30°C Heat: A Simple Conversion to Fahrenheit

Understanding the 30°C Threshold
When the temperature soars to 30 degrees Celsius, it’s a pivotal moment that often marks the transition from comfortable warmth to sweltering heat. For those unfamiliar with the metric system, converting this temperature to Fahrenheit can provide a more relatable perspective. So, let’s delve into the simple process of translating this threshold and explore why it matters.
"Temperature conversions are essential for global communication and understanding. They bridge the gap between different measurement systems, ensuring a shared comprehension of environmental conditions."
The Straightforward Conversion Formula

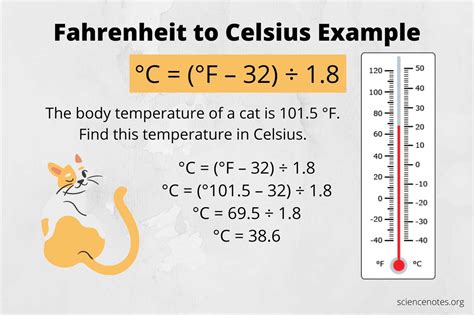
Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is a straightforward process, thanks to a simple formula:
Temperature in Fahrenheit = (Temperature in Celsius x 9/5) + 32
In this case, to convert 30°C to Fahrenheit, we apply the formula:
- Multiply 30°C by 9/5, resulting in 54.
- Add 32 to the product, giving us 86°F.
So, when the thermometer hits 30°C, it’s equivalent to a balmy 86 degrees Fahrenheit. This conversion is a valuable tool for those accustomed to the Fahrenheit scale, helping them grasp the significance of a 30°C day.
The Impact of a 30°C Day
Pros of a 30°C Day
- Ideal for outdoor activities like swimming and picnics.
- Boosts tourism in regions with a reputation for mild weather.
- Encourages a more active lifestyle, promoting exercise and vitamin D absorption.
<div class="con">
<h3>Cons of a 30°C Day</h3>
<ul>
<li>Can lead to heat-related illnesses like heat exhaustion and heat stroke if proper precautions aren't taken.</li>
<li>Increased energy consumption as air conditioning use spikes.</li>
<li>Potential for wildfires in dry, hot conditions.</li>
</ul>
</div>
A 30°C day has both benefits and challenges. While it offers a wonderful opportunity to enjoy the outdoors, it also requires careful planning and awareness to ensure safety and sustainability.
Historical Context
The Fahrenheit scale has a rich history, dating back to the early 18th century when German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit developed it. Fahrenheit initially based his scale on three reference points: the lowest temperature he could achieve using a mixture of ice, salt, and water (which he set at 0°F), the temperature of a mixture of ice and water (set at 32°F), and the average human body temperature (set at 96°F). The scale was later adjusted, and the freezing point of water became the primary reference point.
In contrast, the Celsius scale, developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, with 0°C representing the freezing point and 100°C representing the boiling point at sea level. This scale is now the standard for scientific measurements and is widely used in most countries.
Future Trends

As the world becomes more interconnected and diverse, the ability to understand and communicate temperatures across different scales will only grow in importance. With climate change causing global temperatures to rise, having a shared understanding of temperature scales will be crucial for addressing environmental challenges and ensuring public safety.
Conclusion
The conversion of 30°C to Fahrenheit provides a relatable perspective for those accustomed to the Fahrenheit scale. This simple translation underscores the importance of temperature conversions in our increasingly globalized world. Whether you’re planning a trip abroad or simply trying to understand the weather forecast, mastering temperature conversions is a valuable skill.
How accurate is the Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion formula?
+The conversion formula is highly accurate and reliable. It's based on the precise relationship between the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, ensuring an exact translation. However, it's essential to use the formula correctly and double-check your calculations to avoid any errors.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Why do some countries still use the Fahrenheit scale?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The continued use of the Fahrenheit scale in some countries, notably the United States, is a result of historical traditions and cultural preferences. While the metric system has been adopted worldwide, certain regions have maintained their legacy measurement systems, which can create unique challenges for international communication.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are the benefits of using the Celsius scale over Fahrenheit?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The Celsius scale is simpler and more intuitive, as it's based on the natural freezing and boiling points of water. It's also the standard for scientific measurements, making it more consistent and widely understood. However, both scales have their advantages, and choosing one often depends on personal preference and cultural context.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can temperature conversions be used for other measurement systems, like Kelvin or Rankine?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Absolutely! Temperature conversions can be applied to various measurement systems, including Kelvin and Rankine. Each scale has its unique conversion formula, but the basic principle remains the same: to translate temperatures between different systems for a shared understanding.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>