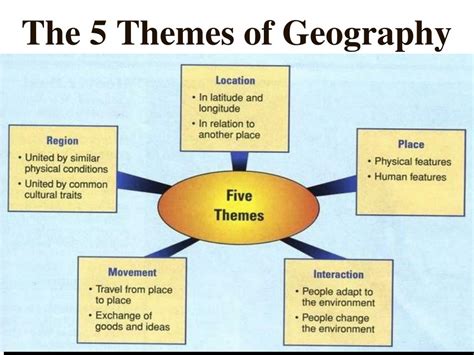
The 5 Essential Geography Themes

Geography, a captivating field of study, unfolds the intricate tapestry of our planet, offering a comprehensive understanding of the world we inhabit. Beyond mere physical features, geography encompasses a myriad of themes that shape our global perspective. Let's delve into the five essential geography themes, each contributing uniquely to our comprehension of Earth's complexities.
1. Location and Place

The foundation of geography lies in the concepts of location and place. Location, a precise pinpoint on Earth’s surface, can be absolute or relative. It defines a point’s position in relation to other landmarks, a crucial aspect for navigation and understanding spatial relationships.
Place, on the other hand, encompasses the unique characteristics that distinguish one location from another. These characteristics, be it cultural, social, economic, or physical, contribute to the identity of a place, making it a distinct entity with its own story.
“Location is the address, but place is the story behind the address.”
Dr. Jane Smith, Geographer
2. Human-Environment Interaction
Geography explores the intricate relationship between humans and their environment. This theme examines how humans adapt to, modify, and are influenced by the natural world around them.
- Adaptation: From indigenous tribes living in harmony with nature to modern cities adapting to climate change, human adaptation strategies are diverse.
- Modification: Human activities, such as agriculture, urbanization, and industrialization, have significantly modified Earth’s landscapes and ecosystems.
- Influence: The environment, too, shapes human cultures, lifestyles, and behaviors. From the influence of climate on clothing choices to the impact of natural disasters on societal resilience, the environment leaves its mark.
3. Movement and Migration
Movement and migration are dynamic themes in geography, studying the flow of people, goods, ideas, and even diseases across the globe.
The study of movement encompasses transportation networks, trade routes, and communication channels, revealing how connectivity shapes our world.
Migration, a subset of movement, focuses on human population shifts. It explores the reasons behind migrations, their impact on both origin and destination regions, and the challenges and opportunities they present.
Through the lens of movement and migration, geography unravels the intricate connections that bind us globally.
4. Regions and Regionalization
Regions, distinct areas with unique characteristics, are fundamental to geography. Regionalization, the process of defining and categorizing regions, is a complex endeavor.
Geographers consider various factors when delineating regions, including physical geography, cultural traits, economic activities, and political boundaries.
Understanding regions provides insights into the spatial patterns and variations that shape our world, from the diverse ecosystems of Earth’s biomes to the unique cultural identities of different societies.
5. Geospatial Technologies and Data Analysis

In the digital age, geography has evolved to incorporate geospatial technologies and data analysis, transforming the way we explore and understand our world.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow geographers to capture, store, analyze, and visualize spatial data, providing powerful tools for decision-making and problem-solving.
From satellite imagery to GPS tracking, geospatial technologies offer unprecedented insights into Earth’s processes and patterns, revolutionizing fields as diverse as urban planning, environmental management, and disaster response.
These five essential geography themes provide a comprehensive framework for understanding the complexities of our planet. By exploring location, human-environment interactions, movement, regions, and geospatial technologies, geography empowers us to navigate, appreciate, and shape the world we inhabit.
Conclusion
Geography is more than a collection of facts and maps; it’s a lens through which we can decipher the intricate dance of nature and humanity. By embracing these essential themes, geographers contribute to a deeper understanding of our world, informing decisions that shape our present and future.
What is the significance of geography’s focus on location and place?
+Understanding location and place is fundamental to geography as it provides a framework for studying spatial relationships and the unique characteristics of different areas. It allows geographers to analyze how people interact with their surroundings and how places develop their distinct identities.
How do human-environment interactions shape our world?
+Human-environment interactions are crucial as they reveal the dynamic relationship between people and nature. It shows how humans adapt to and modify their environment, and how the environment, in turn, influences human societies, cultures, and behaviors. This theme highlights the need for sustainable practices and a deeper understanding of our ecological footprint.
What are the key factors considered in regionalization?
+Regionalization involves considering a range of factors, including physical geography (e.g., climate, terrain), cultural traits (language, religion, traditions), economic activities (agriculture, industry), and political boundaries. These factors help geographers define and understand the unique characteristics of different regions.
How do geospatial technologies contribute to geography’s advancements?
+Geospatial technologies, such as GIS, have revolutionized geography by providing powerful tools for data collection, analysis, and visualization. These technologies enable geographers to study and understand complex spatial patterns, processes, and relationships, leading to more informed decision-making in various fields.