The Ultimate Guide: 63°F to Celsius
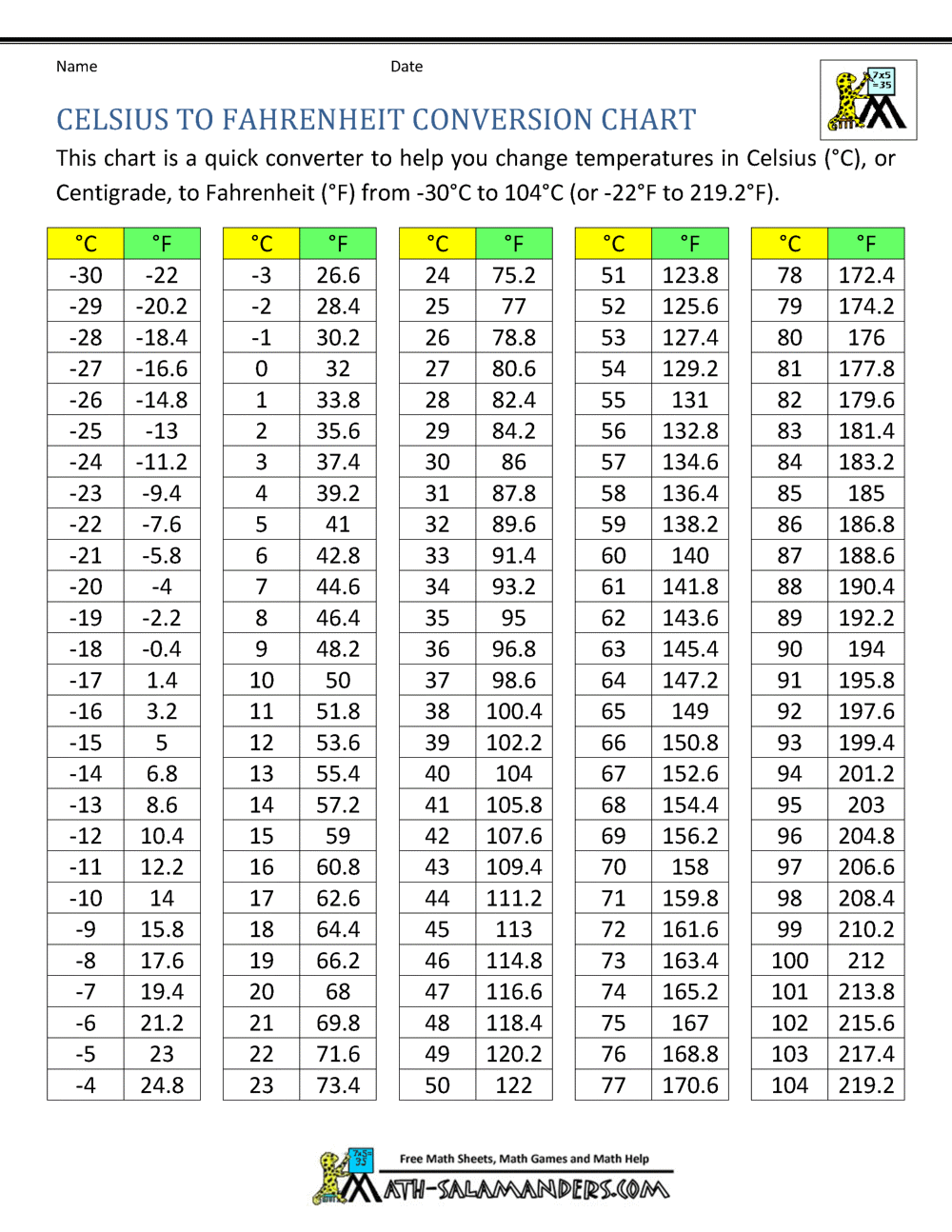
The conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius can often be a tricky task, especially when dealing with specific temperatures like 63°F. But fear not! This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process step by step, providing you with the tools to confidently convert temperatures and understand the underlying principles.
