AST/ALT Ratio: 3 Easy Calculation Tips

The AST/ALT ratio, a valuable metric in liver function assessment, offers insights into liver health and potential damage. Accurate calculation of this ratio is essential for healthcare professionals to monitor and diagnose liver conditions effectively. In this article, we will delve into three straightforward methods to compute the AST/ALT ratio, ensuring precision and ease in liver function evaluation.
Understanding the AST/ALT Ratio
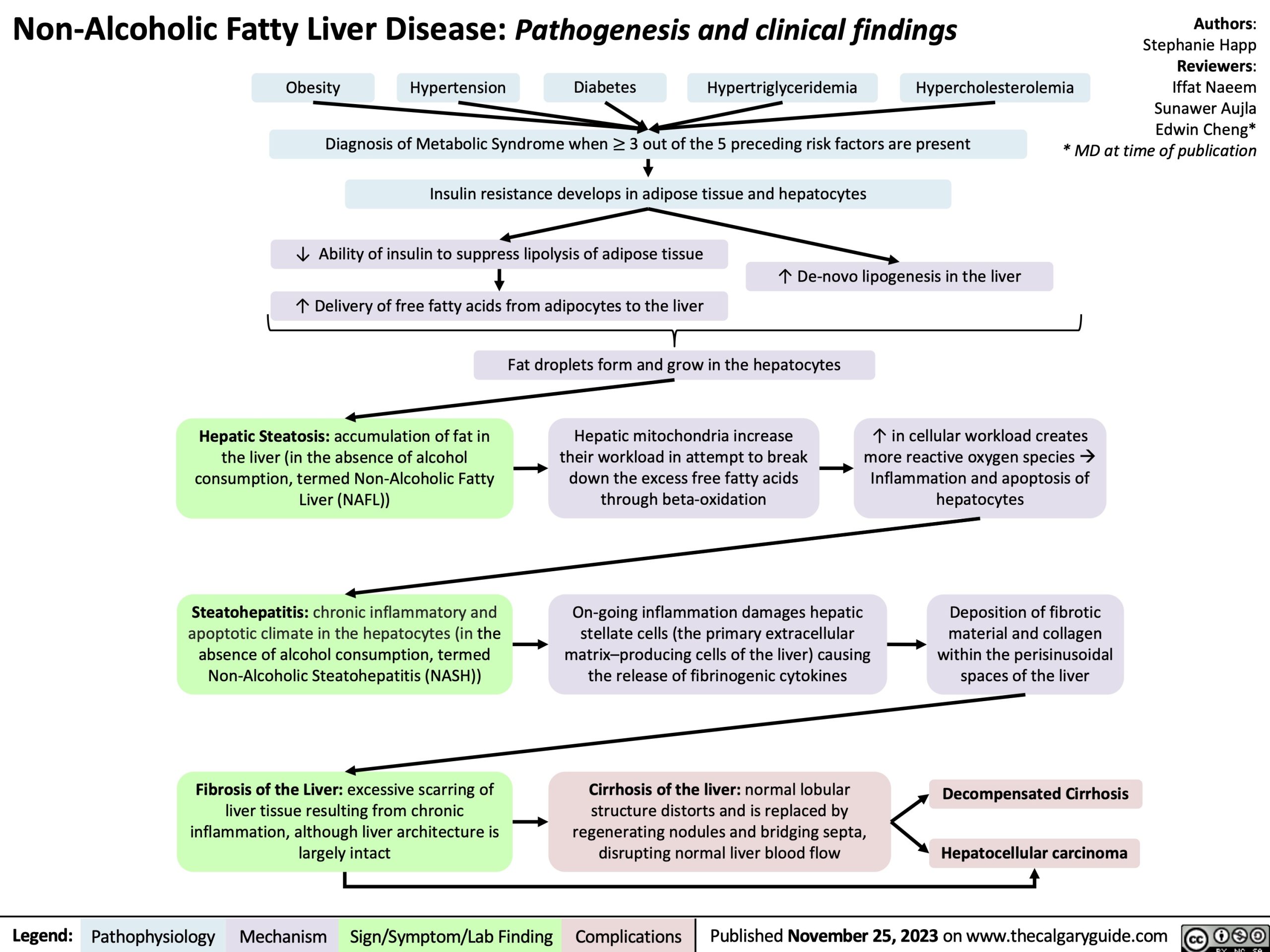
The AST/ALT ratio is derived from the Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) and Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) levels in the blood. These enzymes are indicators of liver health, and their ratio provides additional context to liver enzyme test results. An elevated AST/ALT ratio can suggest specific liver conditions, making it a crucial parameter in liver function interpretation.
Method 1: Manual Calculation

