30°C: A Simple Guide to Fahrenheit

Fahrenheit is a temperature scale commonly used in the United States and a few other countries, while the rest of the world primarily relies on the Celsius scale. Understanding the conversion between these two scales can be beneficial, especially when traveling or dealing with international data. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll focus on the temperature of 30°C and explore how it translates to Fahrenheit.
Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit might seem daunting at first, but with a simple formula and some practice, it becomes a straightforward process. Let’s dive into the world of temperature conversions and discover the magic behind the numbers.
The Fahrenheit Scale: A Historical Perspective

Before we delve into the conversion, let’s take a moment to appreciate the history behind the Fahrenheit scale. It was developed in the early 18th century by a German physicist named Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit. He chose the freezing point of water as his scale’s starting point, setting it at 32 degrees. Interestingly, he initially set the boiling point of water at 212 degrees, which he later adjusted to its current value of 212°F. This scale has been in use for centuries, providing a familiar reference point for many.
Understanding the Conversion Formula
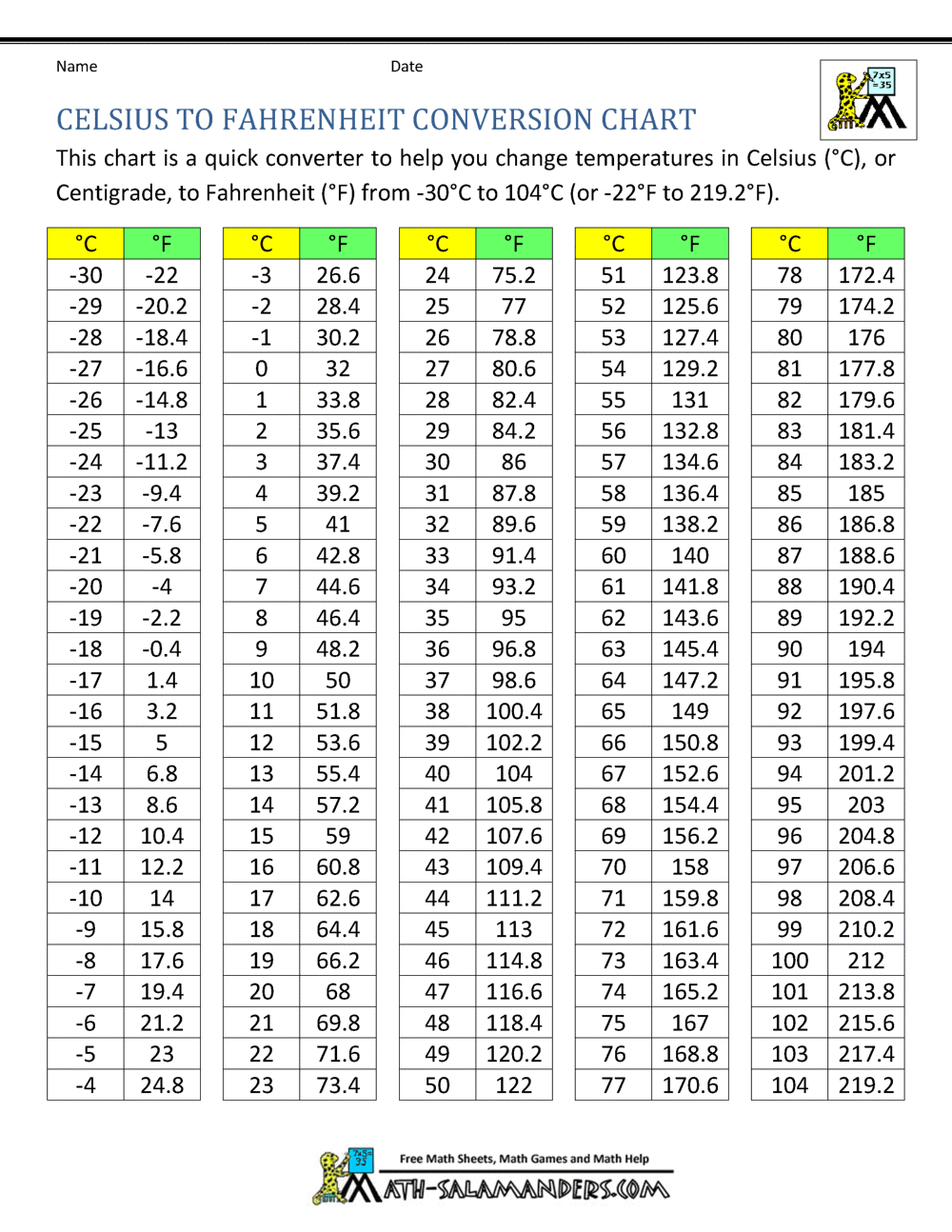
Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit involves a simple mathematical equation. The formula is as follows:
\[ \begin{equation*} \text{Temperature in Fahrenheit} = \left( \text{Temperature in Celsius} \times \frac{9}{5} \right) + 32 \, . \end{equation*} \]
Let’s break down this formula step by step:
- Multiply by 9/5: The first step is to multiply the temperature in Celsius by 9/5. This simple operation already gives us a rough idea of the Fahrenheit value.
- Add 32: After multiplying, we add 32 to the result. This final step completes the conversion, giving us the temperature in Fahrenheit.
Converting 30°C to Fahrenheit: Step by Step
Now, let’s apply this formula to our specific case: converting 30°C to Fahrenheit. Follow these steps:
- Multiply by 9/5: For 30°C, we calculate:
\[ \begin{align*} 30^\circ \text{C} \times \frac{9}{5} &= \frac{270}{5} \\ &= 54 \, . \end{align*} \]
- Add 32: Next, we add 32 to the result:
\[ \begin{equation*} 54 + 32 = 86 \, . \end{equation*} \]
So, 30°C is equal to 86°F.
Practical Application: A Real-Life Scenario
Imagine you’re planning a trip to a country that primarily uses the Celsius scale, and you want to understand the temperature ranges you’ll encounter. Let’s say you’re headed to a city with a forecasted high of 30°C. By converting this temperature to Fahrenheit, you can better grasp the weather conditions you’ll experience.
Using our conversion formula, we find that 30°C is equivalent to 86°F. This information helps you prepare for a warm day, ensuring you pack the right clothing and take the necessary precautions to stay comfortable.
Visualizing the Temperature Conversion
To further enhance our understanding, let’s visualize the conversion between 30°C and 86°F. Here’s a simple table:
| Temperature in Celsius | Temperature in Fahrenheit |
|---|---|
| 30°C | 86°F |

