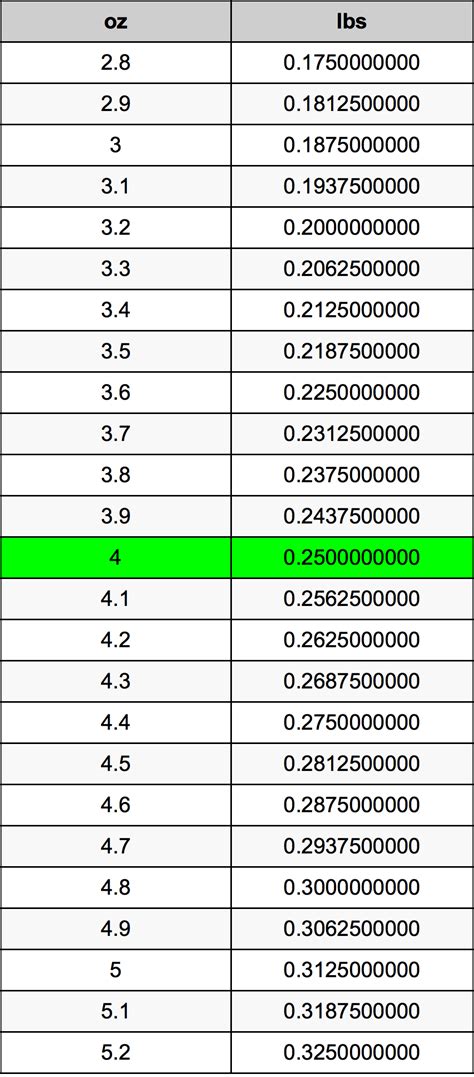
20°C Conversion: 5 Fast Facts
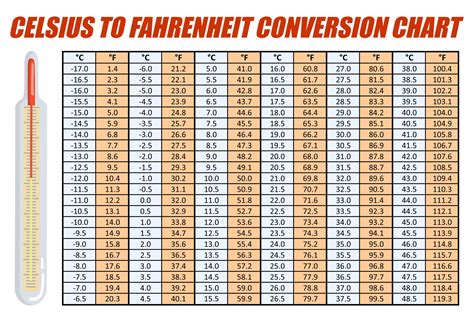
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: One of the most common temperature conversions is from Celsius to Fahrenheit. To convert 20°C to Fahrenheit, use the formula: Fahrenheit = (Celsius x 9/5) + 32. Applying this, 20°C is equivalent to 68°F.
- Kelvin: In scientific and engineering fields, Kelvin is often the preferred unit for temperature measurements. To convert 20°C to Kelvin, add 273.15 to the Celsius value. So, 20°C becomes 293.15 Kelvin.
- Rankine Scale: The Rankine scale is another temperature scale used primarily in engineering applications. The conversion from Celsius to Rankine involves multiplying the Celsius value by 9/5, similar to Fahrenheit, but then adding 491.67. For 20°C, this results in 534.67 Rankine.
- Reaumur Scale: While less common today, the Reaumur scale was once widely used, especially in Europe. To convert 20°C to Reaumur, simply divide the Celsius value by 2. So, 20°C is equivalent to 10°R.
- Conversion to Other Units: Beyond the common scales, there are various other temperature units used in specialized fields. For instance, to convert 20°C to Delisle, you subtract the Celsius value from 373.15, resulting in 173.15°De.
Remember, accurate temperature conversions are essential for precise scientific measurements, meteorological data analysis, and ensuring consistency in various industries.
What is the exact formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit?
+The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is Fahrenheit = (Celsius x 9⁄5) + 32. This formula is widely used and accurate for temperature conversions.
Can you explain the significance of the Kelvin scale in scientific measurements?
+The Kelvin scale is vital in scientific contexts as it starts at absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature. This makes it ideal for precise measurements in fields like physics and chemistry.
Are there any other temperature scales commonly used in specific industries or regions?
+Yes, there are various specialized temperature scales used in different industries and regions. For example, the Rankine scale is commonly used in engineering, while the Reaumur scale was historically popular in Europe.
How do temperature conversions impact real-world applications, such as weather forecasts or industrial processes?
+Accurate temperature conversions are crucial for weather forecasts, ensuring consistent data interpretation. In industrial processes, precise temperature measurements are essential for quality control and safety.