How to Create Area Charts with Dual Lines
Area charts are powerful visualization tools that help us understand trends and patterns in data over time. One popular variation is the dual-line area chart, which allows for the comparison of two sets of data on a single graph. This type of chart is particularly useful when analyzing trends, tracking progress, or identifying relationships between different variables. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the step-by-step process of creating area charts with dual lines, exploring their benefits, best practices, and potential applications.
Understanding Dual-Line Area Charts
A dual-line area chart, often referred to as a stacked area chart or overlapping area chart, displays two or more lines representing different data series on the same graph. Each line represents a distinct variable, and the area beneath the lines is filled with colors or patterns to differentiate the data sets. This visual representation allows for easy comparison and analysis of the relationship between the variables over time.
The key advantage of dual-line area charts is their ability to convey a wealth of information in a single graphic. By presenting multiple data series simultaneously, analysts and decision-makers can quickly identify trends, deviations, and correlations. This makes it an invaluable tool for tracking the performance of different metrics, monitoring the progress of projects, or comparing the effectiveness of strategies.
Real-World Application: Analyzing Sales Trends
Imagine a marketing team wanting to analyze the sales trends of two competing products over the past year. By creating a dual-line area chart, they can visualize the sales performance of each product, comparing their growth, peaks, and dips. This visual representation allows the team to identify which product performed better overall and during specific periods, aiding in strategic decision-making and resource allocation.
Creating Dual-Line Area Charts: A Step-by-Step Guide
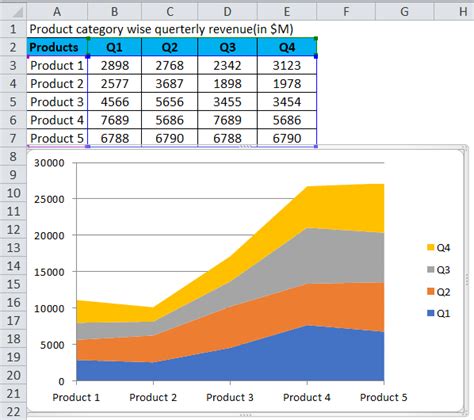
Generating dual-line area charts involves a straightforward process, which we will break down into simple steps. For the purpose of this guide, we will use Excel as our primary tool, as it is widely accessible and offers powerful data visualization capabilities.
Step 1: Prepare Your Data
Begin by organizing your data in a clear and structured manner. Ensure that your dataset includes two columns: one for the categories (e.g., months, quarters, or years) and another for the corresponding data values. Each row should represent a unique data point. For instance, if you are tracking sales data over time, each row would represent a specific month and its corresponding sales figure.
| Category | Data Value |
|---|---|
| Jan | 1500 |
| Feb | 1800 |
| Mar | 2200 |
| ... | ... |
Step 2: Create the Chart
With your data prepared, follow these steps to create a dual-line area chart in Excel:
- Select the entire dataset, including the header row.
- Go to the Insert tab on the Excel ribbon.
- In the Charts group, select Insert Area Chart.
- Choose the Stacked Area chart type.
- A basic dual-line area chart will be created, displaying your data.
Step 3: Customize and Enhance
Once your chart is generated, you can customize it to enhance its visual appeal and clarity. Here are some key customization options:
- Titles and Labels: Add a title to your chart to clearly describe its content. Include axis labels to identify the categories and data values. Ensure that the labels are easily readable and provide context.
- Data Series Colors: Assign distinct colors to each data series (line) to make them visually distinguishable. Choose colors that complement each other and provide a clear contrast.
- Gridlines: Add gridlines to improve readability, especially when dealing with multiple data series. Gridlines can help viewers align data points and understand the scale of the chart.
- Legend: Include a legend to explain the meaning of each data series. Position the legend in a way that doesn't obscure important data.
- Data Point Labels: If needed, add data point labels to specific data points for additional clarity. This is particularly useful when highlighting important milestones or anomalies.
Step 4: Analyze and Interpret
With your customized dual-line area chart, you can now delve into the data and extract valuable insights. Analyze the trends, compare the performance of each data series, and identify any significant patterns or correlations. Consider the following questions:
- Do the data series follow similar trends, or are there notable deviations?
- Are there periods where one data series outperforms the other, and what could be the reasons for this?
- Can you identify any potential relationships or dependencies between the variables?
- Are there any unexpected spikes or dips that require further investigation?
Best Practices for Effective Dual-Line Area Charts
To ensure your dual-line area charts are effective and communicate your data accurately, consider these best practices:
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcrowding your chart with unnecessary elements. Focus on the key data series and ensure they are easily distinguishable.
- Choose Appropriate Colors: Select colors that are visually appealing and accessible to all viewers. Avoid using colors that may cause accessibility issues for colorblind individuals.
- Consistent Scaling: Maintain consistent scaling across your charts to allow for accurate comparisons. Ensure that the scales are appropriate for the range of data values.
- Provide Context: Include relevant contextual information, such as time periods, units of measurement, or any other details that may impact the interpretation of the data.
- Consider Interactive Charts: If your data is dynamic or requires frequent updates, consider creating interactive charts. Interactive charts allow users to explore the data further and drill down into specific details.
Future Implications and Potential Applications
Dual-line area charts have a wide range of applications across various industries and fields. Here are some potential use cases and future implications:
- Business Analytics: In the business world, dual-line area charts can be used to track the performance of different departments, products, or marketing campaigns. They aid in identifying areas for improvement and making informed strategic decisions.
- Healthcare: Healthcare professionals can utilize dual-line area charts to monitor patient progress, track disease prevalence over time, or compare the effectiveness of different treatments.
- Environmental Studies: Scientists and researchers can visualize environmental data, such as temperature changes, pollution levels, or renewable energy generation, to identify trends and make informed decisions regarding sustainability.
- Education: Educators can employ dual-line area charts to track student performance, compare the effectiveness of teaching methods, or analyze the impact of educational interventions.
- Financial Analysis: Financial analysts can use these charts to compare the performance of different investment portfolios, track market trends, or evaluate the impact of economic policies.
Looking Ahead: Emerging Trends
As data visualization continues to evolve, we can expect to see advancements in dual-line area charts and their applications. Some emerging trends include:
- Interactive and Animated Charts: Interactive charts allow users to explore data dynamically, providing a more engaging and immersive experience. Animated transitions can also enhance the visual appeal and help convey complex data stories.
- Machine Learning Integration: Machine learning algorithms can be employed to automatically identify patterns, anomalies, and correlations in data, providing insights that may not be immediately apparent to human analysts.
- Storytelling with Data: Visualizing data in a narrative format can help convey complex information more effectively. Dual-line area charts can be used as part of a data storytelling framework, guiding viewers through a logical sequence of insights.
Can I create dual-line area charts in other software besides Excel?
+Absolutely! While Excel is a popular choice, there are numerous data visualization tools available, such as Tableau, Power BI, and Google Sheets, which offer advanced chart customization and interactive features. Explore these alternatives to find the tool that best suits your needs.
How do I choose the right colors for my dual-line area chart?
+When selecting colors, consider accessibility and readability. Avoid color combinations that may cause issues for colorblind individuals. Opt for high-contrast colors that clearly differentiate the data series. Color-coding can also be used to represent specific meanings or categories.
Are there any limitations to using dual-line area charts?
+Dual-line area charts are most effective when comparing a limited number of data series. With too many lines, the chart may become cluttered and difficult to interpret. Additionally, if your data has significant variations in scale, consider using a different chart type, such as a line chart or a bar chart.