The traditional method involves a simple division of the AST value by the ALT value. For instance, if an individual’s AST level is 35 U/L and their ALT level is 50 U/L, the AST/ALT ratio would be calculated as:
| AST | ALT |
|---|---|
| 35 U/L | 50 U/L |

In this case, the AST/ALT ratio is 0.7.
Step-by-Step Guide to Manual Calculation
- Retrieve the AST and ALT values from the patient’s blood test report.
- Divide the AST value by the ALT value to obtain the ratio.
- Interpret the ratio based on established clinical guidelines. A ratio above 1.0 may indicate specific liver conditions, while a ratio below 1.0 is generally considered normal.
Method 2: Online Calculators
With the advancement of digital health tools, numerous online calculators simplify the AST/ALT ratio computation. These calculators offer a user-friendly interface, allowing healthcare professionals to input AST and ALT values and instantly obtain the ratio.
Benefits of Online Calculators
- Convenience: Online calculators are readily accessible, eliminating the need for manual calculations.
- Accuracy: These tools are designed to provide precise results, ensuring consistency in ratio calculations.
- Data Storage: Some calculators allow for data storage, enabling healthcare professionals to track AST/ALT ratios over time for individual patients.
Choosing the Right Online Calculator
When selecting an online calculator, consider the following:
- Reputation: Opt for calculators from reputable medical websites or healthcare institutions.
- User-Friendliness: Choose a calculator with an intuitive interface for easy data input and interpretation.
- Data Security: Ensure the calculator’s website has secure data handling practices to protect patient information.
Method 3: Laboratory Reports
Many modern laboratories provide comprehensive reports that include calculated AST/ALT ratios alongside AST and ALT values. These reports offer a convenient and reliable way to obtain the ratio, especially when multiple liver function tests are conducted.
Advantages of Laboratory Reports
- Expertise: Laboratory reports are generated by trained professionals, ensuring accurate calculations.
- Contextual Information: Reports often include additional liver function parameters, providing a comprehensive view of liver health.
- Ease of Access: Laboratory reports are easily accessible to healthcare providers, streamlining the diagnostic process.
Interpreting Laboratory Reports
When reviewing laboratory reports, pay attention to the following:
- AST/ALT Ratio: Note the calculated ratio and compare it with established reference ranges.
- AST and ALT Values: Individual AST and ALT values can provide additional insights into liver health and potential issues.
- Other Liver Parameters: Look for other liver function markers like bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and gamma-glutamyl transferase, as they can offer a more holistic view of liver function.
Practical Considerations

While calculating the AST/ALT ratio is crucial, it’s important to remember that it is just one component of liver function assessment. Other liver enzymes and parameters should also be considered for a comprehensive evaluation. Additionally, individual patient factors, medical history, and clinical symptoms play a significant role in liver function interpretation.
Expert Tips
- Regular AST/ALT ratio monitoring can aid in the early detection of liver conditions.
- Consider the patient’s overall health and medication history when interpreting AST/ALT ratios.
- Consult with specialists for complex cases or when AST/ALT ratios are significantly abnormal.
Future Trends in Liver Function Assessment
As medical technology advances, we can expect more sophisticated methods for liver function evaluation. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning may revolutionize liver health monitoring, offering more precise and personalized insights. Additionally, non-invasive imaging techniques are being developed to assess liver function, potentially reducing the need for frequent blood tests.
Staying Informed
Healthcare professionals should stay updated with the latest advancements in liver function assessment to provide the best care to their patients. Regularly reviewing medical journals, attending conferences, and participating in continuing education programs can ensure a comprehensive understanding of liver health evaluation methods.
What is the clinical significance of an elevated AST/ALT ratio?
+An elevated AST/ALT ratio, typically above 1.0, may suggest specific liver conditions such as alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), or chronic hepatitis C. It can also indicate advanced liver disease or cirrhosis. However, the interpretation should always be done in conjunction with other clinical findings and patient history.
Can the AST/ALT ratio vary with age or gender?
+Yes, AST and ALT levels can vary with age and gender. Generally, AST levels tend to be higher in males and increase with age, while ALT levels may be higher in females. However, these variations are relatively small, and the AST/ALT ratio is considered a more stable indicator of liver health.
Are there any specific conditions where the AST/ALT ratio is not a reliable indicator?
+While the AST/ALT ratio is a valuable tool, it may not be as informative in certain conditions. For instance, in acute hepatitis, both AST and ALT levels can be significantly elevated, leading to a normal or near-normal ratio. In such cases, additional liver function tests and clinical evaluation are necessary.



