Quickly Apply Rules to an Entire Sheet

In the fast-paced world of data analysis and management, efficiency is key. When working with large datasets, the ability to apply rules and formatting quickly across an entire sheet can save valuable time and effort. This article explores effective strategies and tools to streamline this process, making your data management tasks more streamlined and efficient.
The Importance of Efficient Data Management
Efficient data management is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. Whether you’re a data analyst, a researcher, or simply someone who works with large datasets regularly, the ability to quickly apply rules and formats ensures accuracy, consistency, and saves precious time. By optimizing your data management processes, you can focus more on interpreting and deriving insights from your data, rather than getting bogged down in tedious formatting tasks.
Utilizing Conditional Formatting
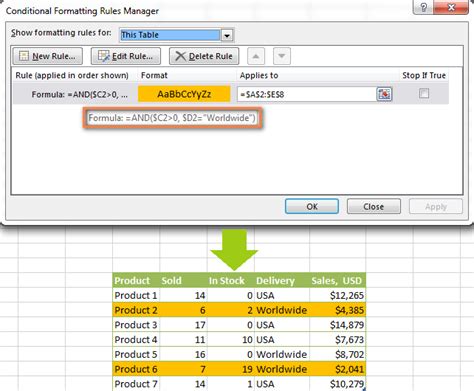
One powerful tool at your disposal is conditional formatting. This feature allows you to apply specific formats to cells based on predefined conditions or rules. For instance, you could highlight all cells containing values above a certain threshold, or format cells based on their text content. Conditional formatting is particularly useful when you need to quickly identify patterns or outliers in your data.
To apply conditional formatting in Microsoft Excel, follow these steps:
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Navigate to the Home tab and click on Conditional Formatting.
- Choose from a variety of predefined rules, or create a New Rule tailored to your specific needs.
- Set the conditions and select the desired formatting options.
- Click OK to apply the conditional formatting to your selected cells.
Advanced Conditional Formatting Techniques
Conditional formatting is a versatile tool that can be adapted to various data management scenarios. For example, you can use it to:
- Highlight cells with specific text or values.
- Format cells based on their position relative to other cells (e.g., top 10% of values).
- Apply color scales or data bars to visualize data distribution.
- Create custom rules using formulas to perform complex comparisons.
By exploring and mastering conditional formatting, you can significantly enhance your data management efficiency.
Using Formulas for Automated Rule Application
Another powerful approach to quickly applying rules across an entire sheet is through the use of formulas. Formulas allow you to perform calculations, manipulate data, and apply specific formats based on the results. This approach is particularly useful when you need to apply consistent formatting or calculations across a large dataset.
For instance, you could use the IF function to apply different formats based on specific conditions. The formula might look something like this:
=IF(A1>50, "High", IF(A1<25, "Low", "Medium"))
In this example, the formula checks the value in cell A1. If it's greater than 50, the cell will display "High." If it's less than 25, it will display "Low." Otherwise, it will display "Medium."
Advanced Formula Techniques
By combining multiple functions and conditions, you can create complex formulas to automate various data management tasks. Some commonly used functions for rule application include:
- IF: As seen above, this function allows you to apply different rules based on specific conditions.
- AND and OR: These functions enable you to combine multiple conditions in your formulas.
- VLOOKUP: This function is useful for retrieving data from another range based on a specific condition.
- COUNTIF and SUMIF: These functions help you count or sum cells based on specific criteria.
By mastering these formula techniques, you can automate a wide range of data management tasks, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
Streamlining with Macros
For more complex or repetitive tasks, macros can be a powerful tool. Macros are essentially a series of commands or actions that you can record and replay, automating various tasks in your spreadsheet. This can be particularly useful when you need to apply a series of rules or formats to an entire sheet.
To create a macro in Microsoft Excel, follow these steps:
- Ensure the Developer tab is visible in your ribbon. If not, right-click on the ribbon and select Customize the Ribbon to add it.
- Navigate to the Developer tab and click on Record Macro.
- Give your macro a name and specify where you want it saved.
- Perform the actions you want to record. This could include selecting cells, applying formats, running formulas, etc.
- Once finished, click Stop Recording.
Now, whenever you need to apply those recorded actions, simply run the macro.
Macro Best Practices
While macros can be incredibly useful, it’s important to use them wisely. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Keep macros simple and focused on a specific task.
- Avoid recording actions that could lead to errors or unexpected results.
- Consider using relative references in your macros to ensure they work correctly regardless of where the data is located.
- Regularly test and update your macros to ensure they remain accurate and efficient.
Leveraging Data Validation

Data validation is a powerful tool to ensure the accuracy and consistency of your data. It allows you to specify rules that data must adhere to when entered into a cell. This can help prevent errors and ensure that your data remains reliable.
To apply data validation in Microsoft Excel, follow these steps:
- Select the cells you want to validate.
- Navigate to the Data tab and click on Data Validation.
- Choose the type of validation you want to apply (e.g., whole number, decimal, text length, etc.).
- Set the criteria and input message as needed.
- Click OK to apply the validation rules.
By using data validation, you can ensure that your data remains clean and reliable, making your analysis and reporting more accurate.
Advanced Data Validation Techniques
Data validation offers a range of options to customize your data entry rules. Some advanced techniques include:
- Using lists to allow only specific values to be entered.
- Creating custom formulas to validate data based on complex conditions.
- Applying input messages and error alerts to guide users and prevent errors.
By mastering data validation, you can ensure that your data remains of the highest quality, enhancing the reliability of your analysis and decision-making.
Conclusion
Efficient data management is a cornerstone of successful data analysis and reporting. By leveraging tools like conditional formatting, formulas, macros, and data validation, you can quickly apply rules and formats across entire sheets, saving time and effort. These techniques, when mastered, will empower you to focus more on deriving insights from your data and less on tedious formatting tasks.
How can I quickly apply a specific format to an entire sheet in Excel?
+To quickly apply a specific format to an entire sheet in Excel, you can use the Format Painter tool. First, select a cell with the desired format. Then, click on the Format Painter button (it looks like a paintbrush) in the Home tab. Now, simply click on each cell or range of cells you want to format. The format will be instantly applied.
What are some best practices for using conditional formatting effectively?
+When using conditional formatting, it’s important to keep it simple and focused. Use clear and concise rules that are easy to understand. Avoid over-formatting, as it can make your data harder to read. Regularly review and update your conditional formatting rules to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
Can I create custom macros in Excel without programming knowledge?
+Yes, Excel provides a user-friendly interface for creating macros, even without programming knowledge. You can record your actions and save them as macros. However, for more complex macros, some basic understanding of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) can be beneficial.