The Formula for Temperature Conversion:
At the heart of temperature conversion lies a simple mathematical formula. To convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius, you subtract 32 from the given Fahrenheit temperature and then multiply the result by \frac{5}{9}. The formula can be expressed as:
\[ \begin{equation*} \text{Temperature in Celsius} = \left( \frac{5}{9} \right) \times \left( \text{Temperature in Fahrenheit} - 32 \right) \end{equation*} \]
Converting 63°F to Celsius:
Let’s apply this formula to our specific temperature, 63°F. Here’s how it breaks down:
\[ \begin{align*} \text{Temperature in Celsius} &= \left( \frac{5}{9} \right) \times (63°F - 32) \\ &= \left( \frac{5}{9} \right) \times 31 \\ &\approx 15.56°C \end{align*} \]
So, when you’re faced with a temperature of 63°F, you can confidently state that it equates to approximately 15.56°C.
Understanding the Conceptual Difference:
Fahrenheit and Celsius represent two different temperature scales, each with its own historical origins and practical applications. Fahrenheit, named after the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries. On the other hand, Celsius, named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, is the more widely used scale internationally and is the standard unit of measurement in the scientific community.
Historical Evolution of Temperature Scales:
The evolution of temperature scales is an intriguing aspect of scientific history. The Fahrenheit scale was introduced in 1724, with the freezing point of water defined as 32 degrees and the boiling point at 212 degrees. Celsius, originally known as the centigrade scale, was developed later, with the freezing point of water set at 0 degrees and the boiling point at 100 degrees. This difference in scale origins contributes to the need for conversion formulas when translating between the two.
Practical Applications:
Understanding temperature conversions is not just an academic exercise; it has practical applications in various fields. Meteorologists, for instance, often need to convert temperatures between Fahrenheit and Celsius to provide weather reports that cater to a global audience. Similarly, in the realm of cooking, knowing how to convert temperatures is crucial for following recipes from different parts of the world.
Tips for Accurate Conversion:
- Always use precise mathematical operations when converting temperatures. Rounding off values too early in the process can lead to less accurate results.
- Double-check your calculations, especially when dealing with critical temperature ranges, such as those required for food safety or medical procedures.
- Utilize online conversion tools or apps for quick and easy conversions, but ensure they provide the necessary level of precision for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the historical origin of the Fahrenheit scale?
+The Fahrenheit scale was introduced by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724. It was based on the freezing point of a saltwater solution and the temperature of a human body, which he defined as 32 degrees and 96 degrees respectively.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How do I remember the conversion formula for Fahrenheit to Celsius?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>A helpful mnemonic for remembering the conversion formula is: <em>"Fahrenheit is fat, so it has more room to grow. Multiply by 5, then divide by 9, and you'll get your Celsius."</em> This reminds you that Fahrenheit has more degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water, and thus, you multiply by a larger number (5) and then divide by a smaller one (9) to convert to Celsius.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some real-world examples where temperature conversion is necessary?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Temperature conversion is crucial in international travel, especially when it comes to understanding weather forecasts and adjusting clothing accordingly. It's also vital in scientific research, where data from different sources might need to be standardized. In healthcare, temperature conversion is necessary when comparing patient data from different regions.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can I use an approximate conversion factor instead of the exact formula?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>While approximate conversion factors like "subtract 30, then divide by 2" might provide a quick estimate, they often lead to less accurate results. For precise calculations, especially in critical applications, it's best to use the exact conversion formula or a reliable conversion tool.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Conclusion:
Temperature conversion may seem daunting at first, but with practice and a solid understanding of the underlying principles, it becomes a straightforward process. Remember, whether you’re planning a trip to a different country or simply curious about the temperature outdoors, knowing how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius will empower you with valuable knowledge.



