Fixing Autosum Excel: 5 Quick Tips
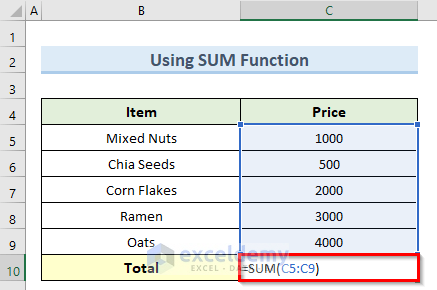
Excel's Autosum feature is a powerful tool for data analysis and automation, allowing users to quickly calculate sums and perform basic arithmetic operations. However, there may be instances where the Autosum function fails to work as expected, leading to frustration and delayed workflows. In this article, we will delve into the common issues and provide you with five quick tips to fix Autosum in Excel, ensuring your calculations are accurate and efficient.
Understanding the Autosum Feature in Excel

Before we delve into the troubleshooting, let’s refresh our understanding of the Autosum feature in Excel. Autosum is a built-in function that automatically calculates the sum of a range of cells, simplifying the process of adding up values. It is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets or when you need to perform repetitive calculations.
When you select a cell and click on the Autosum button, Excel intelligently identifies the adjacent range of cells containing numerical data and applies the SUM function to that range. This saves time and minimizes the risk of errors that might occur with manual calculations.
Common Issues with Autosum

Despite its usefulness, Autosum can sometimes encounter problems, leaving users with unexpected results or even error messages. Here are some common issues you might face:
- Incorrect Range Selection: Autosum may select an incorrect range of cells, leading to an inaccurate sum. This can happen when there are blank cells or non-adjacent data points within the intended range.
- Formula Errors: Autosum relies on the SUM function, which can return errors if the referenced cells contain text, errors, or non-numeric values. This might result in #VALUE!, #DIV/0!, or other error messages.
- Cell Formatting: Differences in cell formatting, such as number formats or custom formats, can cause Autosum to treat certain cells as non-numeric, leading to incorrect calculations.
- Hidden Rows or Columns: Autosum might ignore hidden rows or columns, resulting in an incomplete sum. This can be particularly problematic when dealing with complex spreadsheets.
- Calculation Options: Excel's calculation options, such as iterative calculations or precision as displayed, can affect Autosum's behavior and accuracy.
5 Quick Tips to Fix Autosum in Excel
Now that we’ve identified the common issues, let’s explore some effective strategies to troubleshoot and fix Autosum in Excel.
1. Check and Adjust Cell References
One of the primary reasons for Autosum errors is incorrect cell references. Ensure that the range of cells you intend to sum is correctly selected. If Autosum selects an unexpected range, you can manually adjust the cell references by dragging the fill handle or editing the formula directly.
For instance, if you want to sum the values in cells A1 to A10, but Autosum selects A1 to B10, you can manually correct the formula to =SUM(A1:A10) to ensure the correct range is considered.
2. Verify Cell Formatting
Differences in cell formatting can lead to Autosum ignoring certain cells or returning errors. Ensure that all cells within the selected range have consistent formatting. You can apply a uniform number format to the range using the Format Cells option (Ctrl + 1) to ensure that Autosum recognizes all cells as numeric.
Additionally, be cautious of cells with custom formats, such as date formats or currency symbols, as these might affect the Autosum calculation. Consider using a simple number format, like General, to avoid potential issues.
3. Handle Hidden Elements
Hidden rows or columns can cause Autosum to overlook certain data, resulting in an incomplete sum. Before applying Autosum, ensure that all relevant rows and columns are visible. You can unhide hidden elements using the Format > Unhide option in the context menu.
If you need to work with hidden elements, consider using the SUM function directly, specifying the cell references manually. For example, =SUM(A1:A10,B5:B15) will sum the values in both ranges, including hidden rows or columns.
4. Review Formula Errors
Formula errors, such as #VALUE! or #DIV/0!, can occur when Autosum encounters non-numeric values or division by zero. Carefully review the referenced cells to ensure they contain valid numerical data. If you encounter such errors, identify and rectify the problematic cells before reattempting the Autosum calculation.
In some cases, you might need to use the IFERROR function to handle specific error conditions. For example, =IFERROR(SUM(A1:A10), "Error: Check Data") will display "Error: Check Data" if any error occurs during the sum calculation.
5. Adjust Calculation Options
Excel’s calculation options can impact the behavior of Autosum. If you’re working with complex spreadsheets or large datasets, ensure that the calculation options are set appropriately. You can access the calculation options by navigating to File > Options > Formula > Calculation.
Consider the following options:
- Calculation Mode: Set the calculation mode to Automatic for real-time updates, or choose Manual to control when calculations are performed.
- Iterative Calculation: If your spreadsheet involves iterative calculations, ensure that the iterative calculation options are configured correctly.
- Precision: The precision option controls the accuracy of calculations. Choose an appropriate setting based on your data requirements.
Real-World Example: Troubleshooting Autosum in a Financial Spreadsheet
Let’s consider a real-world scenario to illustrate how these tips can be applied in practice. Imagine you’re working on a financial spreadsheet for a small business, tracking monthly expenses. You’ve set up a simple table with columns for expense categories and corresponding amounts.
| Expense Category | Amount |
|---|---|
| Rent | $1,200 |
| Utilities | $350 |
| Office Supplies | $150 |
| Marketing | $500 |
| Total | =SUM(B2:B5) |
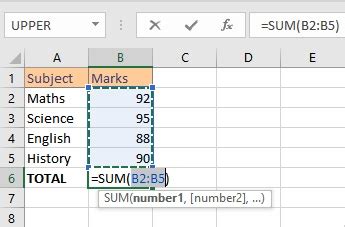
When you click on the Autosum button to calculate the total, you notice that the sum is incorrect. After troubleshooting, you realize that the issue is due to a hidden row. By unhiding the row and reapplying Autosum, you obtain the correct total of $2,200.
Conclusion: Maximizing Efficiency with Autosum

Excel’s Autosum feature is a powerful tool for streamlining calculations and automating repetitive tasks. By understanding the common issues and implementing the tips outlined in this article, you can troubleshoot and fix Autosum-related problems efficiently. Remember to check cell references, verify cell formatting, handle hidden elements, review formula errors, and adjust calculation options as needed.
By mastering these techniques, you'll be able to maximize the efficiency of your Excel spreadsheets and ensure accurate calculations, saving valuable time and minimizing errors. Autosum, when used correctly, can significantly enhance your data analysis capabilities and streamline your workflow.
What if Autosum still doesn’t work after trying these tips?
+If Autosum continues to malfunction, it’s possible that there are more complex issues at play. Consider seeking assistance from an Excel expert or online forums where you can describe your specific problem in detail. Additionally, ensure that your Excel version is up to date, as updates often include bug fixes and improvements.
Can I use Autosum for more complex calculations beyond simple sums?
+Absolutely! Autosum is not limited to simple sums. You can use it with various Excel functions to perform more complex calculations. For example, you can use Autosum with the AVERAGE function to calculate the average of a range of cells, or with the MAX or MIN functions to find the highest or lowest value in a dataset.
Is there a way to automate Autosum calculations for regularly updated datasets?
+Yes, you can set up Autosum calculations to update automatically when new data is added. This is achieved through the use of Excel’s data validation and formula auditing tools. By creating a named range and linking the Autosum formula to that range, you can ensure that the sum is automatically recalculated when new data is entered.


