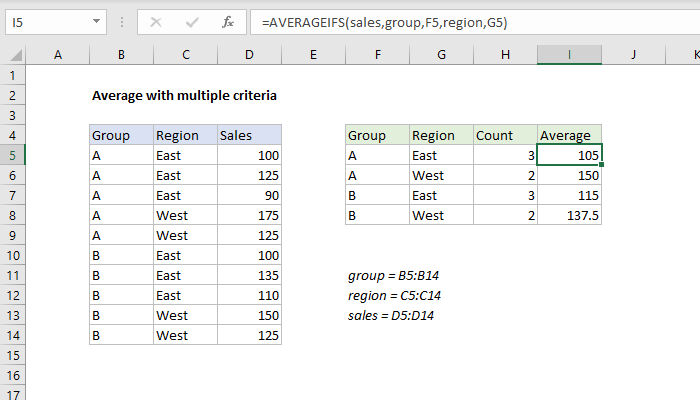
Average with Multiple Criteria Formula: =SUMIFS(sales_range, product_range, "Widget A", region_range, region_name, channel_range, channel_name) / COUNTIFS(product_range, "Widget A", region_range, region_name, channel_range, channel_name)
In this formula:
- sales_range refers to the range of cells containing the sales amounts.
- product_range is the range of cells containing the product names.
- region_range is the range of cells containing the region names.
- channel_range is the range of cells containing the channel names.
- "Widget A" is the specific product for which we want to calculate the average.
- region_name and channel_name are the specific region and channel, respectively.
The SUMIFS function sums up the sales amounts that meet all the specified criteria, while the COUNTIFS function counts the number of cells that meet those same criteria. By dividing the sum by the count, we get the average sales for "Widget A" in the specified region and channel.
Step 4: Apply the Formula
Once you’ve constructed the formula, you can apply it to your Excel sheet. Simply enter the formula into the cell where you want the average to appear, and Excel will do the rest. You can then drag the formula down or across to calculate averages for other products, regions, or channels, as needed.
Step 5: Visualize Your Data
To further enhance your analysis, consider creating charts or graphs to visualize the average sales data. Excel offers a wide range of chart types, from basic column charts to more advanced bubble charts or pivot charts. Visual representations of your data can help you identify trends, patterns, and outliers more easily.
Advanced Techniques and Tips
Mastering Excel’s AVERAGE function with multiple criteria opens up a world of possibilities for advanced data analysis. Here are some additional techniques and tips to enhance your skills:
Utilize Named Ranges
Excel allows you to assign names to cell ranges, making your formulas more readable and easier to manage. Instead of referring to specific cell ranges in your formula, you can use named ranges like “SalesAmount,” “ProductNames,” etc. This improves the clarity and maintainability of your formulas.
Combine with Other Functions
The power of Excel lies in its ability to combine multiple functions to achieve complex calculations. For example, you can use the AVERAGE function with multiple criteria in conjunction with other functions like VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, or even more advanced functions like XLOOKUP or SUMIF with arrays. These combinations can help you tackle even more complex data analysis tasks.
Handle Errors Gracefully
When working with complex formulas, it’s common to encounter errors like #DIV/0! or #N/A. Excel provides error-handling functions like IFERROR or ISERROR to gracefully manage these situations. You can use these functions to display custom messages or alternative calculations when errors occur.
Optimize Performance
Large datasets or complex formulas can impact Excel’s performance. To optimize performance, consider using Excel’s Table feature, which automatically expands formulas as you add or remove rows. Additionally, you can use the Table’s filtering and sorting capabilities to quickly analyze your data.
Explore Advanced Functions
Excel offers a vast array of advanced functions that can further enhance your data analysis capabilities. Functions like AVERAGEIFS, AVERAGEA, AVERAGEIF, and AVERAGEPIVOT can provide more flexible and powerful ways to calculate averages based on specific criteria.
