Arizona's Voter Demographic Breakdown
The Diverse Electorate of Arizona: Unveiling the State’s Voter Demographics
In the heart of the American Southwest, Arizona boasts a vibrant and diverse population, and its electoral landscape reflects this rich tapestry of communities. From the bustling cities to the vast deserts, Arizona’s voters are a microcosm of the nation’s demographic trends, with unique characteristics that shape the state’s political dynamics. Let’s delve into the intricate breakdown of Arizona’s voter demographics, exploring the factors that influence the state’s electoral outcomes.
The Demographic Mosaic Arizona’s population is a mosaic of diverse ethnicities, ages, and backgrounds, and this diversity is mirrored in its electorate. According to the latest census data, the state’s population comprises a significant Hispanic/Latino community, with a presence across various age groups. This demographic group has been steadily growing, and its impact on the state’s politics cannot be overstated.
Alongside the Hispanic/Latino population, Arizona is home to a sizable Native American community, particularly in the northern regions. The state’s Native American voters have a rich history of political engagement and have played a crucial role in shaping policies that impact their tribal lands and communities.
The white population in Arizona, while still the majority, is diverse in its own right, encompassing a range of ages, socioeconomic backgrounds, and political ideologies. From the retirees flocking to the sunny cities to the younger professionals drawn to the tech hubs, this demographic segment is far from monolithic.
Furthermore, Arizona’s Asian and Pacific Islander communities, while smaller in number, have a growing influence, particularly in urban areas. Their political engagement and cultural impact are increasingly shaping the state’s discourse.
Aging Dynamics and Millennial Impact One of the most intriguing aspects of Arizona’s voter demographics is the interplay between its aging population and the rising influence of younger generations. The state has a significant number of retirees, drawn by its climate and retirement communities. This older demographic has traditionally been a reliable voting bloc, with unique concerns and priorities.
However, the millennial and Gen Z populations are rapidly catching up, and their political engagement is reshaping the state’s trajectory. These younger voters, often more progressive and tech-savvy, are demanding a greater say in policy decisions. Their engagement in issues ranging from climate change to social justice is a testament to their growing influence.
Urban vs. Rural Divide Arizona’s electoral map is also shaped by the classic urban-rural divide. The state’s largest cities, Phoenix and Tucson, are demographic melting pots, reflecting the state’s overall diversity. These urban centers are hubs of political activism and have a significant impact on statewide elections.
In contrast, Arizona’s rural areas, particularly in the northern and eastern regions, have a different demographic composition and political leanings. These communities, often closer-knit and more conservative, play a crucial role in state and local politics, influencing policies related to agriculture, land use, and traditional values.
The Role of Education and Socioeconomics Education and socioeconomic status are also key factors in understanding Arizona’s voter demographics. The state’s educational landscape is diverse, with a mix of public and private institutions, ranging from prestigious universities to community colleges. This diversity extends to the electorate, with varying levels of educational attainment influencing political perspectives.
Socioeconomic factors, such as income and employment, also play a significant role. Arizona’s economy, driven by sectors like technology, healthcare, and tourism, offers diverse employment opportunities. However, income inequality and the cost of living are issues that resonate with many voters, shaping their political choices.
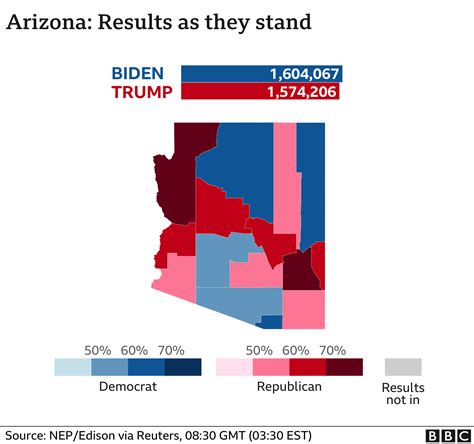
Political Engagement and Turnout Arizona’s voter demographics are not just about numbers; they are about engagement and participation. The state has a proud tradition of political activism, with a high voter turnout in recent years. This engagement is driven by a variety of factors, including a competitive political landscape and a history of close elections.
However, challenges such as voter suppression and access to polling stations persist, particularly in rural and minority communities. Efforts to increase voter registration and ensure equal access to the ballot box are ongoing, with grassroots organizations and political parties working to empower every eligible voter.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Electoral Landscape Arizona’s voter demographic breakdown is a dynamic and ever-evolving story, reflecting the state’s rich cultural heritage and its place in the modern American political landscape. As the state continues to grow and evolve, its electoral map will be shaped by the unique characteristics of its diverse communities.
Understanding these demographics is crucial for policymakers, candidates, and voters themselves. It allows for more inclusive policies, targeted outreach, and a deeper appreciation of the issues that resonate with different segments of Arizona’s population.
In the upcoming elections, Arizona’s voters will once again have their say, and their collective voice will shape the state’s future. Whether it’s through ballot initiatives, local elections, or the all-important presidential contests, Arizona’s diverse electorate will continue to be a force to be reckoned with.
The Pros and Cons of Arizona's Demographic Diversity

How has Arizona’s voter demographic changed over the years?
+Arizona’s voter demographic has undergone significant changes over the years. The state has seen a steady increase in its Hispanic/Latino population, which has had a notable impact on the political landscape. Additionally, the millennial and Gen Z populations are increasingly making their presence felt, demanding attention to issues like climate change and social justice.
What are the key challenges faced by Arizona’s diverse electorate?
+Challenges faced by Arizona’s diverse electorate include voter suppression, access to polling stations, and ensuring equal representation for all communities. Efforts to increase voter registration and engagement are ongoing to address these issues.
How do urban and rural areas influence Arizona’s political landscape?
+Arizona’s urban-rural divide plays a significant role in its political landscape. The state’s largest cities, Phoenix and Tucson, are diverse and politically active, while rural areas have their own unique demographic composition and political leanings, influencing policies related to land use and traditional values.
What impact does education have on Arizona’s voter demographics?
+Education is a key factor in Arizona’s voter demographics. The state’s diverse educational landscape, ranging from public schools to prestigious universities, influences political perspectives and engagement. Higher levels of educational attainment often correlate with increased political participation.
How does Arizona’s aging population affect its electoral outcomes?
+Arizona’s aging population has traditionally been a reliable voting bloc, with unique concerns and priorities. However, the rising influence of younger generations, particularly millennials and Gen Z, is reshaping the state’s electoral landscape, bringing new issues and perspectives to the forefront.


