3 Steps to DNA Replication
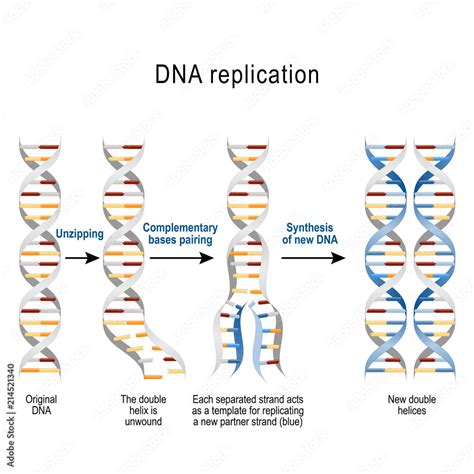
The intricate process of DNA replication, essential for cellular life, unfolds through a series of precisely coordinated steps. Here, we unravel the core mechanisms that underpin this fundamental biological event.
Step 1: Unwinding the Double Helix

The journey commences with the unwinding of the iconic double helix structure of DNA. This process, known as DNA melting, is facilitated by specialized enzymes called helicases. These molecular machines unzip the DNA strand, creating a replication fork, a Y-shaped structure where new DNA strands are synthesized.
Helicases are the powerhouse behind DNA replication, ensuring the accurate separation of the DNA strands.
Step 2: Priming the Replication Site

Once the DNA is unwound, a primer, typically a short RNA fragment, is synthesized by another enzyme, primase. This primer provides a starting point for the replication process, allowing the addition of DNA nucleotides.
The primase enzyme acts as a crucial catalyst, initiating the replication process by creating the RNA primer.
Step 3: Synthesizing New DNA Strands
The synthesis of new DNA strands is a meticulous process, driven by DNA polymerases. These enzymes add complementary nucleotides to the template strand, following the rules of base pairing. The newly synthesized DNA strands grow in a 5’ to 3’ direction, ensuring fidelity and accuracy.
Pros of DNA Replication
- Ensures accurate transmission of genetic information
- Maintains genetic diversity and variation
- Facilitates cell division and growth
Cons of DNA Replication
- Errors can lead to mutations
- Complex process with multiple steps
- Requires energy and resources
Conclusion
In summary, DNA replication is a meticulously orchestrated process, involving the coordinated actions of various enzymes. From unwinding the DNA to priming the replication site and synthesizing new strands, each step is vital for ensuring the faithful reproduction of genetic material.
How does DNA replication ensure genetic continuity?
+DNA replication is the process by which genetic information is faithfully copied, allowing for the transmission of hereditary traits from one generation to the next. It ensures that each new cell receives an identical copy of the DNA, maintaining genetic continuity.
What are the key enzymes involved in DNA replication?
+The key enzymes involved in DNA replication include helicases, which unwind the DNA, primase for primer synthesis, and DNA polymerases for new DNA strand synthesis. These enzymes work in harmony to ensure accurate and efficient replication.
Can DNA replication errors lead to genetic disorders?
+Yes, errors during DNA replication can result in genetic mutations, which may lead to various genetic disorders. These mutations can affect protein function or disrupt normal cellular processes, potentially causing diseases.
How is DNA replication regulated in the cell cycle?
+DNA replication is tightly regulated in the cell cycle. It occurs during the S phase, ensuring that the DNA is replicated only once per cell cycle. Regulatory proteins control the activation and progression of DNA replication to maintain cell integrity.