This table provides a quick reference, allowing us to see the direct relationship between the two scales.
Common Temperature Conversions: A Reference Guide
Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a skill that comes in handy in various situations. Here’s a quick reference guide for some common temperature conversions:
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|
| -40°C | -40°F |
| -18°C | 0°F |
| 0°C | 32°F |
| 10°C | 50°F |
| 20°C | 68°F |
| 30°C | 86°F |
| 40°C | 104°F |
| 50°C | 122°F |
FAQ Section: Unraveling Common Queries
Q: Why do some countries use Celsius, while others use Fahrenheit?
A: The choice of temperature scale is often influenced by historical and cultural factors. Celsius, also known as the centigrade scale, is widely used in scientific and meteorological contexts and is the standard in most countries. Fahrenheit, on the other hand, has its roots in the early thermometers developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit. Its adoption in the United States and a few other countries is largely due to historical conventions.
Q: Is it possible to convert temperatures without a calculator?
A: Absolutely! While a calculator can make the process quicker, you can mentally estimate the conversion with a bit of practice. Remember that for every 5 degrees Celsius, the Fahrenheit scale increases by approximately 9 degrees. This rough estimate can be a handy tool when you need a quick conversion.
Q: What are some practical applications of temperature conversions?
A: Temperature conversions are essential in various fields, including meteorology, culinary arts, and healthcare. For meteorologists, understanding temperature scales allows for accurate weather forecasting and reporting. In the kitchen, chefs often need to convert recipes between Celsius and Fahrenheit. Additionally, in healthcare, temperature readings in Celsius can be converted to Fahrenheit for patients who are more familiar with that scale.
Q: How can I remember the conversion formula?
A: One memorable way to recall the conversion formula is to think of it as a fraction: 9/5. Multiply the temperature in Celsius by this fraction, and then add 32 to get the temperature in Fahrenheit. This simple fraction serves as a quick reminder for the entire formula.
Q: Are there any temperature scales other than Celsius and Fahrenheit?
A: Indeed, there are other temperature scales, such as the Kelvin scale, which is commonly used in scientific contexts. The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, making it useful for measuring extremely low temperatures. Additionally, the Rankine scale, used in some engineering fields, is similar to the Kelvin scale but starts at the same freezing point as Fahrenheit.
By understanding these temperature scales and their conversions, we can better navigate the diverse world of temperature measurements and interpretations.