Real-World Application
The art of mastering Excel’s AVERAGE function with multiple criteria has wide-ranging applications across industries. Here’s a real-world example from the field of finance:
A financial analyst working for a large investment bank needs to analyze the performance of various investment portfolios. Each portfolio contains a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets, and the analyst wants to calculate the average return on investment (ROI) for each portfolio while considering specific criteria such as asset class, geographic region, and investment strategy.
By utilizing Excel's AVERAGE function with multiple criteria, the analyst can efficiently calculate the average ROI for each portfolio, allowing for a detailed analysis of performance. This data can then be used to make informed investment decisions, allocate resources effectively, and identify areas for improvement.
In this example, the AVERAGE function with multiple criteria empowers the analyst to slice and dice the data, gaining valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making. It showcases how mastering this Excel feature can have a real impact on business outcomes.
Future Implications and Trends

As data analysis continues to evolve, Excel remains at the forefront of spreadsheet software, constantly introducing new features and improvements. Here are some future implications and trends related to Excel’s AVERAGE function with multiple criteria:
Powerful Visualizations
Excel’s visualization capabilities are continuously improving. With each new version, Excel introduces more advanced chart types and interactive features. These enhancements allow users to create visually appealing and informative charts, making it easier to communicate complex data stories.
Enhanced Functionality
Excel’s developers are committed to enhancing the software’s functionality. We can expect to see improvements in the AVERAGE function and its related functions, making them more flexible and powerful. This could include adding new arguments or improving performance for large datasets.
Integration with Power Platform
Microsoft’s Power Platform, which includes Power BI, Power Apps, and Power Automate, is gaining traction in the business world. Excel’s integration with these tools is becoming increasingly seamless, allowing users to connect their Excel data to Power BI for advanced data visualization and analysis.
Cloud Integration
The move towards cloud-based solutions is transforming the way we work with data. Excel’s integration with Microsoft’s cloud services, such as OneDrive and SharePoint, is becoming more robust. This allows users to collaborate on Excel workbooks in real-time, access their data from anywhere, and leverage the power of the cloud for data storage and analysis.
AI-Assisted Analysis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing data analysis. Excel is expected to integrate more AI-powered features, such as intelligent data analysis and automated insights. These features will help users identify patterns and trends in their data more efficiently, providing valuable insights with minimal effort.
Conclusion
Mastering Excel’s AVERAGE function with multiple criteria is a powerful skill that opens up a world of advanced data analysis possibilities. By understanding the need for criteria-based averaging, learning the art of constructing complex formulas, and exploring advanced techniques, you can unlock the full potential of Excel for your data analysis needs. As Excel continues to evolve, embracing these future trends and implications will ensure you stay at the forefront of data analysis, enabling you to make informed decisions and drive business success.
How does the AVERAGE function with multiple criteria work in Excel?
+
The AVERAGE function with multiple criteria allows you to calculate the average value based on specific conditions or criteria. You can use functions like SUMIFS and COUNTIFS to sum and count the values that meet all the specified criteria, and then divide the sum by the count to get the average.
What are some real-world applications of the AVERAGE function with multiple criteria?
+
This function is widely used in various industries for data analysis. For example, in sales analysis, it can be used to calculate the average sales for a specific product across different regions and channels. In finance, it can help calculate average returns on investment for various portfolios with specific criteria.
Can I use named ranges in the AVERAGE function with multiple criteria formulas?
+
Yes, you can assign names to cell ranges in Excel and use those named ranges in your formulas. This improves readability and makes your formulas more maintainable.
Are there any advanced functions that can be used alongside the AVERAGE function with multiple criteria?
+
Absolutely! Excel offers a range of advanced functions like AVERAGEIFS, AVERAGEA, AVERAGEIF, and AVERAGEPIVOT that can provide more flexibility and power when calculating averages based on specific criteria.
How can I optimize performance when working with large datasets and complex formulas?
+
To optimize performance, consider using Excel’s Table feature, which automatically expands formulas as you add or remove rows. Additionally, leverage the Table’s filtering and sorting capabilities for quick data analysis. You can also explore Excel’s cloud integration and Power Platform integration for more efficient data handling and collaboration.