Unraveling the Mystery: 87 F to Celsius
Conversion Conundrum: Unveiling the Temperature Transformation
The temperature scale, an intricate system that has evolved over centuries, often presents curious challenges. One such enigma arises when converting the seemingly straightforward temperature of 87 Fahrenheit to its Celsius counterpart. This conversion, though seemingly simple, holds a layer of complexity that demands an exploration of the underlying principles and a deeper understanding of temperature scales. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel this mystery, shedding light on the intricacies of temperature conversions and their real-world implications.
A Historical Perspective: Fahrenheit and Celsius, A Tale of Two Scales
To comprehend the enigma of 87 Fahrenheit, we must first revisit the historical origins of temperature scales. The Fahrenheit scale, named after the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, was introduced in the early 18th century. It is a temperature scale based on fixed reference points, with 32 degrees representing the freezing point of water and 212 degrees signifying its boiling point at sea level. In contrast, the Celsius scale, developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, is anchored on the freezing and boiling points of water, with 0 degrees for freezing and 100 degrees for boiling. These scales, though serving the same purpose, employ distinct reference points, leading to unique conversions for each temperature.
The Mathematics Behind Temperature Conversion
Converting temperatures between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales involves a simple mathematical formula. The formula for this conversion is as follows:
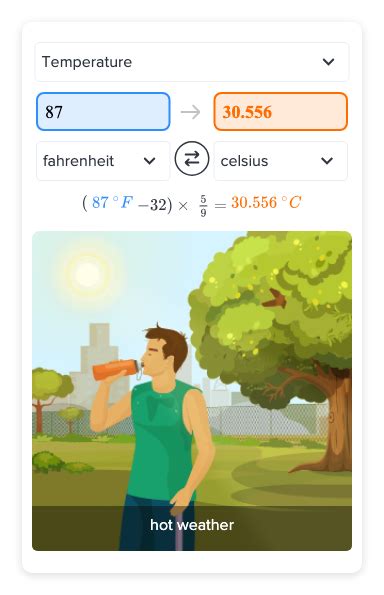
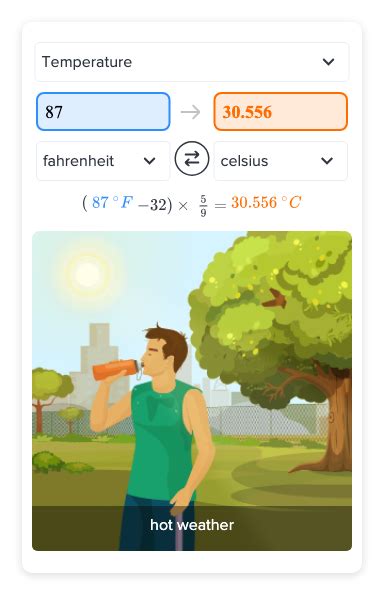
Celsius = (Fahrenheit - 32) * 5⁄9
Plugging in the value of 87 Fahrenheit, the calculation yields:
Celsius = (87 - 32) * 5⁄9 = 30.56 Celsius
Thus, 87 Fahrenheit is equivalent to approximately 30.56 degrees Celsius. However, this mathematical process, while straightforward, underscores the fundamental differences between the two scales and the nuances of temperature conversion.
Practical Applications: Why Temperature Conversion Matters
Temperature conversion is not merely an academic exercise; it has real-world implications and applications across various fields. In meteorology, accurate temperature conversion is essential for understanding weather patterns and making forecasts. In healthcare, precise temperature measurements are crucial for diagnosing and treating illnesses. Additionally, in industries like aviation and engineering, temperature conversions are vital for safety and operational considerations. Understanding how to convert temperatures between scales is, therefore, not just a mathematical curiosity but a practical necessity.
Exploring Further: Beyond Fahrenheit and Celsius
While our focus has been on the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales, it’s worth noting that there are other temperature scales in use, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. The Kelvin scale, for instance, is often used in scientific and engineering contexts, with absolute zero as its starting point. Additionally, the Rankine scale, similar to the Kelvin scale, is used in certain engineering applications. These alternative scales offer different perspectives on temperature measurement and have their own conversion formulas.
A Word of Caution: Accuracy and Precision in Temperature Conversion
While temperature conversion formulas provide a reliable method for transforming temperatures between scales, it’s important to note that precision and accuracy are crucial. Small variations in temperature can have significant implications, particularly in scientific and industrial applications. Therefore, when performing temperature conversions, it’s essential to use accurate and up-to-date conversion factors and to consider the specific context in which the temperature is being used.
Unlocking the Mystery: Key Takeaways
- The conversion of 87 Fahrenheit to Celsius results in approximately 30.56 degrees Celsius.
- Temperature conversion is a mathematical process that highlights the differences between temperature scales.
- Practical applications of temperature conversion span various fields, including meteorology, healthcare, and engineering.
- While Fahrenheit and Celsius are commonly used, other scales like Kelvin and Rankine have their own unique characteristics and uses.
- Precision and accuracy are paramount in temperature conversion, especially in critical scientific and industrial contexts.
In unraveling the mystery of 87 Fahrenheit, we’ve delved into the historical origins of temperature scales, explored the mathematical conversion process, and examined the real-world implications of temperature conversion. This journey underscores the importance of understanding temperature scales and their conversions, not just as an academic exercise but as a practical necessity in various domains. As we navigate the complexities of temperature measurement, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate world of thermodynamics and the role it plays in our daily lives.


