9 Inch to MM: The Conversion Guide

Understanding metric conversions is a valuable skill, especially when navigating the world of measurements. One common conversion that often arises is converting inches to millimeters (mm). In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of this conversion, providing you with the knowledge and tools to accurately convert between these two units of measurement.
The Basics of Inch and Millimeter Conversions

Inches and millimeters are both widely used units of length, with inches being more prevalent in countries that follow the imperial system, such as the United States, while millimeters are part of the metric system, which is the standard in most countries worldwide.
The conversion between inches and millimeters is straightforward, and it is an essential skill for anyone involved in manufacturing, engineering, design, or even everyday tasks like purchasing items with international sizing.
Understanding the Conversion Factor
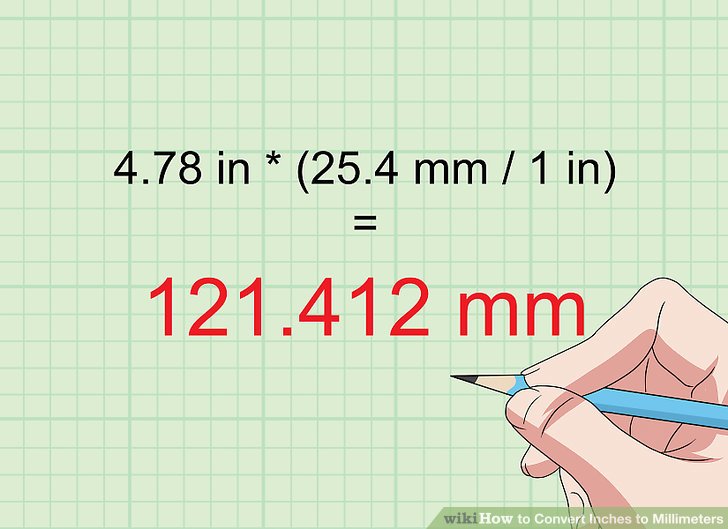
To convert inches to millimeters, you need to know the conversion factor, which is a simple ratio between the two units. One inch is equivalent to 25.4 millimeters.
This conversion factor is the key to accurately converting any measurement from inches to millimeters and vice versa. It allows us to bridge the gap between the imperial and metric systems, ensuring precision and consistency in measurements.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
- Identify the length or size in inches that you want to convert.
- Multiply the inch value by the conversion factor: 25.4.
- The result of this multiplication will give you the equivalent length in millimeters.
For example, let's say you have a piece of paper that is 8.5 inches long. To find its length in millimeters, you would perform the following calculation:
8.5 inches x 25.4 millimeters per inch = 215.9 millimeters
So, the 8.5-inch paper is approximately 215.9 millimeters long.
Real-World Applications and Scenarios

Converting inches to millimeters is not just a theoretical exercise; it has numerous practical applications across various industries and everyday situations.
Manufacturing and Engineering
In manufacturing and engineering, precision is paramount. Many components and products are designed and manufactured using both imperial and metric units. Converting between inches and millimeters is crucial to ensure that specifications are met accurately.
For instance, imagine a mechanical engineer designing a new machine part. The part's dimensions might be provided in inches, but the manufacturing facility might require the specifications in millimeters. Accurate conversion is essential to prevent errors and ensure a perfect fit.
International Trade and Commerce
In the global marketplace, businesses often deal with suppliers and customers from different countries, each with their preferred measurement systems. Converting inches to millimeters is vital for international trade, especially when dealing with product specifications, packaging, and shipping.
Consider a fashion brand that sources its fabrics from a European manufacturer. The fabric width might be given in millimeters, but the brand's local market primarily uses inches. Accurate conversion ensures that the fabric width is correctly communicated and understood by all parties involved.
Travel and Daily Life
Even in our daily lives, understanding inch-to-millimeter conversions can be beneficial. When traveling to countries that use the metric system, you might encounter distances or sizes that are given in millimeters. Converting these measurements can help you navigate and make informed decisions.
For example, if you're renting a car in Europe and the rental agreement specifies the fuel tank capacity in liters, you can quickly convert this to gallons (a common imperial unit) to better understand how far you can travel on a full tank.
Common Scenarios and Their Conversions
To further illustrate the practicality of inch-to-millimeter conversions, let’s explore some common scenarios and the conversions involved.
Screen Size and Resolution
In the world of technology, screen size and resolution are often specified in inches. However, many users prefer to think in millimeters. Here are some common screen sizes and their equivalent millimeter dimensions:
| Inch Size | Millimeter Size |
|---|---|
| 4.7 inches | 119.4 millimeters |
| 6.0 inches | 152.4 millimeters |
| 10.1 inches | 256.54 millimeters |
Paper Sizes
Paper sizes, especially for printing and publishing, are often standardized in millimeters. However, many people are more familiar with the traditional letter and A-series sizes in inches. Let’s look at some common paper sizes and their conversions:
| Paper Size (Inches) | Paper Size (Millimeters) |
|---|---|
| Letter (8.5 x 11 inches) | 215.9 x 279.4 millimeters |
| A4 (8.27 x 11.69 inches) | 210 x 297 millimeters |
| Legal (8.5 x 14 inches) | 215.9 x 355.6 millimeters |
Accuracy and Precision in Conversions
When converting between inches and millimeters, it’s crucial to maintain accuracy and precision. Even small errors can have significant consequences, especially in critical applications.
To ensure precise conversions, it's recommended to use reliable conversion tools or calculators. These tools often provide decimal places, ensuring that the converted value is as accurate as possible.
Rounding Considerations
In some cases, you might need to round the converted value to a specific decimal place or whole number. This is especially true when dealing with manufacturing tolerances or when presenting data to stakeholders.
For instance, if you're converting a length of 5.25 inches to millimeters, the exact conversion is 133.35 millimeters. However, if you need to round it to the nearest millimeter, it would be 133 millimeters.
Future Implications and Standardization

As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the need for accurate and consistent measurement systems becomes more evident. While the metric system is the international standard, the imperial system still has a strong presence, especially in certain industries and regions.
Efforts are ongoing to promote the adoption of the metric system globally, which would simplify conversions and reduce errors. However, for now, being proficient in converting between inches and millimeters remains a valuable skill.
Conclusion
Understanding how to convert 9 inches to millimeters and other related conversions is an essential skill for anyone navigating the world of measurements. Whether you’re an engineer, a business professional, or simply a curious individual, this knowledge empowers you to bridge the gap between different measurement systems.
By following the simple conversion process and utilizing the conversion factor, you can accurately convert inches to millimeters and vice versa. This skill is applicable across various industries and everyday situations, ensuring precision and clarity in communication and understanding.
Remember, accurate conversions are the key to successful collaboration and effective problem-solving in a diverse and interconnected world.
How accurate are these conversions in real-world applications?
+The accuracy of inch-to-millimeter conversions heavily depends on the precision required for the specific application. In most cases, the conversion factor of 25.4 is sufficient for general purposes. However, for critical applications like manufacturing or scientific research, additional decimal places might be necessary to ensure utmost accuracy.
Are there any online tools or apps that can help with these conversions?
+Absolutely! There are numerous online conversion tools and apps available that can simplify the process of converting inches to millimeters and vice versa. These tools often provide quick and accurate conversions, making them handy for on-the-go measurements.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when converting inches to millimeters?
+Some common mistakes include using an incorrect conversion factor, failing to consider rounding, and not accounting for the decimal places needed for precision. Always double-check your calculations and consider the specific requirements of your application to avoid errors.