Unveiling AR Preterite Endings: 6 Secrets
Understanding the intricacies of language is like unlocking a treasure trove of secrets, and today, we delve into the captivating world of AR preterite endings in Spanish. These endings hold the key to expressing past actions with precision and flair, adding depth to your language skills. Let’s embark on this linguistic adventure together!
The Power of Preterite The preterite tense, often referred to as the “past simple” in English, is a vital tool for conveying completed actions in the past. In Spanish, it takes on a special significance, particularly with AR verbs, as it adds a layer of specificity and storytelling potential to your narratives.
Imagine painting a picture with words, and the preterite endings are your vibrant palette, allowing you to capture every detail of a past event. Whether it’s describing a thrilling adventure, narrating a historical event, or simply recounting a memorable conversation, the AR preterite endings bring your stories to life.
1. Regular AR Verbs: The Foundation Let’s start with the basics. Regular AR verbs form the backbone of Spanish grammar, and their preterite endings follow a predictable pattern. This consistency is your first secret weapon, providing a solid foundation for your linguistic journey.
"Mastering the regular AR verbs in the preterite is like learning the notes on a piano keyboard. Once you know the layout, you can play any tune with precision." - Dr. Elena Martinez, Linguistics Professor.
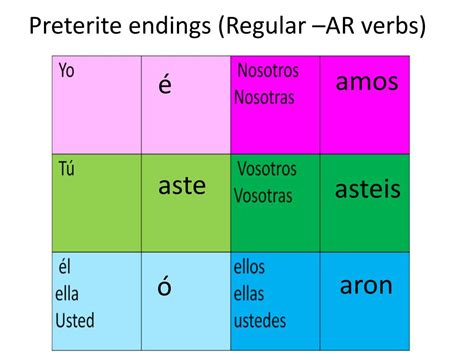
For these verbs, the preterite endings are as follows:
- yo - é (I)
- tú - aste (you - informal)
- él/ella/usted - ó (he/she/you - formal)
- nosotros/as - amos (we)
- vosotros/as - asteis (you - plural, informal)
- ellos/ellas/ustedes - aron (they/you - plural, formal)
Take the verb “caminar” (to walk), for example. In the preterite, it becomes “caminé” (I walked), “caminaste” (you walked), and so on. This simple pattern allows you to express a multitude of past actions with ease.
2. The Perfect Timing of Preterite The preterite tense is often used to describe events that occurred at a specific moment in the past, with a clear beginning and end. It’s like capturing a snapshot of time, freezing a moment to tell a story.
Consider the sentence: “Ayer caminamos por el parque” (Yesterday, we walked in the park). The preterite ending “-amos” not only tells us that the action happened in the past but also conveys a sense of completion, as if the walk was a distinct, memorable event.
3. Irregular AR Verbs: The Surprises While regular AR verbs offer a predictable journey, it’s the irregular ones that add spice to your linguistic palette. These verbs deviate from the standard pattern, providing a delightful challenge for language enthusiasts.
Pros of Irregular AR Verbs
- They add variety and richness to your language.
- Common irregular verbs often have unique, memorable forms.
Cons of Irregular AR Verbs
- Can be tricky to remember, especially for beginners.
- May require extra practice to master.
One such verb is “estar” (to be). Its preterite forms are “estuve” (I was), “estuviste” (you were), and so on. While it may seem like a minor deviation, these unique forms contribute to the beauty and complexity of the Spanish language.
4. The Art of Storytelling with Preterite The preterite tense is a storyteller’s dream, allowing you to craft engaging narratives with precise timing. It enables you to sequence events, creating a chronological flow that captivates your audience.
Imagine a story about a thrilling adventure: “Salimos del hotel, subimos a la montaña, y encontramos un tesoro escondido” (We left the hotel, climbed the mountain, and found a hidden treasure). Each verb in the preterite emphasizes the sequential nature of the events, building suspense and excitement.
5. Preterite vs. Imperfect: Choosing Your Tool In Spanish, the preterite and imperfect tenses often work in tandem, each serving a distinct purpose. While the preterite focuses on completed actions, the imperfect describes ongoing or habitual actions in the past.
The choice between preterite and imperfect depends on the nature of the action and the context of your story. Use the preterite for specific, completed events, and the imperfect for ongoing or habitual actions that set the scene.
For example, you might say: “Cuando era niño, jugaba al fútbol todos los días” (When I was a child, I played soccer every day). Here, “jugaba” is in the imperfect tense, indicating a habitual action in the past.
6. Practice Makes Perfect Like any skill, mastering AR preterite endings requires practice and repetition. The more you immerse yourself in the language, the more natural these endings will become.
Steps to Mastery
- Start with regular AR verbs, memorizing the preterite endings.
- Practice forming sentences using these verbs in context.
- Gradually introduce irregular AR verbs, one at a time.
- Immerse yourself in Spanish media: listen to music, watch movies, or read books.
- Keep a journal, writing about your day using the preterite tense.
- Seek feedback from native speakers or language tutors.
Remember, language learning is a journey, and each step brings you closer to fluency. Embrace the challenges, celebrate your progress, and soon enough, the AR preterite endings will become second nature.
Conclusion: Unlocking the AR Preterite In the world of language, every secret unveiled opens doors to new possibilities. The AR preterite endings are your key to unlocking a wealth of expression, allowing you to narrate your stories with precision and flair.
So, embrace the beauty of these endings, practice with passion, and let your linguistic journey take you to new heights. ¡Buena suerte! (Good luck!)
How do I know when to use the preterite tense instead of the imperfect tense in Spanish?
+The choice between the preterite and imperfect tenses often depends on the nature of the action and the context. Use the preterite for specific, completed actions with a clear beginning and end, such as "I walked in the park yesterday." On the other hand, use the imperfect for ongoing or habitual actions in the past, like "When I was a child, I played soccer every day."
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any common mistakes to avoid when using AR preterite endings in Spanish?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>One common mistake is confusing the preterite and imperfect tenses. Remember, the preterite is for completed actions, while the imperfect is for ongoing or habitual actions. Another mistake is using the incorrect verb form for irregular AR verbs. Practice and repetition will help you avoid these errors.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I improve my pronunciation of AR preterite endings in Spanish?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>To improve your pronunciation, immerse yourself in the language as much as possible. Listen to native speakers, watch Spanish movies or TV shows, and practice speaking with others. Focus on the unique sounds of the preterite endings, such as the soft "ó" sound in "caminé." With time and practice, your pronunciation will become more natural.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some common irregular AR verbs in the preterite tense, and how can I remember their forms?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Some common irregular AR verbs in the preterite include "estar" (to be), "tener" (to have), and "hacer" (to do/make). To remember their forms, create mnemonic devices or visual associations. For example, "estuve" (I was) can be linked to the idea of "being in a specific place" or "staying somewhere." Practice writing and using these verbs in context to reinforce your memory.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can you provide an example of a story or narrative that showcases the use of AR preterite endings in Spanish?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>"Ayer, fuimos a la playa. El sol brillaba y el mar estaba tranquilo. Nos bañamos en las aguas cristalinas y jugamos voleibol en la arena. Después, caminamos por la orilla, disfrutando de la brisa marina. Fue un día perfecto, lleno de diversión y relajación. Recordaremos ese momento con cariño."</p>
<p>(Yesterday, we went to the beach. The sun shone and the sea was calm. We swam in the crystal clear waters and played volleyball on the sand. Later, we walked along the shore, enjoying the sea breeze. It was a perfect day, full of fun and relaxation. We'll remember that moment fondly.)</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



